Chapter: Biotechnology Applying the Genetic Revolution: Recombinant Proteins
Proteins and Recombinant DNA Technology
Recombinant Proteins
PROTEINS
AND RECOMBINANT DNA TECHNOLOGY
Proteomics has opened the
door to identify more and more clinically relevant proteins. Once identified,
these proteins need to be studied in detail, including expression of the
protein in model organisms by using recombinant DNA techniques. Some proteins
will become therapeutic agents and large amounts of purified protein will be
required.
Once a gene has been cloned,
the protein it encodes can be produced in large amounts with relative ease.
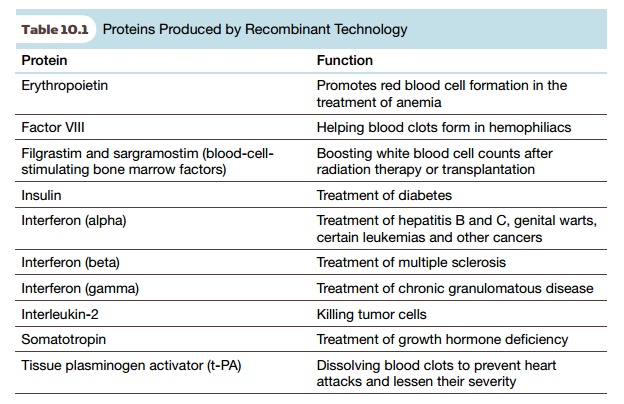
Some examples of such recombinant
proteins are given in Table 10.1. Smaller, nonprotein molecules, which seem
simpler to an organic chemist, would need half a dozen proteins (enzymes)
working in series to synthesize them. Thus, paradoxically, proteins, despite
being macromolecules, have been more susceptible to genetic engineering than
simpler products such as antibiotics. Pathway engineering to produce small
organic molecules will be discussed in the following chapter.
Expressing a gene for
large-scale production brings extra problems compared to a laboratory setting.
The more copies of a gene that a cell contains, the higher the level of the
gene product. Thus cloning a gene onto a high-copy-number plasmid will usually
give higher yields of a gene product. However, high-copy plasmids are often
unstable, especially in the dense cultures used in industrial situations. Although
the presence of antibiotic resistance genes on most plasmids provides a method
to maintain the plasmid in culture, antibiotics are expensive, especially on an
industrial scale. One solution to prevent plasmid loss is to integrate the
foreign gene into the chromosome of the host cell. This, however, decreases the
copy number of the cloned gene to one. Attempts have been made to insert
multiple copies of cloned genes in tandem arrays. However, the presence of
multiple copies results in instability due to recombination between homologous
sequences of DNA.
Related Topics