Chapter: Biotechnology Applying the Genetic Revolution: Recombinant Proteins
Expression of Eukaryotic Proteins in Bacteria
EXPRESSION
OF EUKARYOTIC PROTEINS IN BACTERIA
In Previews pages,
Recombinant DNA Technology, we discussed the basics of cloning genes onto a
variety of vectors. Successful expression of cloned genes depends on several
factors. Obviously, bacterial genes will usually be expressed when carried on
cloning vectors in bacterial host cells, provided that they are next to a
suitable bacterial promoter. Special plasmids known as expression vectors are often used to enhance gene expression. As
noted in Previews Pages, these provide a strong promoter to drive expression of
the cloned gene. Expression vectors also contain genes for antibiotic
resistanace to allow selection of the vector and therefore the recombinant
protein. In addition, they must have an origin of replication appropriate to
the host.
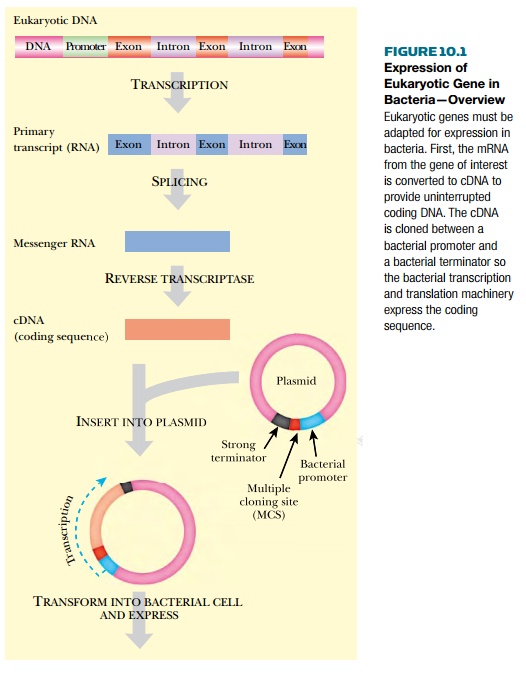
The expression of eukaryotic proteins is more problematic. Although eukaryotic cells can be used to express eukaryotic proteins, bacteria are simpler to grow and manipulate genetically. Therefore it is often desirable to express eukaryotic proteins in bacteria (Fig. 10.1). Because eukaryotic promoters do not work in bacterial cells, it is necessary to provide a bacterial promoter. In addition, bacteria cannot process introns; therefore it is standard procedure to clone the cDNA version of eukaryotic genes, which lacks the introns and consists solely of uninterrupted coding sequence. In fact, the cDNA version of eukaryotic genes is generally used, even for expression in eukaryotic cells, not only to avoid possible processing problems, but also because the amount of DNA is much smaller and consequently easier to handle.
Even if a cloned gene is
transcribed at a high level, production of the encoded protein may be limited
at the stage of protein synthesis. Different mRNA molecules are translated with
differing efficiencies. Several factors are involved:
(a) Strength of the ribosome binding site–ribosome interaction
(b) mRNA stability and/or secondary structure
(c) Codon usage
In addition to standard
expression vectors, more sophisticated vectors exist to optimize these other
aspects of protein production. In this chapter we will discuss the use of
translation vectors and fusion vectors to increase the synthesis of a
recombinant protein from a cloned gene.
Related Topics