Chapter: Mechanical : Computer Aided Design : Fundamentals of Computer Graphics
Product cycle
Product cycle
Product cycle integrate processes, people, data, and business and gives a product information for industries and their extended activity. Product cycle is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from starting, through design and manufacture, to repair and removal of manufactured products.
Product cycle methods assist association in managing with the rising difficulty and engineering challenges of developing new products for the worldwide competitive markets.
Product lifecycle management (PLM) can be part of one of the following four fundamentals of a manufacturing information technology structure.
(i) Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
(ii) Supply Chain Management (SCM)
(iii) Enterprise resource planning (ERP)
(iv) Product Planning and Development (PPD).
The core of PLM is in the formation and management of all product information and the technology used to access this data and knowledge. PLM as a discipline appeared from tools such as CAD, CAM and PDM, but can be viewed as the combination of these tools with processes, methods and people through all stages of a product’slife cycle. PLM is not just about software technology but is
also a business approach.
Product Cycle Model
There are several Product cycle models in industry to be considered, one of the possible product
cycle is given below (Fig.1.1.):
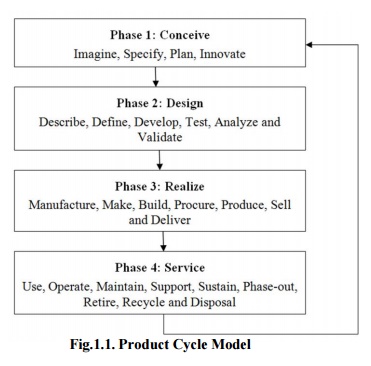
Fig.1.1. Product Cycle Model
Step 1: Conceive
Imagine, Specify, Plan, Innovate
The first step is the definition of the product requirements based on company, market and customer. From this requirement, the product's technical data can be defined. In parallel, the early concept design work is performed defining the product with its main functional features. Various media are utilized for these processes, from paper and pencil to clay mock-up to 3D Computer Aided Industrial Design.
Step 2: Design
Describe, Define, Develop, Test, Analyze and Validate
This is where the completed design and development of the product begins, succeeding to prototype testing, through pilot release to final product. It can also involve redesign and ramp for improvement to existing products as well as planned obsolescence. The main tool used for design and development is CAD. This can be simple 2D drawing / drafting or 3D parametric feature based solid/surface modeling.
This step covers many engineering disciplines including: electronic, electrical, mechanical, and civil. Besides the actual making of geometry there is the analysis of the components and assemblies.
Optimization, Validation and Simulation activities are carried out using Computer Aided Engineering (CAE) software. These are used to perform various tasks such as: Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD); Finite Element Analysis (FEA); and Mechanical Event Simulation (MES). Computer Aided Quality (CAQ) is used for activities such as Dimensional tolerance analysis. One more task carried out at this step is the sourcing of bought out components with the aid of procurement process.
Step 3: Realize
Manufacture, Make, Build, Procure, Produce, Sell and Deliver
Once the design of the components is complete the method of manufacturing is finalized. This includes CAD operations such as generation of CNC Machining instructions for the product’s component as well as tools to manufacture those components, using integrated Computer Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software.
It includes Production Planning tools for carrying out plant and factory layout and production simulation. Once details components are manufactured their geometrical form and dimensions can be verified against the original data with the use of Computer Aided Inspection Equipment (CAIE). Parallel to the engineering tasks, sales and marketing work take place. This could consist of transferring engineering data to a web based sales configuration.
Step 4: Service
Use, Operate, Maintain, Support, Sustain, Phase-out, Retire, Recycle and Disposal.
The final step of the lifecycle includes managing of information related to service for repair and maintenance, as well as recycling and waste management information. This involves using tools like Maintenance, Repair and Operations Management software.
Related Topics