Chapter: Mechanical : Computer Aided Design : Fundamentals of Computer Graphics
2D, 3D Display Control Facilities and Transformations
2 – D DISPLAY CONTROL FACILITIES
The essential steps for 2D graphics are:
1. Convert the geometric representation of the model to lines (ter med Vectors)
2. Transform the lines from the model coordinate system to the screen coordinate system (termed windowing)
Select those lin es that are within the part of the model that it is wished to display known as the c lipping step
4. Instruct the display device to draw the vectors The Stages in graphics pipeline are shown.
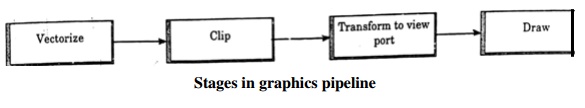
1. Vector Generation
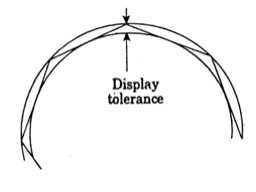
The aim of vector display of a curve is to use sufficient vectors for the curve to appear smooth. The number needed is controlled by the display tolerance, which is maximum deviation of the vector representation from the true curve shape.
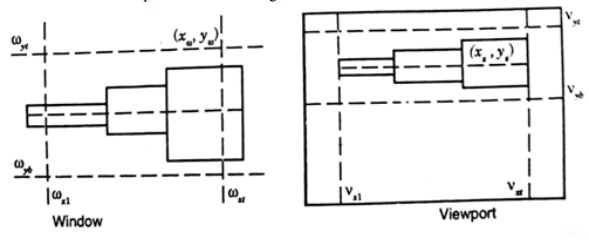
2. Windowing Transformation
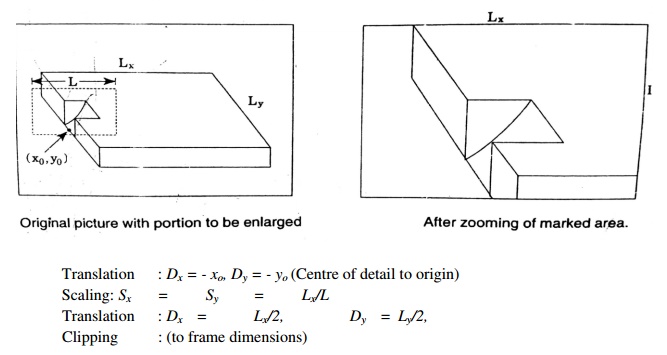
When it is necessary to examine in detail a part of a picture being displayed, a window may be placed around the desired part and the windowed area magnified to fill the whole screen and multiple views of the model may also be shown on the same screen.
The window is a rectangular frame or boundary through which the user looks onto the model. The viewport is the area on the screen in which the contents of the window are to be presented as an image.
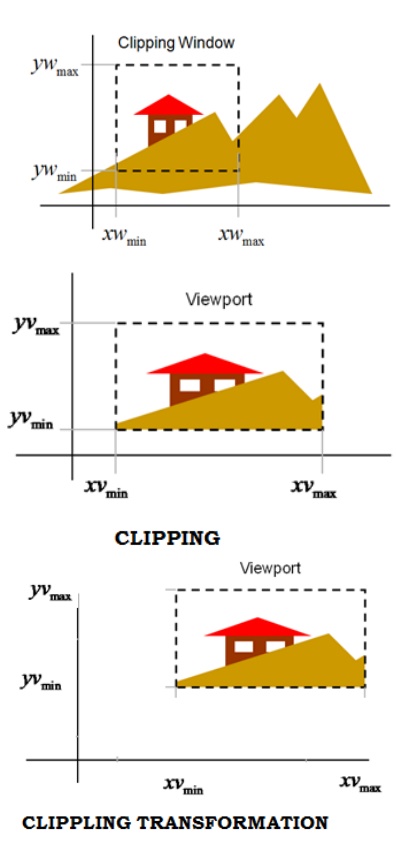
3. Clipping Transformation
The clipping is an operation to plot part of a picture within the given window of the plotting area and to discard the rest.
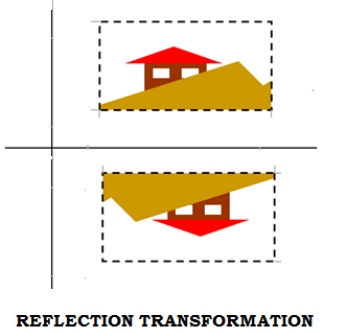
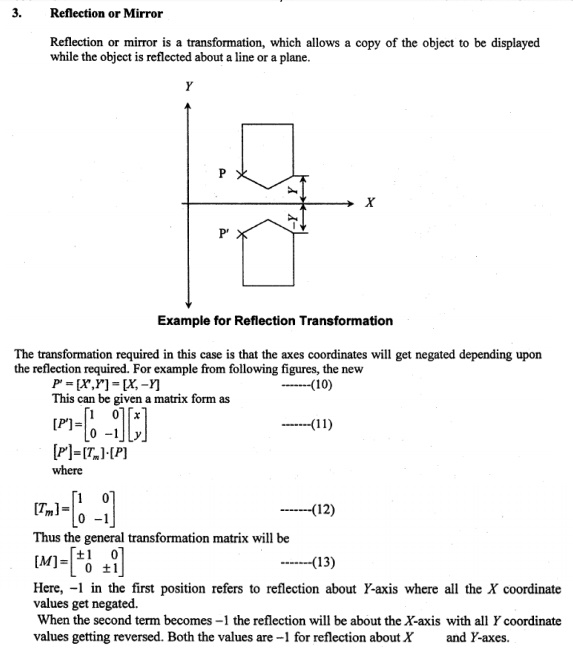
4. Reflection Transformation
Reflection about any axis
5. Zooming
This transformation is carried out to provide enlarged or shrunk view of a picture detail
2– D TRANSFORMATIONS
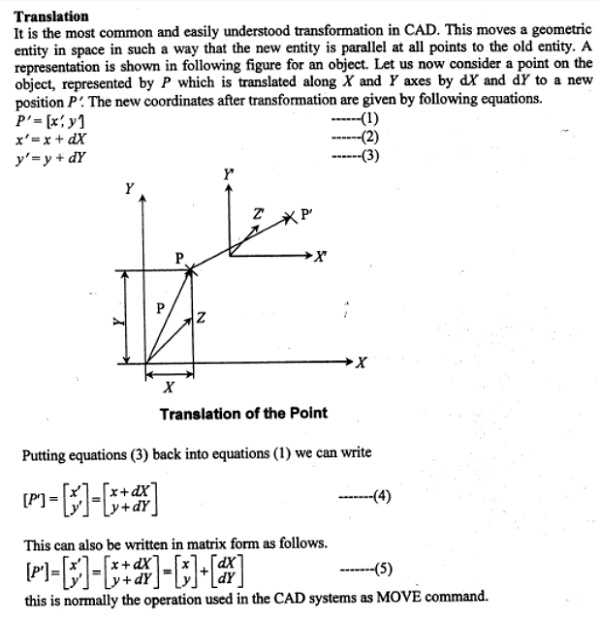
i. Translation
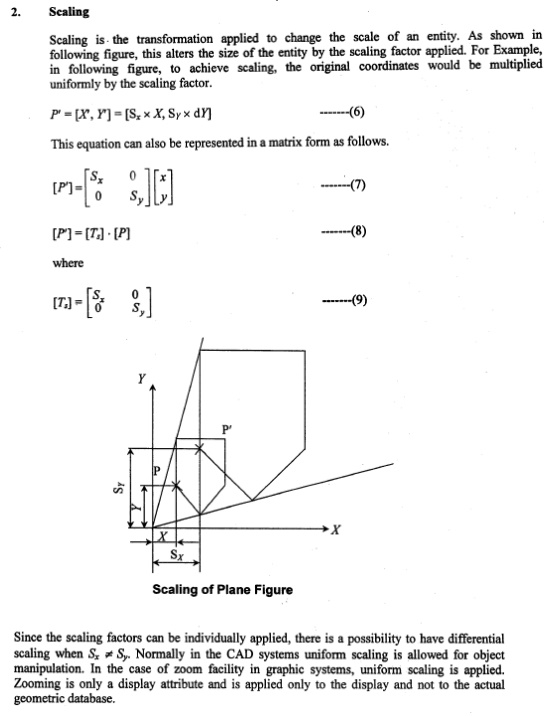
ii. Scaling
iii. Reflection with mirror
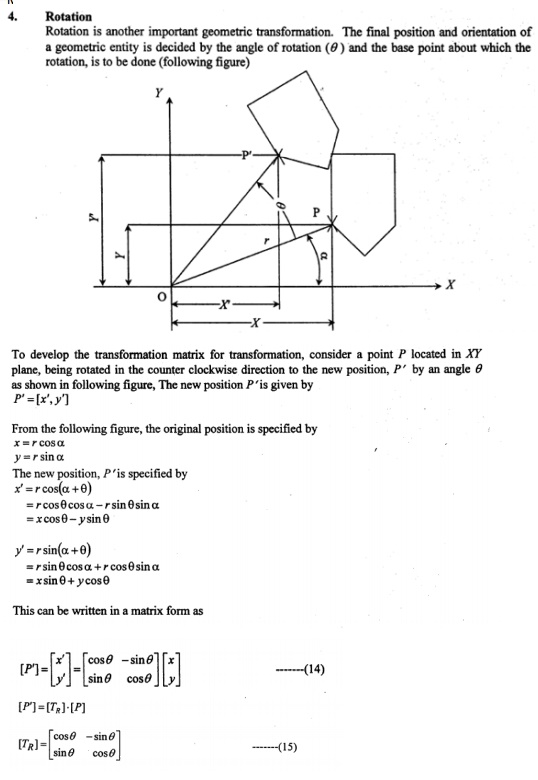
iv. Rotation
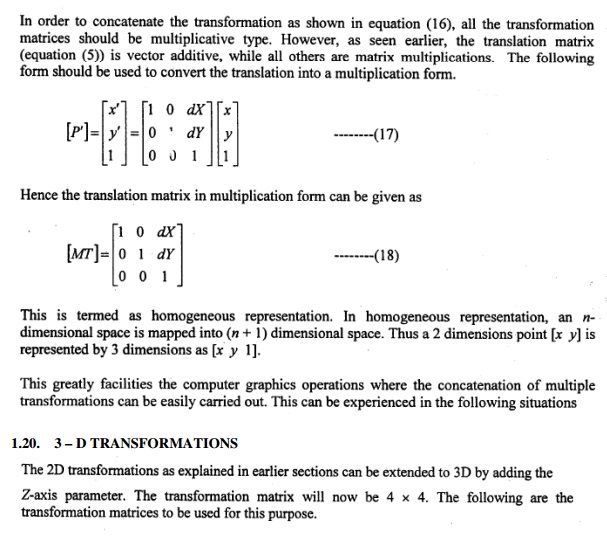
HOMOGENEOUS CO-ORDINATES
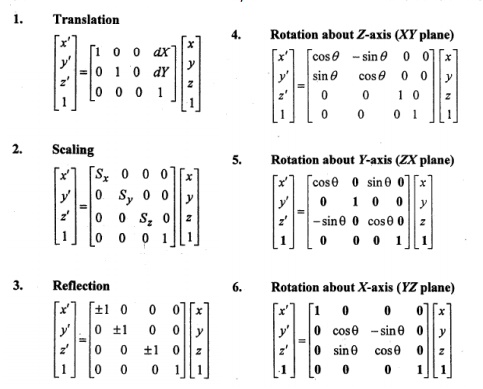
3 – D TRANSFORMATIONS
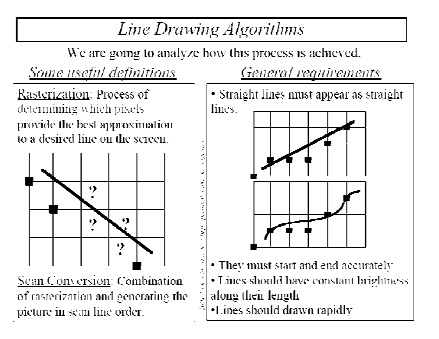
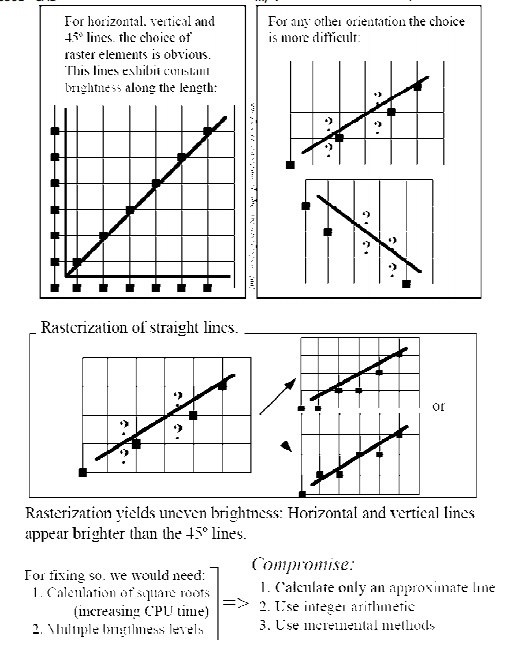
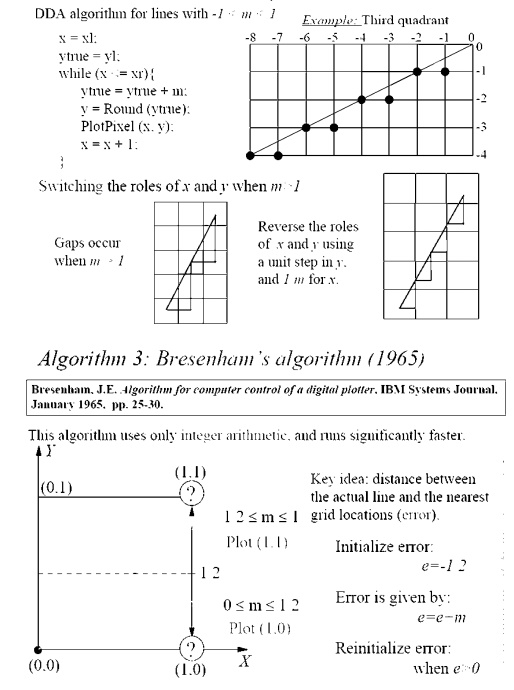
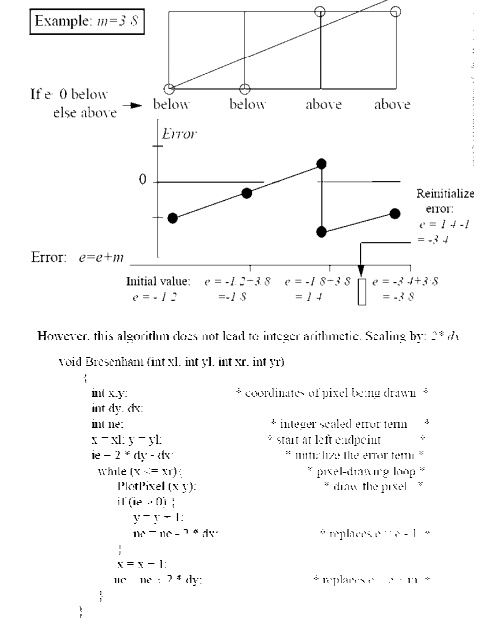
LINE DRAWING ALGOORITHMS

Related Topics