Chapter: Mechanical : Metrology and Measurements : Measurement of Power, Flow and Temperature Related Properties
Pitot tube
Pitot tube
An obstruction type primary element used mainly for fluid velocity measurement is the Pitot tube.
Principle
Consider Figure which shows flow around a solid body. When a solid body is held centrally and stationary in a pipeline with a fluid streaming down, due to the presence of the body, the fluid while approaching the object starts losing its velocity till directly in front of the body, where the velocity is zero. This point is known as the stagnation point. As the kinetic head is lost by the fluid, it gains a static head. By measuring the difference of pressure between that at normal flow line and that at the stagnation point, the velocity is found out. This principle is used in pitot tube sensors.
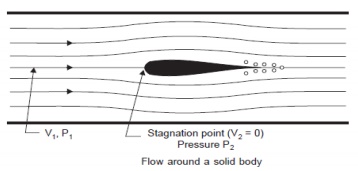
Fig 5.21 Flow through solid body
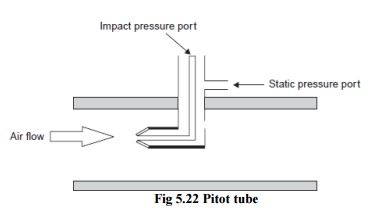
Fig 5.22 Pitot tube
A common industrial type of pitot tube consists of a cylindrical probe inserted into the air stream, as shown in Figure. Fluid flow velocity at the upstream face of the probe is reduced substantially to zero. Velocity head is converted to impact pressure, which is sensed through a small hole in the upstream face of the probe. A corresponding small hole in the side of the probe senses static pressure. A pressure instrument measures the differential pressure, which is proportional to the square of the stream velocity in the vicinity of the impact pressure sensing hole.
The velocity equation for the pitot tube is given by,
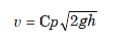
Advantages
1. No pressure loss.
2. It is relatively simple.
3. It is readily adapted for flow measurements made in very large pipes or ducts
Disadvantages
1. Poor accuracy.
2. Not suitable for dirty or sticky fluids and fluids containing solid particles.
3. Sensitive to upstream disturbances.
Related Topics