Chapter: Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology: The Endocrine System
Parathyroid Glands and Parathyroid hormone (PTH)
PARATHYROID GLANDS
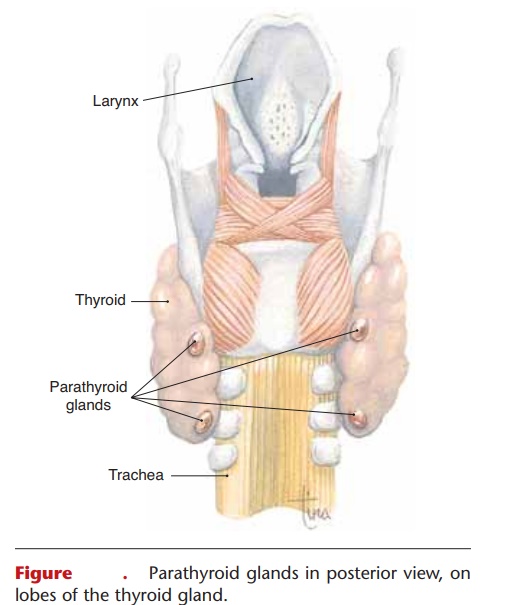
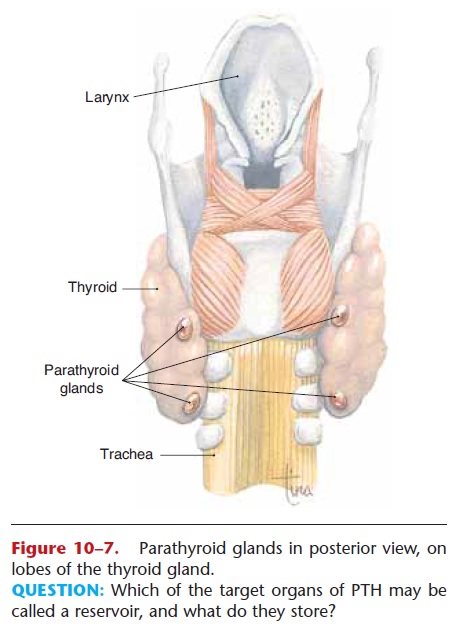
There are four parathyroid glands: two on the back of each lobe of the thyroid gland (Fig. 10–7). The hor-mone they produce is called parathyroid hormone.
PARATHYROID HORMONE
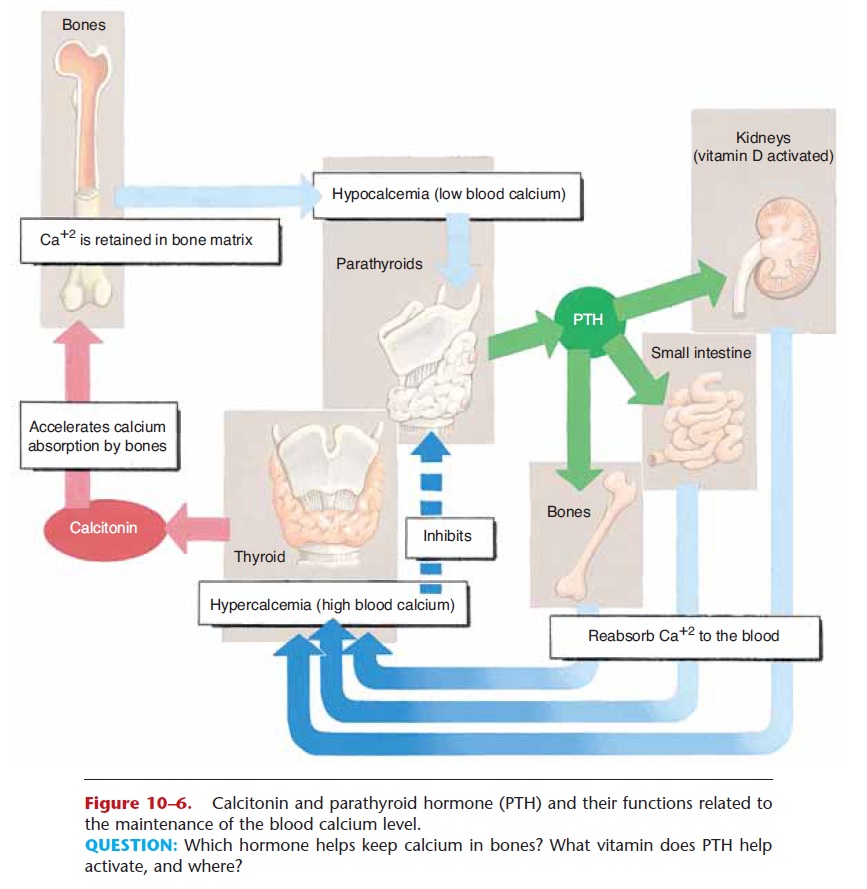
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) is an antagonist to cal-citonin and is important for the maintenance of nor-mal blood levels of calcium and phosphate. The target organs of PTH are the bones, small intestine, and kid-neys.
PTH increases the reabsorption of calcium and phosphate from bones to the blood, thereby raising their blood levels. Absorption of calcium and phos-phate from food in the small intestine, which also requires vitamin D, is increased by PTH. This too
raises the blood levels of these minerals. In the kid-neys, PTH stimulates the activation of vitamin D and increases the reabsorption of calcium and the excre-tion of phosphate (more than is obtained from bones). Therefore, the overall effect of PTH is to raise the blood calcium level and lower the blood phosphate level. The functions of PTH are summarized in Table 10–4.

Secretion of PTH is stimulated by hypocalcemia, a low blood calcium level, and inhibited by hypercal-cemia. The antagonistic effects of PTH and calcitonin are shown in Fig. 10–6. Together, these hormones maintain blood calcium within a normal range. Calcium in the blood is essential for the process of blood clotting and for normal activity of neurons and muscle cells.
As you might expect, a sustained hypersecretion of PTH, such as is caused by a parathyroid tumor, would remove calcium from bones and weaken them. It has been found, however, that an intermittent, brief excess of PTH, such as can occur by injection, will stimulate the formation of more bone matrix, rather than matrix reabsorption. This may seem very strange—the oppo-site of what we would expect—but it shows how much we have yet to learn about the body. PTH is being investigated as a possible way to help prevent osteo-porosis.
Related Topics