Chapter: Paediatrics: Neonatology
Paediatrics: Newborn life support
Neonatology
Newborn life support
All who attend deliveries should
be proficient in newborn resuscitation, ideally taught on a recognized course
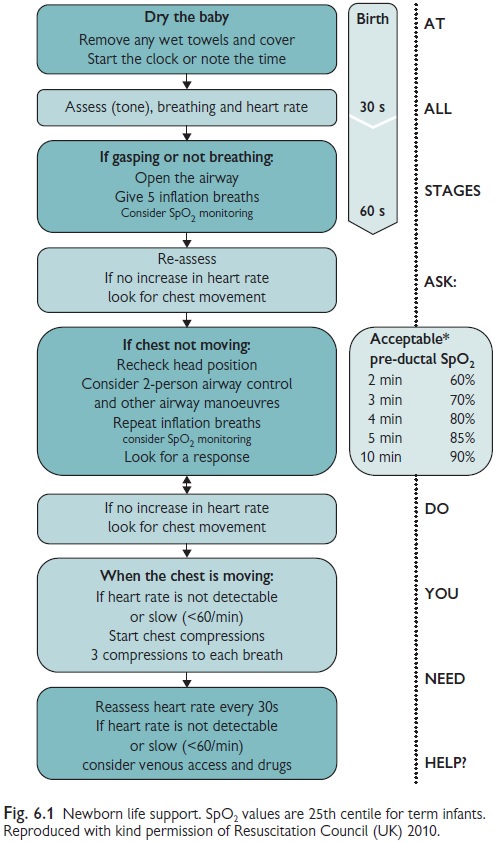
(newborn life support (NLS) or equivalent). The algorithm on demonstrates a
general approach to resuscitation (see Fig. 6.1). Preterm infants require
special consideration.
Before birth
·
Check
equipment.
·
Ask
about: Gestation? Foetal distress? Meconium?
At birth
·
For
uncompromised babies, a delay in cord clamping of at least one minute is
recommended.
·
There
is insufficient evidence to recommend a delay in babies who require
resuscitation.
Meconium
·
Vigorous
infants born through meconium stained liquor do NOT require airway suctioning
either on the perineum or the resuscitaire.
·
Pale,
floppy, poor respiration, or bradycardia? Inspect oropharynx and perform
suction if required.
·
If
appropriate expertise is available, tracheal intubation and suction may be
useful in non-vigorous babies. If expertise not available, or if attempted
intubation is prolonged or unsuccessful, start mask ventilation, particularly
if there is persistent bradycardia.
Lung inflation
·
Inflation
breaths are given initially, use air (21% O2).
·
3s
each breath, 7 30cmH20 (term infants)—give in sets of 5.
·
Once
the chest is moving, ventilation breaths (shorter and gentler) are given at a
rate of 30–40/min if required.
Airway manoeuvres
·
Jaw
thrust (2 person technique very useful).
·
Direct
inspection of oropharynx and airway suction.
·
Guedel
airway.
·
Intubation
(if competent).
Chest compressions
·
Rate
7100/min, using two thumbs technique.
·
3
chest compressions per lung inflation (3:1 ratio).
·
Re-assess
infant after each 30secs (15 cycles).
Drugs
·
Give
through umbilical venous catheter (UVC) or IO (high dose endotracheal tube
(ETT) adrenaline can be considered).
· Remember, drugs are B.A.D. (Bicarbonate/Adrenaline/Dextrose 10%).
Related Topics