Chapter: Human Nervous System and Sensory Organs : Brain Stem and Cranial Nerves
Otic Ganglion
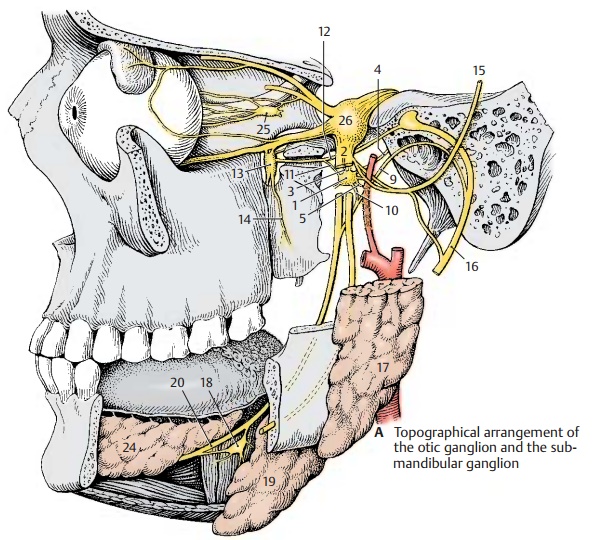
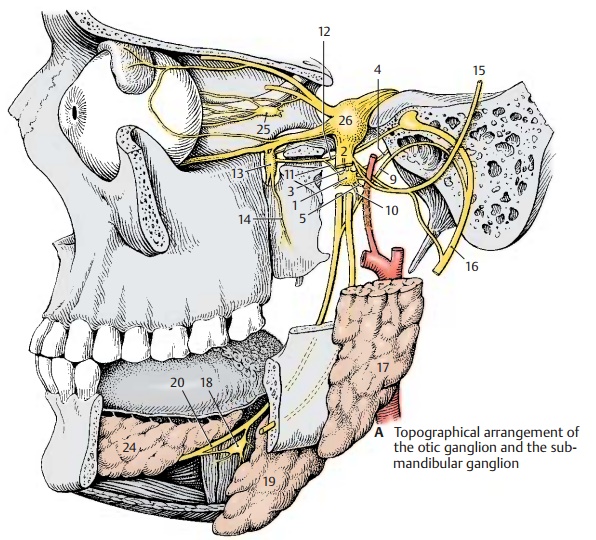
Otic Ganglion
The otic
ganglion (AB1) is a flat body lying
below the oval foramen on the medial side of the mandibular nerve (A2),
from where sensory and motor fibers (sensorimotorroots)
(AB3) enter the ganglion and
passthrough without synapsing. The pregan-glionic parasympathetic fibers originate
from the inferior salivatory nucleus.
They run in the glossopharyngeal nerve and branch off, together with the
tympanic nerve, from the inferior ganglion of the glos-sopharyngeal nerve in
the petrous fossula to the tympanic cavity. The fibers leave the tympanic
cavity through the hiatus for the lesser petrosal nerve as a fine branch, the lesser petrosal nerve (AB4) (parasympatheticroot). The nerve runs beneath the duramater along
the surface of the petrous bone and reaches the otic ganglion after passing
through the foramen lacerum. The fibers of the sympathetic root (AB5)
originate from the plexus of the middle meningeal artery.
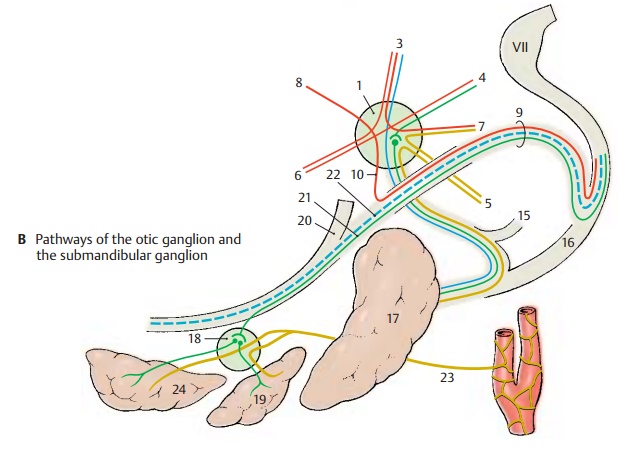
The
motor fibers from the motor root of the trigeminal nerve pass through the
ganglion and leave it in the nerve to
tensor veli palatine (B6) (soft
palate) and in the nerve to
tensortympani (B7) (for the
muscle that tightensthe tympanic membrane). Motor
fibers (B8) for the levator veli palatini from the facial
nerve (VII) are thought to run in the chorda tympani (AB9) and cross over into the gan-glion via the communicating branch withchorda tympani (AB10). They pass throughwithout synapsing and enter via a
com-municating branch (A11) the greaterpetrosal nerve (A12), in which they reachthe pterygopalatine ganglion (A13). They pass to the palate in the palatine nerves (A14).
The
postganglionic secretory (parasympa-thetic) fibers together with sympathetic
fibers enter the auriculotemporal nerve (AB15) via a communicating branch and
from here into the facial nerve (AB16) via another anastomosis. The
fibers then ramify in the parotid gland
(AB17) together with branches of the
facial nerve. Apart from the parotid gland, they supply the buccal and labial
glands via the buccal nerve and the in-ferior alveolar nerve.
Related Topics