Chapter: Human Nervous System and Sensory Organs : Brain Stem and Cranial Nerves
Cross Section at the Level of the Hypoglossal Nerve - Medulla Oblongata
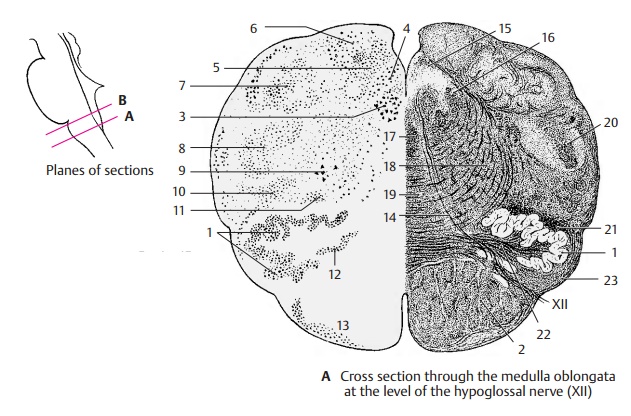
Medulla Oblongata
The semi-schematic cross sections show the cellular stain (Nissl) on the left and the corresponding fiber stain (myelin) on the right.
Cross Section at the Level of the Hypoglossal Nerve
The dorsal part, the tegmentum, shows the cranial nerve nuclei, and the ventral part shows the olive (AB1) and the pyramidaltract (AB2).
In the tegmentum, the magnocellular nu-cleus of the hypoglossal nerve (AB3) lies me-dially, and dorsally to it lie the posterior nu-cleus of the vagus nerve (AB4) and the soli-tary nucleus (AB5); the latter nucleus con-tains a large number of peptidergic neurons. The posterior funiculi of the spinal cord ter-minate dorsolaterally in the gracilis nucleus (A6) and in the cuneate nucleus (AB7) where the secondary sensory pathway, the mediallemniscus, originates. Ventrally to thecuneate nucleus lies the spinal nucleus of thetrigeminal nerve (AB8). The large cells of the ambiguous nucleus (AB9) stand out in thecenter of the field; they lie in the region of the reticular formation, of which only the slightly denser lateral reticular nucleus
(AB10) can be delimited. The olive (AB1), the fibers of which extend to the cerebellum, is accompanied by two nuclei, the posterior accessory olivary nucleus (AB11) and the medial accessory olivary nu-cleus (AB12). Along the ventral aspect of thepyramid stretches the arcuate nucleus (AB13) where collaterals of the pyramidal tract synapse (arcuatocerebellar tract).
The fibers of the hypoglossal nerve (A14) cross the medulla oblongata to reach their exit point between pyramid and olive. The posterior longitudinal fasciculus (Schütz’s bundle) (AB15) lies dorsally to thehypoglossal nucleus; laterally lies the soli-tary tract (AB16) and ventrally the medial longitudinalfasciculus (AB17). From the nucleiof the posterior funiculus, the internal ar-cuate fibers (AB18) radiate broadly into the medial lemniscus (AB19). The spi-nal tract of the trigeminal nerve (AB20) runs laterally, and the centraltegmental tract (A21) (extrapyramidalmotor tract, p. 144, A) descends dorsally to the main olivary nucleus. The fibers of the olivocerebellar tract (AB22) run through thehilum of the olive, while the superficial ar-cuate fibers (AB23) (arcuate nucleus, cere-bellum) run along the lateral part of the olive. The ventral area is occupied by the pyramidal tract (AB2).
Related Topics