Chapter: Microbiology and Immunology: Morphology and Physiology of Bacteria
Morphology and Physiology of Bacteria
Morphology and Physiology of
Bacteria
Introduction
All living beings can be classified into three kingdoms: Plant,Animal, and Protista. Microorganisms are a heterogeneousgroup of several
distinct living structures of microscopic size, classified under the kingdom
Protista. The kingdom Protista includes unicellular organisms, such as
bacteria, fungi, proto-zoa, and algae. Based on the differences in cellular
organization and biochemistry, the kingdom Protista has been divided into three
groups: prokaryotes, eukaryotes, and the most recently described
archaebacteria.
Prokaryotes: Bacteria and blue green algae
are prokary-otes. Bacteria are unicellular free living organisms having both
DNA and RNA. They are capable of performing all essential processes of life,
e.g., growth, reproduction, and metabolism. They do not show any true branching
except Actinomycetales, the higher bacteria. Bacteria lack chloro-phyll unlike
blue green algae, which contain chlorophyll.
Eukaryotes: Fungi, algae other than blue
green, protozoa,and slime moulds are eukaryotes.
Archaebacteria: These are more closely
related to eukary-otes than prokaryotes. They however do not include any human
pathogens.
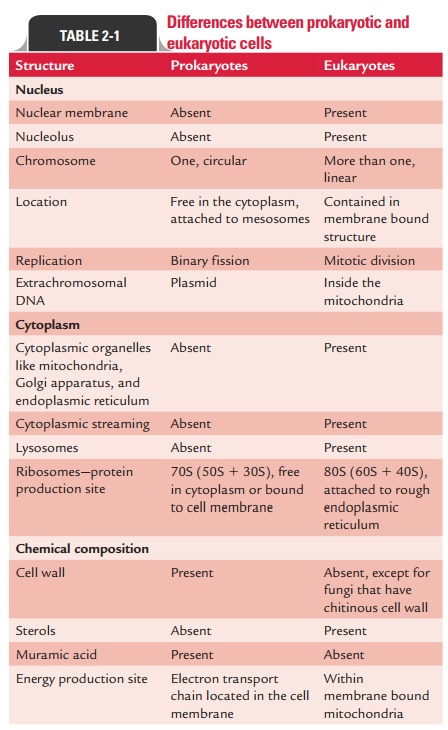
Differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes have been summarized
in Table 2-1.
Related Topics