Chapter: Special Electrical Machines : Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor
Microprocessor Based Control of PMSE
MICROPROCESSOR BASED CONTROL OF PMSE
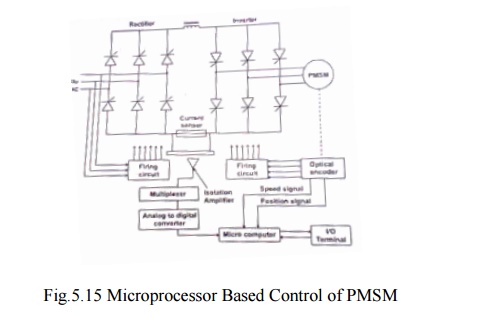
Fig 5.15 shows the block diagram of microprocessor based permanent magnet synchronous motor drive.
The advent of microprocessor has raised interest in digital control of power converter systems and electronics motor drives since the microprocessor provides a flexible and low cost alternative to the conventional method.
For permanent magnet synchronous motor drive systems, microprocessor control offers several interesting features principally improved performance and reliability, versatility of the controller, reduced components and reduced development and manufacturing cost. In the block diagram of the microprocessor controller PMSM shown in fig 5.15, the permanent magnet synchronous motor is fed from a current source d.c link converter system, which consists of a SCR invertor through rectifier and which is operated from three phase a.c supply lines, and its gating signals are provided by digitally controlled firing circuit.
The optical encoder which is composed of a coded disk attached to the motor shaft and four optical sensors, providing rotor speed and position signals. The invertor triggering pulses are synchronized to the rotor position reference signals with a delay angle determined by an 8-bit control input. The inverter SCR‘s are naturally commutated by the machines voltages during normal conditions. The speed signals, which is a train of pulses of frequency, proportional to the motor speed, is fed to a programmable counter used for speed sensing.
The stator current is detected by current sensor and amplified by optically isolated amplifier. The output signals are multiplexed and converted to digital form by a high speed analog to digital converter.
The main functions of the microprocessor are monitoring and control of the system variables for the purpose of obtaining desired drive features. It can also perform various auxiliary tasks such as protection, diagnosis and display. In normal operation, commands are fetched from the input-output terminals, and system variables (the dc link current, the rotor position and speed) are sensed and fed to the CPU. After processing, the microprocessor issues control signal to the input rectifier, then the machine inverter, so as to provide the programmed drive characteristics.
Related Topics