Chapter: Total Quality Management : Introduction
Total Quality Management
TOTAL QUALITY MANAGEMENT
INTRODUCTION
TOTAL = Made up of the whole
QUALITY = Degree of excellence a product or
service provides
MANAGEMENT = Act, art or science /manner of handling, controlling, directing etc
Meaning
TQM is a structured system for
satisfying internal and external customers and suppliers by integrating the
business environment, continuous improvement and breakthrough with development,
improvement and maintenance cycles while changing organizational culture.
What Is Quality

Quality
basically defines what is required, and how it can be achieved. It also implies
complying with the necessities, and suitability of being used. The realm of
quality has been changing rapidly from just manufacture, to numerous other
disciplines like finance, information technology, and human resources. The
benefits of implementing a quality management system are numerous, including
creation of quality products, and quality systems. Quality management system
software is extremely useful for implementing a quality management system, and
excellent quality control, resulting into total quality management. Software
testing procedures are used extensively, to ensure that only the quality
products are produced, while those not meeting the quality standards are
rejected.
What Is A Quality Management System
A quality
management system can be defined as the implementation of dedicated activities
in a project to obtain continuous improvement, and enhance the organization
efficiency. The foremost effort of this system is to correctly and precisely
define the procedure that will cause creation of quality products and quality
services. The aim is to prevent the errors while within the project, and not
after a product has been delivered to the user. There are many benefits to a
quality management system, due to which the organizations are devoting more
efforts to improve quality management.
Benefits of Quality Management Systems
The trend
of implementing a quality management procedure is gaining popularity in all
organizations, since there are tremendous benefits in using a quality
management system. Some of the benefits are explained below:
Achievement Of Project
Scope
This
system facilitates a business, to attain the objectives that have been defined
in the organization strategy. It ensures the achievement of stability and
reliability regarding the techniques, equipment, and resources being used in a
project. All project activities are integrated and aligned towards the
achievement of quality products. These efforts commence by identifying the
customer needs and expectations, and culminate in their contentment.
Customer Satisfaction
A fully
recognized and implemented quality management system, will ensure that the
customer is satisfied by meeting their requirements, and will thus enhance the
confidence of the customer. Attaining customer satisfaction is a great
achievement for the organization, that will assist in capturing the market, or
increase the market share.
Consistent Products
Implementing
a quality management system can assist to attain more consistency in the
project activities, and enhance the effectiveness by improvement in the
resources and time usage.
Implementation Of Best Practices & Process
Improvement
The discipline of quality includes the efforts directed towards the improvement of processes, being used to maintain consistency, reduce expenditures, and ensure production within the schedule baseline. The systems, products, and processes are continually improved by the implementation of best practices, like modern manufacture techniques, use of primavera project management software including Primavera P6, and the use of proper quality control techniques.
Increase In Production
Improved
production is achieved due to proper evaluation techniques being applied, and
better training of the employees. A strict process control is directed towards
performance consistency, and less scrap. Supervisors experience less late night
problematic phone calls, since the employees are trained on troubleshooting.
Less Rework
Quality
is measured continuously due to the appropriate procedures that ensure
immediate corrective actions on occurrence of defects. Since efforts are
directed towards quality products, rework due to warranty claims is minimized.
This reduction increases customer confidence, and increase in business.
Increased Financial Performance
The
discipline of quality includes the efforts directed towards the improvement of
processes, being used to maintain consistency, reduce expenditures, and ensure
production within the schedule baseline. The systems, products, and processes
are continually improved by the implementation of best practices, like modern
manufacture techniques, use of primavera project management software including
Primavera P6, and the use of proper quality control techniques.
Increase In Market Share
Other
quality management system benefits include proper management of project risks
and costs, and identification of development prospects. This results in an
increase in market share and reputation, and capability to react to industry
opportunities.
Improvement In Internal Communications
The
quality management system emphasizes the issues related to operations
management. This encourages frequent interaction between project departments or
groups, and promotes harmony. All these factors contribute to improved quality,
and customer satisfaction.
Implementation Of Quality
Management System
An
efficient quality management system should initially accurately determine the
expectations and needs of the customers, and subsequently transform this into
quality products. For the successful implementation of a TQM system, it is
essential that the executive management
should provide full support and leadership, provision of a suitable quality
policy, and establishment of measurable goals. The project management team
should be involved in the quality system, and suitable training be arranged to
enhance the skills. A useful system should be a tactical tool that is intended
to facilitate the achievement of project goals. Evaluation of the usefulness,
efficiency, and ability of a quality management system is crucial. Review and
examination should be performed regularly to audit the quality requirements,
achievement of the project objectives, and ensuring customer satisfaction. This
review will ensure that the quality management system benefits are being fully
obtained, and amendments in the system are implemented wherever necessary.
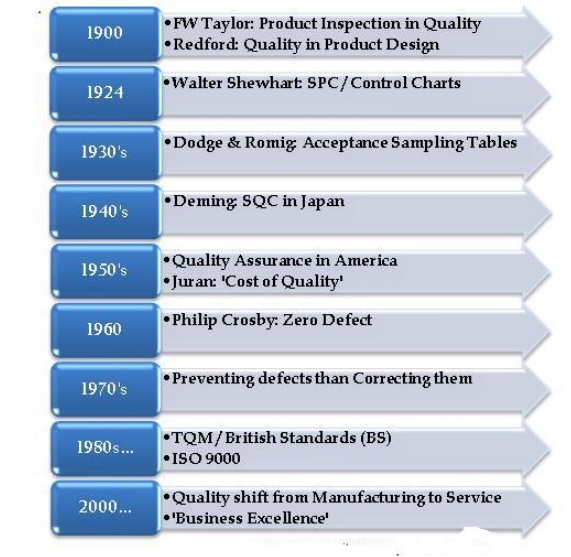
Evolution of Quality Control
DEFINING QUALITY:
Quality
can be quantified as follows Q = P / E
where,
Q =
Quality
P =
Performance
E =
Expectation
THE
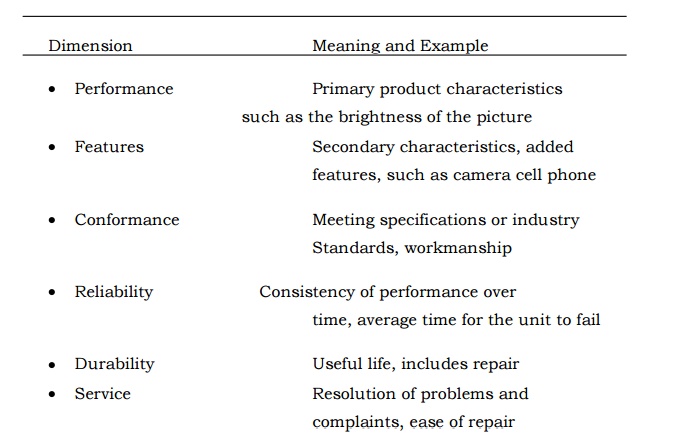
DIMENSION OF QUALITY

IMPORTANT POINTS TO BE NOTED WHILE QUALITY PLANNING
:
1. Business,
having larger market share and better quality, earn returns much higher than
their competitors.
2. Quality
and Market share each has a strong separate relationship to profitably.
3. Planning
for product quality must be based on meeting customer needs, not just meeting
product specifications.
4. For same
products. We need to plan for perfection. For other products, we need to plan
for value.
BASIC
CONCEPT OF TQM
1. A
committed and involved management to provide ling term, top to bottom
organizational support.
It is useless to embark on a
quality journey without the top management‘s commitment to quality. Top
management must participate in the quality programme. They must also
participate on quality improvement teams and also act as coaches to other teams
2. An un – wavering focus on the customer both internally
and externally. The employees of the organization in
the first place. Mangers must listen to the suggestions and recommendations
made by the employees to improve quality.
This aspect of listening to the
voice of customers leads to the emphasis of design quality and defect the prevention.
3. Effective involvement and utilization of entire
workforce.
TQM is everyone‘s responsibility
in an organization. All workers in and organization must be oriented towards
TQM and all personnel must be trained in TQM, statistical process control and
other appropriate quality improvement skills.
4. Continuous improvement of the business and production
process.
Continuous improvement refers to
constant refinement and improvement of products, services and organizational
systems to yield improved value to consumers.
Areas such as on-time delivery,
scrap reduction, supplier management, customer satisfaction, etc. are good
quality projects to begin continuous improvement.
5. Treating suppliers as partner
The traditional relationship
between the buyer and the supplier has been adversarial in nature. Each tried
to extract the maximum out of each other. There was lack of trust on each
other.
To ensure good relationship with
suppliers, frequent change of suppliers should be avoided and suppliers should
be few in number so that true partnering can occur.
6. Establishing performance measures for the process.
Performance measure is an integral
part of the quality process. If an organization cannot measure its progress, it
is useless for it to go on a quality journey. Performance measures such as
percentage of non conformance, absenteeism, customer satisfaction, etc., should
be determined for each functional area.
Definition for TQM
Total Quality Management (TQM) is a comprehensive and structured
approach to organizational management
that seeks to improve the quality of products and services through ongoing
refinements in response to continuous feedback.
HISTORICAL
REVIEW
Ø The concept of specification of
labour was introduced during the industrial revolution
Ø As a result a worker no longer
made the entire product, only a portion. This change brought about a decline in
workmanship
Ø Because productivity increased
there was a decrease in cost, which result in lower customer expectations
Ø As products become more
complicated and jobs more specialized, it became necessary to inspect product
after manufacturing
Ø In 1942 W.A. Shewhart of Bell
Telephone Laboratories developed a statistical chart for the control of product
variables. This is beginning of SQC
Ø In some decade H.F. Dodge and H.G.
Romig both of Bell telephone laboratories developed the area of acceptance
sampling as a substitute for 100% inspection. It is recognized by 1942
Ø In 1946 the American society for
Quality Control was formed. Now it is American Society for Quality
Ø In 1950 W. Edwards Deming who
learned SQC from shewhart, gave a series of lectures on statistical methods to
Japanese Engineers
Ø Un 1954 Joseph M. Juran made his
first trip to Japan and further he emphasized management‘s responsibility to
achieve quality
By this concept the Japanese set
the quality standard for the rest of the world In 1960 the first quality
circles were formed for quality improvement by Japanese workers
Ø By 19770‘s and 80‘s U.S. managers
were making frequent trips to Japan to learn about the Japanese miracle
Ø In 1980‘s the automotive industry
began to emphasizes statistical process control (SQC)
Ø Emphasis on quality continued in the auto industry in
the year 1990‘s. when
the Saturn automobile ranked first in customer satisfaction in 1996
Ø ISO 9000 became the world wide
model for quality system
TQM FRAMEWORK
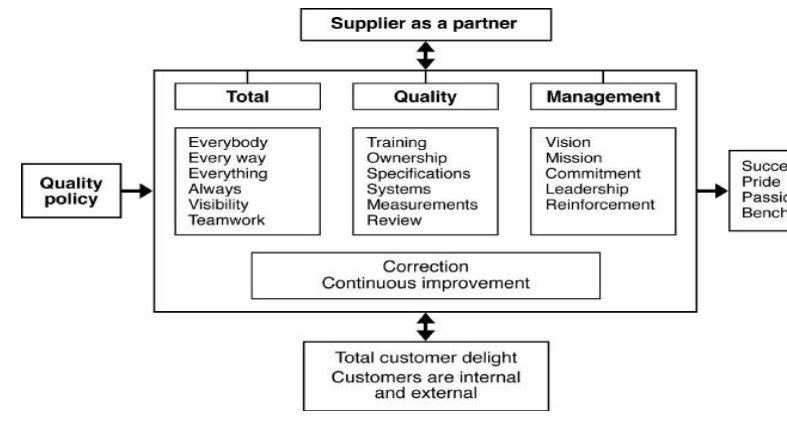
PRINCIPLES
OF TQM
1. Customer focus
2. Leadership
3. Involvement of people
4. Continuous improvement/ long-term
5. Systematic improvement/ approach
6. Problem prevention
7. Quality as everyone‘s job
8. Mutually beneficial
THE DEMING PHILOSOPHY
In 1950 he taught SPC concepts and
the importance of quality to the leading CEO‘s
of Japanese industry. He developed
the following fourteen points as a
theory for management for
improvement of quality productivity and competitive position.
1.Create
and publish the aims and purposes of the organization
Organization must develop a long
term view at least 10 yrs Plan to stay in business by setting long range goals
Resources must be allocated for
research, training and continuing education to achieve the goals
Innovation in promoted to ensure
that the product or services does not become absolute
Organizational philosophy is
developed to send the message that everyone is part of the organization
2.Learn
the new philosophy
Organization must seek
never-ending improvement and refuse to accept non-conformance.
Customer satisfaction is the
number one priority
The organization must concentrate
on defect prevention rather that defect detection.
Everyone should involved in the
quality journey and change his or her attitude about quality
Supplier must help to improve
quality
Share the information relative to
customer expectations
3.Understand
the purpose of inspection
Mass inspection is costly and un
reliable it is replace by statistical techniques It is required for self and
supplier
Mass inspection is managing for
failure and defect prevention is managing for success.
4.Stop
awarding business based on price alone
Awarding business based on the low
bid, because price has no meaning without quality
To examine how customer
expectations are affected and provide feedback to the supplier regarding the
quality
5.Improve
constantly and forever the system
Management must have take more
responsibility for problems by actively finding and correcting problemsSo that
quality and productivity are continually and permanently improved and costs are
reduced.
The focus is preventing problems
before they happen.
Responsibility is assigned to
teams to remove the causes of problems and continually improve the process.
6.Institute
training
Employee must be oriented
Management must allocate resources to train employee to perform their jobs
Everyone should be trained in statistical methods and monitor the need for
further training.
7.Teach
and institute leadership
Improving supervision is
management‘s responsibility Training in statistical methods Supervisors not
focusing on negative fault findings,
He create positive supportive
Communication must be clear from the top management to supervisor and to
operators
8.Drive
out fear, create trust and create a climate for innovation.
By providing workers with adequate
training, good supervision and proper tools to do the job as well as removing
physical dangerous.
When people are treated with
dignity fear can be eliminated and people will work for the general good of the
organization.
This climate will provide ideas
for innovations and improvement.
9.Optimize
the efforts of teams, groups, and staff areas.
Barriers internally like levels of
management among department within department etc. Barriers externally like
with customers and suppliers The barriers exist because of poor communication,
ignorance of the organization mission, completion, fear and personal grudges.
To overcome these attitudes need to be changed communication channel opened,
project teams organized, training for teamwork.
10.Eliminate
exhortations for the work force
Exhortations that ask for
increased productivity without providing specific improvements methods They do
not produce a better product or service, because the workers limited by the
system Improvements in the process cannot be made unless the tools and methods
are available.
11.a)
Eliminate numerical quotas for the work force
Instead of quotas, management must
learn and institute methods for improvements. Quotas and work standards focus
on quality rather that quality. Quotas should be replaced with statistical
method of process control.
b.)
Eliminate management by objectives
Management must learn the
capabilities of the processes and how to improve them Management by numerical
is an attempt to manage without knowledge of what to do
12. Remove barriers that rob people of pride
of workmanship
Loss of pride in workmanship
exists throughout organization because Workers do not know how to relate the
organization mission
They are being blamed for system
problems
Poor designs lead to the production of ―Junk‖
In adequate training is provided
In adequate or in-efficient
equipment is provided for
Performing the required work.
13.
Encourage Education and self-improvement for everyone
What an organization need is
people who are improving with education
A long term commitment to continuously
train and educate people must be made by management
Everyone should be retained as the
organization requirements change to meet the changing environment
14.
Take action to accomplish the transformation
Management has to accept the
primary responsibility for the never ending improvement of the process.
Management must be committed,
involved and accessible if the organization is to succeed in implementing the
new philosophy.
BARRIERS
/ OBSTACLES IN IMPLEMENTATION OF TQM
Lack
of management commitment
The management commitment should
be clearly communicated both verbally and in action to the organization.
If the workers feel that the
management is doing only the talking about no action is initiated on TQM then
they too will lack necessary commitment and motivation to implement TQM
principles.
Inability
to change organizational culture
The past culture should be
unlearned and the new culture should be learnt. This gives rise to enormous
resistance to change from the employees.
It is very difficult for an
organization to make a culture change.
Improper
planning
When planning for TQM all the
constitutes should be involved in the development of the implementation plan
and any modification that occur as the plan evolves. Rapid planning will ensure
that the TQM fails.
Planning should be done on the
customer front, employee‘s front and the supplier front.
Lack
of continuous training and education
Training and education is an
ongoing process for everyone in the organization. The training needs of the
employees must be determined and a plan should be developed to satisfy those
needs.
Training and education are most
effective when senior management conducts the training programme based on the
principles of TQM
Incompatible
organizational structures and isolated individuals and department
Lack of co ordination and
difference of opinion among departments and individuals in an organization will
create implementation problems.
The use of multifunctional teams
can help to break this barrier.
Restructuring of the organization
may be needed to make the organization more responsive to the needs of the
customers.
Ineffective
measurement techniques and lack of access to data and results
In order to improve the process,
one has to measure the present position. Mechanisms to measure the present
position should be available in the organization.
Once the measurement is done the
data should be made available to the necessary mangers to make decisions.
Any clogging of data to the
managers will become a barrier to TQM implementation.
Playing
inadequate attention to internal and external customers
Organizations
have to understand the changing needs and expectations of the customers both
internal and external.
Effective feedback mechanisms that
provide data for decision making are necessary for this understanding.
One way to overcome this is to
give the right people in the organization, a direct access to the customers.
Inadequate
use of empowerment and teamwork
Individuals should be empowered to
make decisions and take responsibility to make decisions that affect the
efficiency of the process of production.
Teams should be formed and need to
have proper training. The team‘s recommendations should be adopted whenever
possible.
CONTRIBUTIONS
OF JURAN‟S :
1. Identify customers
2. Determine customer needs
3. Translate
4. Establishment units of measurement
5. Establish measurements
6. Develop product
7. Optimize product design
8. Develop process
9. Optimize process capability
10.
Transfer
CONTRIBUTIONS
OF CROSBY‟S :
1. Management commitment
2. Quality improvement team
3. Quality measurement
4. Cost of quality evaluation
5. Quality awareness
6. Corrective action
7. Zero defect program
8. Supervisor training
9. Zero defects day
10.
Goal
setting
11.
Error
cause removal
12.
Recognition
13.
Quality
councils
14.
Do
it over again
Related Topics