Human Reproduction - Menstural cycle | 12th Zoology : Chapter 2 : Human Reproduction
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 2 : Human Reproduction
Menstural cycle
Menstural
cycle
The menstrual or
ovarian cycle occurs approximately once in every 28/29 days during the
reproductive life of the female from menarche (puberty) to menopause except
during pregnancy. The cycle of events starting from one menstrual period
till the next one is called the menstrual cycle during which cyclic changes
occurs in the endometrium every month. Cyclic menstruation is an indicator of
normal reproductive phase (Fig. 2.9).
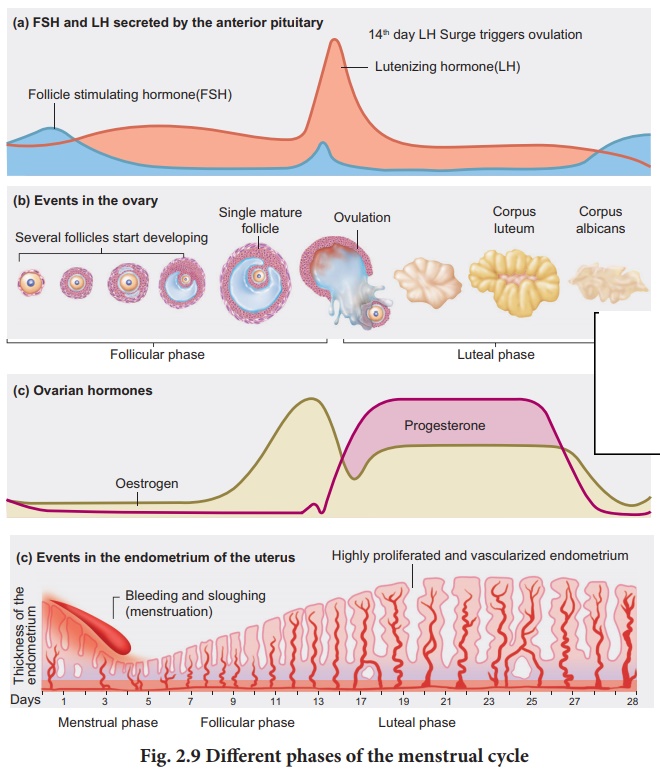
Menstrual cycle
comprises of the following phases
1.
Menstrual phase
2.
Follicular or proliferative phase
3.
Ovulatory phase
4.
Luteal or secretory phase
1. Menstrual phase
The cycle starts with
the menstrual phase when menstrual flow occurs and lasts for 3-5 days.
Menstrual flow is due to the breakdown of endometrial lining of the uterus, and
its blood vessels due to decline in the level of progesterone and oestrogen.
Menstruation occurs only if the released ovum is not fertilized. Absence of
menstruation may be an indicator of pregnancy. However it could also be due to
stress, hormonal disorder and anaemia.
2. Follicular or proliferative phase
The follicular phase
extends from the 5th day of the cycle until the time of ovulation. During this
phase, the primary follicle in the ovary grows to become a fully mature
Graafian follicle and simultaneously, the endometrium regenerates through
proliferation. These changes in the ovary and the uterus are induced by the
secretion of gonadotropins like FSH and LH, which increase gradually during the
follicular phase. It stimulates follicular development and secretion of oestrogen
by the follicle cells.
3. Ovulatory phase
Both LH and FSH attain
peak level in the middle of the cycle (about the 14th day). Maximum secretion
of LH during the mid cycle called LH surge induces the rupture of the
Graafian follicle and the release of the ovum (secondary oocyte) from the ovary
wall into the peritoneal cavity. This process is called as ovulation.
4. Luteal or secretory phase
During luteal phase, the remaining part of the Graafian follicle is transformed into a transitory endocrine gland called corpus luteum. The corpus luteum secretes large amount of progesterone which is essential for the maintenance of the endometrium.If fertilisation takes place, it paves way for the implantation of the fertilized ovum.
The uterine wall secretes nutritious fluid in the uterus for
the foetus. So, this phase is also called as secretory phase. During
pregnancy all events of menstrual cycle stop and there is no menstruation.
In the absence of
fertilisation, the corpus luteum degenerates completely and leaves a scar
tissue called corpus albicans. It also initiates the disintegration of
the endometrium leading to menstruation, marking the next cycle.
POLY CYSTIC OVARY SYNDROME (PCOS)
PCOS is a complex endocrine system disorder that affects women in their
reproductive years. Polycystic means ‘many cysts’. It refers to many partially
formed follicles on the ovaries, which contain an egg each. But they do not
grow to maturity or produce eggs that can be fertilized. Women with PCOS may
experience irregular menstrual cycles, increased androgen levels, excessive
facial or body hair growth (hirsutism),
acne, obesity, reduced fertility and increased risk of diabetes. Treatment for
PCOS includes a healthy lifestyle, weight loss and targeted hormone therapy.
Related Topics