Human Reproduction - Maintenance of pregnancy and embryonic development | 12th Zoology : Chapter 2 : Human Reproduction
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 2 : Human Reproduction
Maintenance of pregnancy and embryonic development
Maintenance
of pregnancy and embryonic development
The inner cell mass in
the blastula is differentiated into epiblast and hypoblast
immediately after implantation. The hypoblast is the embryonic endoderm
and the epiblast is the ectoderm. The cells remaining in between the
epiblast and the endoderm form the mesoderm. Thus the transformation of the
blastocyst into a gastrula with the primary germ layers by the movement of the
blastomeres is called gastrulation. Each germ layer gives rise to
specific tissues, organs and organ systems during organogenesis.![]()
![]()
The extra embryonic
membranes namely the amnion, yolk sac, allantois and chorion
protect the embryo from dessication, mechanical shock and help in the
absorption of nutrients and exchange of gases (Fig. 2.12). The amnion is
a double layered translucent membrane filled with the amniotic fluid. It
provides a buoyant environment to protect the developing embryo from injury,
regulates the temperature of the foetus and provides a medium in which the
foetus can move. The yolk sac forms a part of the gut and is the source of the
earliest blood cells and blood vessels.
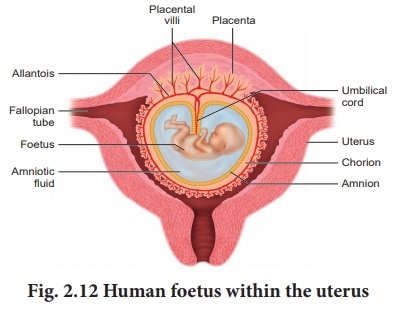
The allantois forms a
small out pocketing of embryonic tissue at the caudal end of the yolk sac. It
is the structural base for the umbilical cord that links the embryo to the
placenta and ultimately it becomes part of the urinary bladder. The chorion is
the outermost membrane which encloses the embryo and all other membranes and
also helps in the formation of the placenta.
The trophoblast cells in
the blastocyst send out several finger like projections called chorionic
villi carrying foetal blood and are surrounded by sinuses that
contain maternal blood. The chorionic villi and the uterine tissues form the
disc-shaped placenta. Placenta is a temporary endocrine organ formed
during pregnancy and it connects the foetus to the uterine wall through the
umbilical cord. It is the organ by which the nutritive, respiratory and
excretory functions are fulfilled. The embryo’s heart develops during the
fourth week of pregnancy and circulates blood through the umbilical cord and
placenta as well as through its own tissues.
The primary germ layers
serve as the primitive tissues from which all body organs develop. The ectoderm
gives rise to the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), peripheral
nervous system, epidermis and its derivatives and mammary glands. The
connective tissue, cartilage and bone, muscles, organs of urinogenital system
(kidney, ureter and gonads) arise from the mesoderm. The endodermal derivatives
are epithelium of gastrointestinal and respiratory tract, liver,
pancreas, thyroid and parathyroids.
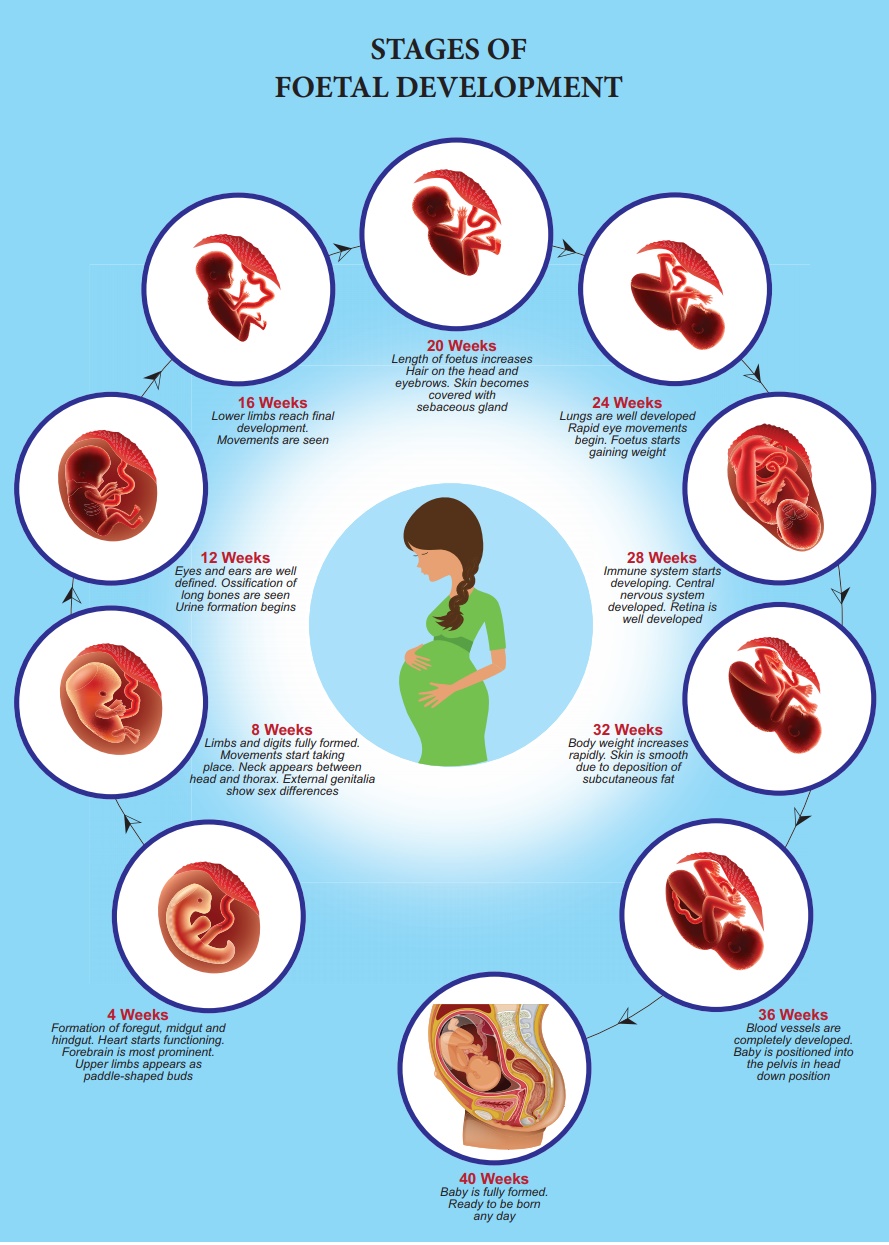
Human pregnancy lasts
for about 280 days or 40 weeks and is called the gestation period.
It can be divided for convenience into three trimesters of three months
each. The first trimester is the main period of organogenesis,
the body organs namely the heart, limbs, lungs, liver and external genital
organs are well developed. By the end of the second trimester, the face
is well formed with features, eyelids and eyelashes, eyes blink, body is
covered with fine hair, muscle tissue develops and bones become harder. The
foetus is fully developed and is ready for delivery by the end of nine months (third
trimester).
During pregnancy, the
placenta acts as a temporary endocrine gland and produces large quantities of human
Chorionic
Gonadotropin (hCG), human Chorionic Somatomammotropin (hCS) or human Placental Lactogen (hPL), oestrogens and progesterone which are essential for a normal pregnancy. A hormone called relaxin is also secreted during the later phase of pregnancy which helps in relaxation of the pelvic ligaments at the time of parturition. It should be noted that hCG, hPL and relaxin are produced only during pregnancy. In addition, during pregnancy the level of other hormones like oestrogen and progesterone, cortisol, prolactin, thyroxine, etc., is increased several folds in the maternal blood. These hormones are essential for supporting foetal growth.
Related Topics