Book Back Important Questions Answers | Choose the Correct Answers | Short, brief Answers - Human Reproduction: Questions and Answers (Evaluation) | 12th Zoology : Chapter 2 : Human Reproduction
Chapter: 12th Zoology : Chapter 2 : Human Reproduction
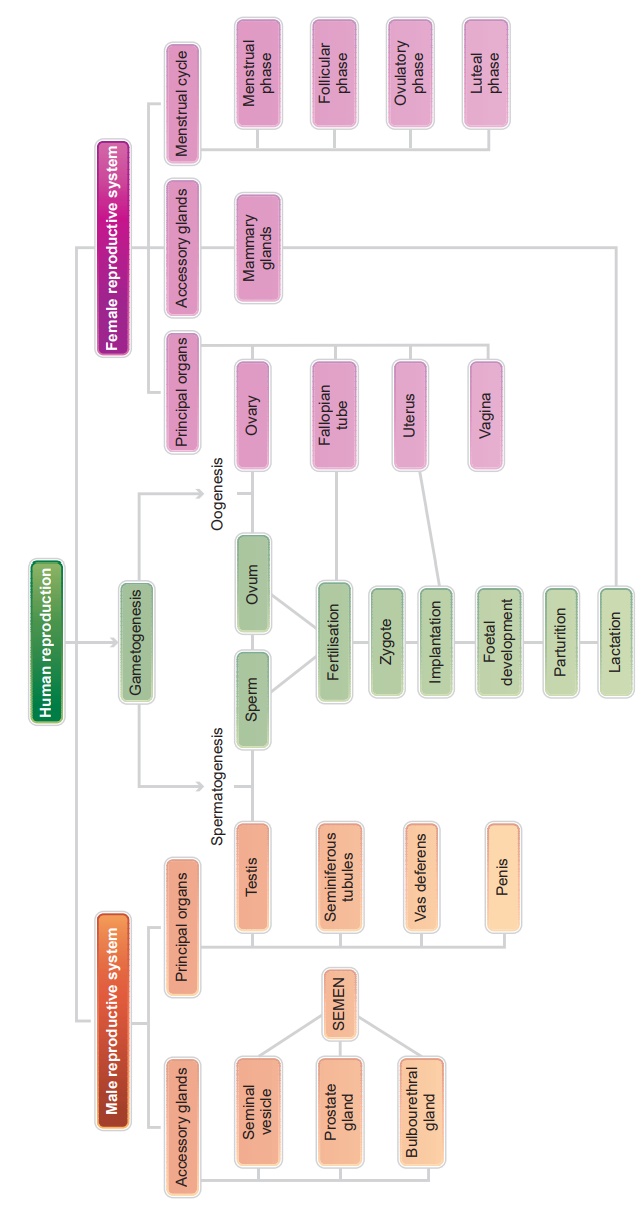
Human Reproduction: Questions and Answers (Evaluation)
Evaluation
1. The mature sperms are stored in the
a. Seminiferous tubules
b.Vas deferens
c. Epididymis
d. Seminal vesicle
Answer: c) Epididymis
2. The male sex hormone testosterone is secreted from
a. Sertoli cells
b. Leydig cell
c. Epididymis
d. Prostate gland
Answer: b) Leydig
cell
3. The glandular accessory organ which produces the largest proportion of semen is
a. Seminal vesicle
b. Bulbourethral gland
c. Prostate gland
d. Mucous gland
Answer: a) Seminal
vesicle
4. The male homologue of the female clitoris is
a. Scrotum
b. Penis
c. Urethra
d.Testis
Answer: b) Penis
5. The site of embryo implantation is the
a. Uterus
b. Peritoneal cavity
c. Vagina
d. Fallopian tube
Answer: a) Uterus
6. The foetal membrane that forms the basis of the umbilical cord is
a. Allantois
b. Amnion
c. Chorion
d. Yolk sac
Answer: a) Allantois
7. The most important hormone in intiating and maintaining lactation after birth is
a. Oestrogen
b. FSH
c. Prolactin
d. Oxytocin
Answer: c) Prolactin
8. Mammalian egg is
a. Mesolecithal and non cleidoic
b. Microlecithal and non cleidoic
c. Alecithal and non cleidoic
d. Alecithal and cleidoic
Answer: c) Alecithal
and non cleidoic
9. The process which the sperm undergoes before penetrating the ovum is
a. Spermiation
b. Cortical reaction
c. Spermiogenesis
d. Capacitation
Answer: Capacitation
10. Painful menstruation is termed as
a. Dysmenorrhoea
b. Menorrhagia
c. Amenorrhoea
d. Oligomenorrhoea
11. The milk secreted by the mammary glands soon after child birth is called
a. Mucous
b. Colostrum
c. Lactose
d. Sucrose
Answer: b) Colostrum
11B. Colostrum is rich in
a. Ig E
b. Ig A
c. Ig D
d. Ig M
12. The Androgen Binding Protein (ABP) is produced by
a. Leydig cells
b. Hypothalamus
c. Sertoli cells
d. Pituitary gland
Answer: c) Sertoli
cells
13. Which one of the following menstrual irregularities is correctly matched?
a. Menorrhagia – excessive menstruation
b. Amenorrhoea - absence of menstruation
c. Dysmenorrhoea - irregularity of menstruation
d. Oligomenorrhoea – painful menstruation
Answer: b)
Amenorrhoea - absence of menstruation
14. Find the wrongly matched pair
a. Bleeding phase - fall in oestrogen and progesterone
b. Follicular phase - rise in oestrogen
c. Luteal phase - rise in FSH level
d. Ovulatory phase - LH surge
Answer: c) Luteal
phase - risein FSH level
Answer the following type of questions
Assertion (A) and Reason (R)
a. A and R are true, R is the correct explanation of A
b. A and R are true, R is not the correct explanation of A
c. A is true, R is false
d. Both A and R are false
15. A – In human male, testes are extra abdominal and lie in scrotal sacs.
R – Scrotum acts as thermoregulator and keeps temperature lower by 2oC for normal sperm production .
a. A and R are true, R is the correct explanation of A
b. A and R are true, R is not the correct explanation of A
c. A is true, R is false
d. Both A and R are false
(a) A and R are true, R is the correct explanation of A
Answer: a) A and R are true, R is the correct explanation of A
16. A – Ovulation is the release of ovum from the Graafian follicle.
R – It occurs during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle.
a. A and R are true, R is the correct explanation of A
b. A and R are true, R is not the correct explanation of A
c. A is true, R is false
d. Both A and R are false
Answer: c) A is true,
R is false
17. A – Head of the sperm consists of acrosome and mitochondria.
R – Acrosome contains spiral rows of mitochondria.
a. A and R are true, R is the correct explanation of A
b. A and R are true, R is not the correct explanation of A
c. A is true, R is false
d. Both A and R are false
d) Both A and R are
false
18. Mention the differences between spermiogenesis and spermatogenesis.

Spermiogenesis
Transformation of
spermatids into mature spermatozoa is called spermiogenesis
Spermatogenesis
Production of male
gemetes (sperms) in the seminiferous tabules of the testes is called
spermatogenesis.
19. At what stage of development are the gametes formed in new born male and female?
Male :
• Spermatogenesis starts
at the age of puberty. It is initiated by the release of Gonadotropin Releasing
Hormone (GnRH) by the hypothalamus.
Female :
• During foetal
development, oogonia or egg mother cells are formed in the foetal ovary.
Primary oocytes are formed and they are temporarily arrested at this stage. At
puberty secondary oocyte is formed from primary oocytes and the ovum is formed
during fertilization.
20. Expand the acronyms
a. FSH b. LH c. hCG d. hPL
a) FSH - Follicle
stimulating Hormones.
b) LH - Luteinzing
Hormone
c) hCG - human
Chorionic Gonadotropin
d) hPL - human
Placental Lactogen.
21. How is polyspermy avoided in humans?
• Fertilisation is
accomplished when sperm fuses with a ovum.
• Next, the cortical
granules from the cytoplasm of the ovum from a barrier around the ovum. This is
called fertilisation membrane.
• It prevents the
further penetration of other sperms. Thus poly spermy is prevented.
22. What is colostrum? Write its significance.
• Colostrum is a
nutrient rich fluid produced by human female immediately after parturition.
• It is yellowish, It
has immune, growth and tissue repair factors.
• It is a natural
antimicrobial agent stimulating the infant's immune system.
• It has less lactose.
It has no fat. It has proteins, vitamin A, minerals.
• It is rich in IgA antibodies.
• It protects the
injant's digestive tract against bacterial infection.
23. Placenta is an endocrine tissue. Justify.
During pregnancy, the
placenta acts as a temporary endocrine gland. It produces the following
hormones.
• hCG - human Chorionic
Gonadotropin.
• human chorionic
somatomammotropin. (hCS) (or) human placenal Lactogen (hPL)
• Oestrogen
• Progesterone
• Relaxin (relax pelvic
ligaments during parturition)
Thus hormones are essential
for a normal pregnancy.
24. Draw a labeled sketch of a spermatozoan.
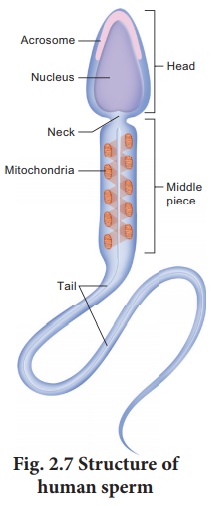
25. What is inhibin? State its functions.
• Sertoli cell or nurse
cell is in the stratified epithelium of sertoli cell. They secrete a hormone
called inhibin.
• It is involved in the
negative feedback control of sperm production.
26. Mention the importance of the position of the testes in humans.
• Testes are in a skin
sac called scrotum.
• Scrotum hangs outside
the abdominal cavity because viable sperms cannot be produced at normal body
temperature.
• Outside the abdominal
cavity the temperature is 2-3° C lower than the normal internal body
temperature.
• Thus scrotum acts as a
thermoregulator for spermatogenesis
27. What is the composition of semen?
• Semen is a milky white
fluid with sperms and the seminal plasma.
• Seminal plasma is an
alkaline fluid with fructose sugar, ascorbic acid, prostag land in, and
vesiculase.
• Vericulase is a
coagulating enzyme. It enhances sperm motility.
28. Name the hormones produced from the placenta during pregnancy.
• hCG - human Chorionic
Gonadotropin.
• hCS - human Chorionic
Somatomammotropin.
• hPL - human Placental
Lactogen.
• Oestrogens
• Progesterone
• Relaxin.
29. Define gametogenesis.
• Gametogenesis is the
formation of gametes.
• Sperms and ova are
produced from primary sex organs like testis and ovary.
• Meiosis plays a
significant role in gametogenesis.
30. Describe the structure of the human ovum with a neat labelled diagram.
• Human ovum is non -
cleidoic and alecithal.
• It is microscopic in
nature.
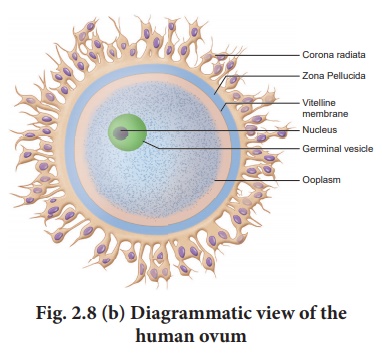
• It's cytoplasm is
called Ooplasm. Ooplasm contains large nucleus called germinal vesicle.
• It has outer thick
coat of follicular cells called corona radiata.
• The middle thick layer
is called zona pellucida.
• The inner thin
transparent layer is called vitelline membrane.
• Between the vitelline
membrane and zona pellucida is a narrow space called perivitelline space.
31. Give a schematic representation of spermatogenesis and oogenesis in humans.
It occurs in the
seminiferous tubules.
1. Multiplication phase
• Primoridial germ cells
migrate into the testes.
• They become sperm
mother cell or spermatogonia
• At puberty, the
spermatogonia undergoes mitosis. It continues throughout life.
2. Growth phase
• Spermatogonia go to
the central lumen of semeniferous tubule.
They get modified and
enlarged into primary spermatocytes, (diploid)
3. Maturation phase
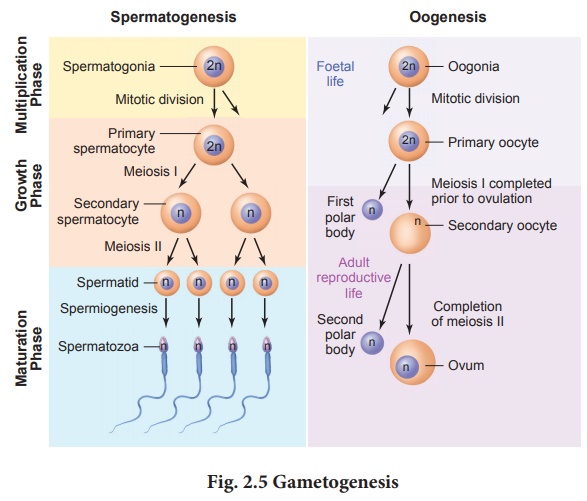
• Primary spermatocytes
undergo first meiotic division to form two secondary spermatocytes (haploid)
• The secondary
spermatocytes undergo second meiotic division to form 4 haploid spermatids.
4. Spermiogenesis
• Transformation of
spermatids into mature spermatozoa.
Oogenesis :
It is the process of
development of female gamete ovum (egg) in ovary.
1. Proliferation phase
• Cells in the germinal
epithelium to foetal ovary divide by mitosis.
• Thus millions of
Oogonia or egg mother cells are formed.
2. Growth phase
• Oogonia form primary
Oocytes by meiosis. (prophase I of Meiosis I)
• Primary Oocytes
surrounded by single layer of granulosa cells is called primary follicles. Many
of them degenerate.
• Primary follicles
surrounded by many layers of granulosa cells. These are called secondary
follicles.
• A fluid filled space
called antrum is formed in secondary follicle. Thus it is transformed into
tertiary follicle.
• Primary Oocyte in
tertiary follicle grows in size.
3. Maturation pause
• Primary Oocyte
completes first meiotic division and forms secondary Oocyte.
• Large haploid
secondary Oocyte and first polar body is formed. First polar body
disintegrates.
• During fertilisation
secondary Oocyte undergoes second meiosis. Thus a large cell ovum and second
polar body are formed. Second polar body degenerates.
32. Explain the various phases of the menstrual cycle.
Menstrual cycle.
• It occurs in every
28/29 days. It is from puberty (menarche) to menopause (except during
pregnancy).
• The cycle of events
from one menstrual period till the next one is called the menstrual cycle.
Phases of menstrual cycle
1. Menstrual phase.
• Progesterone,
oestrogen level decreases.
• So uterine endometrial
lining and the blood vessels break.
(a) FSH and LH secreted by the anterior pituitary (b) Events in the ovary (c) Overian hormones (d) Events in the endometrium of the uterus
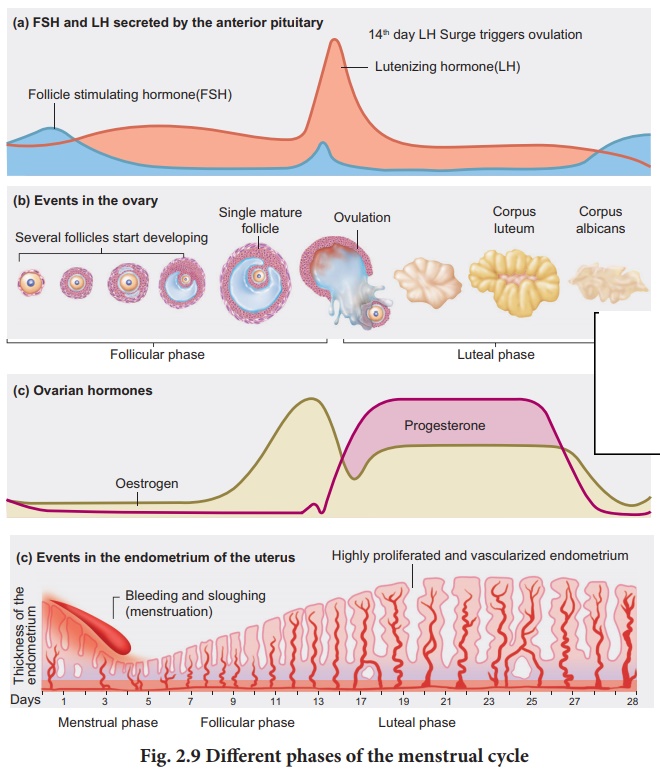
• It results in
menstrual flow for 3-5 days.
• It occurs only if the
ovum is not fertilised.
• Absence of
menstruation indicates pregnancy.
• It is also due to
stress, hormonal disorder and anaemia.
2. Follicular Phase or Proliferative Phase (From day 5)
• Secretion of FSH and
LH induces the following changes.
• Primary follicle of
ovary becomes the mature graffian follicle.
• Endometrium
regenerates.
• Follicular development
is stimulated.
Oestrogen is secreted
by the follicle cells.
3. Ovulatory Phase (about 14th day)
• LH and FSH attain peak
level.
• LH surge (increase)
induces the rupture of graffian follicle.
• Ovum (secondary
Oocyte) is released from the ovary wall into peritoneal cavity. This process is
called ovulation.
4. Luteal or Secretory Phase.
• The remaining part of
the graafian follicle becomes a transitory endocrine gland. It is called corpus
luteum.
• Corpus luteum secretes
progesterone. It is needed for the maintenance of endometrium.
• After fertilisation
the progesterone helps in implantation, of fertilised ovum.
• Uterine wall secretes
nutritive fluid for the foetus. So this phase is called as secretory phase.
• No menstruation occurs
during pregnancy.
• In the absence of
menstruation, the corpus luteum degenerates. It becomes a scartissue called
Corpus albicans.
• It initiates the next cycle.
33. Explain the role of oxytocin and relaxin in parturition and lactation.
Role of Relaxin in parturition and lactation :
• Relaxin is secreted by
the placenta. It is found in corpus luteum.
• It relaxes pelvic
ligaments.
• It dilates the cervix
• It created continuous
powerful contractions
• The amnion ruptures
• The amniotic fluid
flows through vagina.
• It is followed by the
foetus.
• The placenta and the
remains of, the umbilical cord is called 'after birth' It is expelled out after
delivery.
Role of oxytocin :
• It causes the Let Down
Reflox
• Ejection of milk from
the alveoli of mammary glands.
• During lactation, it
stimulates the contraction of the empty uterus. Now uterus return to prepregnancy
size.
34. Identify the given image and label its parts marked as a, b, c and d
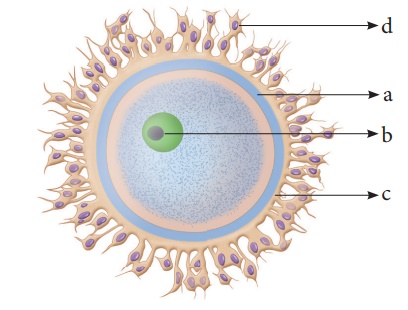
The given image is
'human ovum'
a. Vitelline Membrane
b. Nucleus.
c. Zona Pellucida.
d. Corona radiata.
35. The following is the illustration of the sequence of ovarian events (a-i) in a human female.
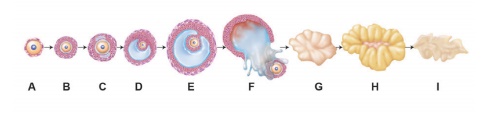
a) Identify the figure that illustrates ovulation and mention the stage of oogenesis it represents.
b) Name the ovarian hormone and the pituitary hormone that have caused the above-mentioned events.
c) Explain the changes that occurs in the uterus simultaneously in anticipation.
d) Write the difference between C and H.
a) Figure 'F'
illustrates ovulation. It represents ovulatory phase of Oogenesis.
b) Ovarian hormone -
Progesterone, Oestrogen.
Pituitary hormone -
FSH (Follicle stimulating hormone) LH (Luteinizing Hormone).
c) Change in uterus
• Endometrium
regenerates.
• Fertilisation paves
way for the implantation of fertilised ovum.
• uterine wall secretes
nutritious fluid for the foetus. So luteal phase is called Secretory phase.
d) C - Secondary
Follicle
H - Corpus luteum.

Secondary follicle
• Found in follicular
phase (or) proliferative phase.
• It is surrounded by
many layers of granu losa cells and a new theca layer
• Later it becomes
graafian follicle
Corpus luteum
• Found in luteal phase
(or) secretory phase.
• It is a transitory
endocrine gland secreting progesterone.
• Later it becomes a
scar called corpus albicans.
Related Topics