Chapter: Human Nervous System and Sensory Organs : Brain Stem and Cranial Nerves
Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus
Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus
The medial longitudinal fasciculus is not a
uniform fiber tract but contains different fiber systems that enter and exit at
various levels. It reaches from the rostral midbrain into the spinal cord and
interconnects numerous nuclei of the brain stem. On cross sections through the
brain stem, it is found in the middle of the tegmentum, ventrally from the
central gray.
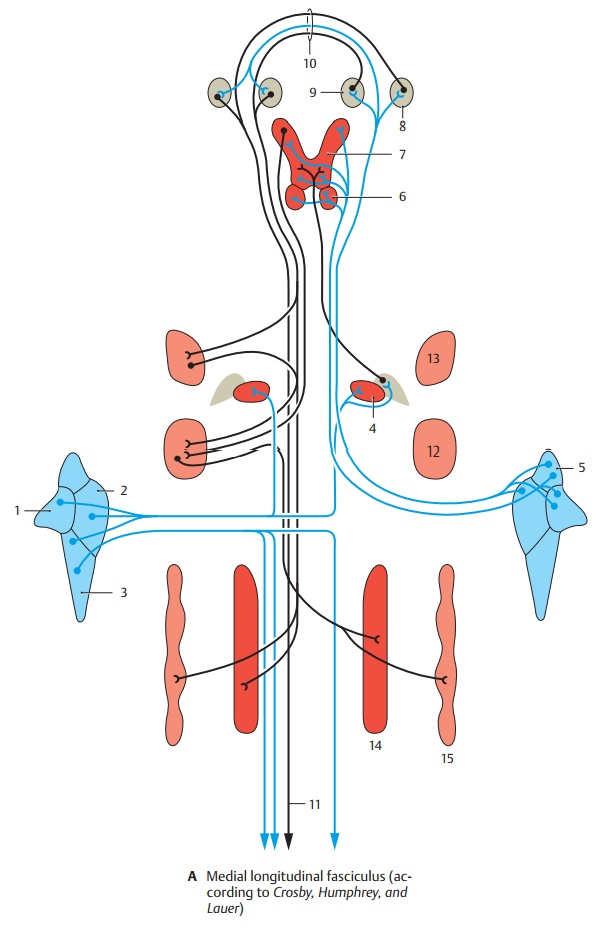
Vestibular part. Crossed and uncrossedfibers run
in the longitudinal fasciculus from the lateral (A1), medial (A2), and
infe-rior (A3) vestibular nuclei to
the abducens nucleus (A4) and to the
motor cells of the anterior horn of the cervical spinal cord. From the superior
vestibular nucleus (A5), fibers
ascend to the ipsilateral trochlear nu-cleus (A6) and oculomotor nucleus (A7).
The vestibular fibers finally terminate in the ipsilateral or contralateral
interstitial nu-cleus of Cajal (A8)
and in Darkshevich’s nu-cleus (A9)
(decussation of the epithalamic commissure [A10]). The longitudinal fasciculus connects the vestibular
apparatus with the eye and neck muscles and with the extrapyramidal system.
Extrapyramidal part.The interstitial nu-cleus of Cajal
and Darkshevich’s nucleus are intercalated in the course of the longitudi-nal
fasciculus. They receive fibers from the striatum and pallidum and crossed
fibers from the cerebellum. They send a fiber tract, the interstitiospinal fasciculus (A11),
in the longitudinal fasciculus to the caudal brain stem and into the spinal
cord.
Internuclear part.This consists of connect-ing
fibers between motor nuclei of cranial nerves, namely, between abducens nucleus
(A4) and oculomotor nucleus (A7), facial nucleus (A12) and oculomotor nucleus, fa-cial
nucleus and motor nucleus of the trigeminal nerve (A13), hypoglossal nucleus (A14)
and ambiguous nucleus (A15).
The
interconnections of motor nuclei of cranial nerves allow certain muscle groups
to interact functionally, for example, during the coordination of eye muscles
with themovements of the eyeball, coordination of eyelid muscles during opening
and closing of the eyelids, and coordination of mastica-tory muscles and
muscles of tongue and pharynx during swallowing and speaking.
Related Topics