Chapter: Physics : Crystal Physics
Low temperature solution growth : Slow cooling and Slow evaporation method
SOLUTION GROWTH
Low temperature solution growth
The
low temperature solution growth is suitable for materials which decompose at
high temperature and undergo phase transformation below the melting point.
There
are two methods of low temperature solution growth. They are
i.
Slow cooling method
ii.
Slow evaporation method
SLOW COOLING METHOD
Slow
cooling is the easiest method to grow bulk single crystals from solution. This
technique needs only a vessel only a vessel for the solution, in which the
crystals grow.
The
temperature at which crystallization begin is in the range of 45oC
to 75oC and the lower limit of the cooling is the room temperature.
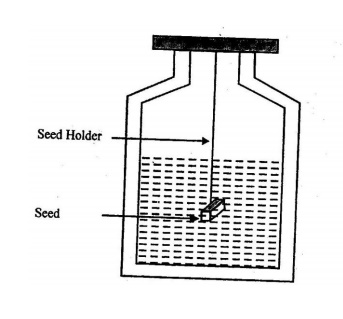
SLOW EVAPORATION METHOD
In
this method, the saturated solution is kept at a particular temperature and
provision is made for evaporation. The basic apparatus (Manson Jar
crystallizer) used for the solution growth technique is shown in the figure
Typical
growth conditions involve temperature stabilization at about 0.05oC
and rate of evaporation of a few mm3/h.
ADVANTAGES
i.
This is a simple and convenient method
of growing single crystals of large size.
ii.
Growth of strain and dislocation free
crystals.
iii.
Permits the growth of prismatic crystals
by varying the growth conditions.
iv.
Only method which can be used for
substances that undergo decomposition before melting.
DISADVANTAGES
i.
The growth substance should not react
with the solvent
ii.
This method is application from
substances fairly soluble in solvent
iii.
Small crystals are also formed on the
walls of the vessel near the surface of the liquid. These tiny crystals fall in
the solution and hinder the growth of the crystal
iv.
A variable rate of evaporation may
affect the quality of the crystal
Related Topics