Chapter: Physics : Crystal Physics
Lattice Parameters or Unit Cell Parameters
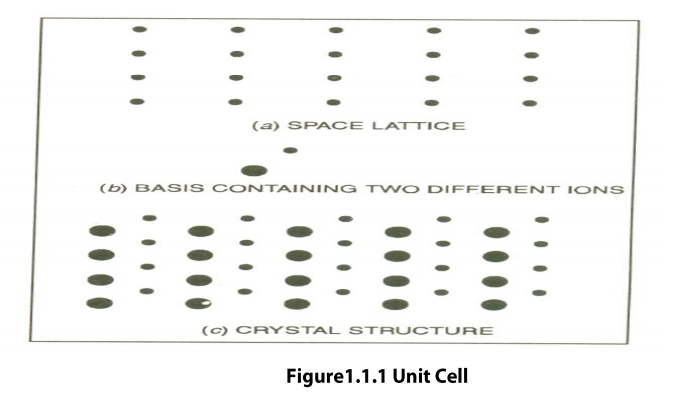
Unit Cell is defined as the smallest geometric figure or pattern, the repetition of which gives the actual crystal structure. This is also defined as undamental elementary pattern o minimum of atoms or molecules or groups of molecules, which represents total characteristics of the material or the crystal.
Lattice Parameters or Unit Cell Parameters
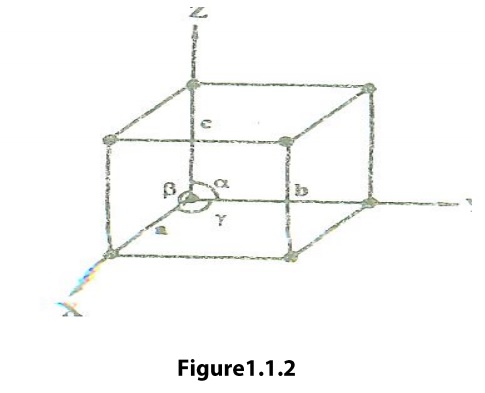
The lines drawn parallel to the lines of
intersection of any three faces of the Unit Cell which do not lie in the same
plane are called Crystallographic Axis.
The intercepts a,b, c (i.e., the distance
between the two lattices points ) are nothing but the edges of the unit cell,
which defines the dimensions of unit cell. These intercepts are known as its primitives or
characteristic intercepts on the axes.
These three quantities a, b, c is also called
the fundamental translational vectors or axial lengths. The angles (a,b), (b,c)
and (c,a) are denoted by α,ẞ,γ respectively. These three angles (α,ẞ,γ) are
called Interfacial angle.
But the intercept (a,b,c) and the interracial
angle (α,ẞ,γ) constitutes the lattice parameters o the unit cell.
The actual size o the unit cell can be
determined by knowing the values o intercepts and interracial angles.
Primitive Cells.
A Primitive Cellsis the simplest type
of the unit cell, which contains only one lattice point per unit cell.
(Contains lattice points at its corner only)
Example: Simple Cubic
Non Primitive Cell
A Non Primitive Cell is one, which contains
more than one lattice point per unit cell.
Example: BCC and FCC contain more than one
unit cell.
If the number of lattice points per unit cell
is two (BCC), three and four(FCC), then the unit cell is called doubly primitive,
triply primitive and Quadruple Primitive respectively.
Related Topics