Chapter: Physics : Crystal Physics
Characteristics of the Unit Cell
Characteristics
of the Unit Cell
In this section, we discuss some of the
important parameters, which are used to describe the crystal structure of the
material. A unit cell is characterized by the following parameters.
·
Number of atoms per unit cell.
·
Coordination number
·
Atomic Radius
·
Packing factor (or) packing density
No
of atoms per unit cell:
The
number of atoms possessed by a unit cell is known as number of atoms per unit
cell.
The distribution of atoms is different for
different lattice structure. This can be determined if the arrangement of atoms
inside the cell is known.
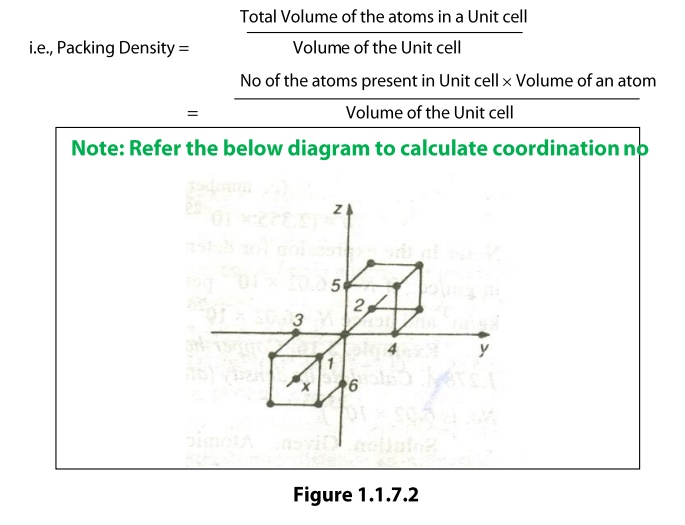
Coordination
Number
The coordination number of an atom in a
crystal is the number atoms directly surrounding with that atom. If the
coordination number is high, then the structure will be more closely packed. It
signifies the tightness of packing of atoms in the crystal.
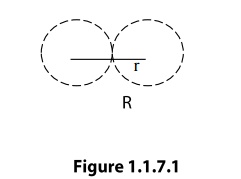
Atomic
radius
Atomic radius is defined as half of the
distance between any two nearest neighboring atoms, which have direct contact
with each other, in a crystal of a pure element. It is usually expressed in
terms of cube edge ‘a’(Lattice paramenter).
Packing
Factor
The packing density is the ratio between
the total volume occupied by the atoms or the molecule in an unit cell and the
volume of the unit cell.
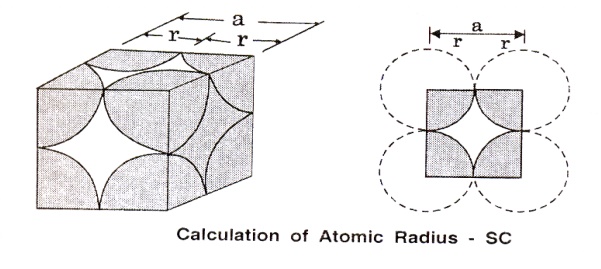
A simple cubic (SC) unit cell consists
of eight corner atoms as shown in the figure
(i)
Number
of atoms per unit cell
In
actual crystal, each and every corner atoms is shared by eight adjacent unit
cells. Therefore, each and every corner atoms contribute 1/8 of its part to
aone unit cell. Hence the total number of atoms present in the unit cells is
1/8 x 8 = 1 atom.
(ii)
Coordination
number
The
coordination number of a simple cubic unit can be calculated as follows. Let us
consider any corner atom; there are four nearest neighbors in its own plane.
There is another nearest neighbor in a plane, which lies just above this atom,
and another just below this atom. Therefore, the total number of nearest
neighbors is six and hence the coordination number is 6.
(iii)
Atomic
radius
For
a simple cubic unit cell, the atomic radius is given by, r=a/2, where ‘a’ is
the side of the unit cell and is equal to the distance between centers of the
two nearest atoms.
(iv)
Packing
factor
Number
of the atoms per unit cell=1
Volume
of one atom v = 4/3 πr3
Where
r is the atomic radius
Slide
of the unit cell, a=2r
Atomic
radius r=a/2
Total
volume of the unit cell V=a3
We
know the packing factor= v/V
Substituting
for v and V, we have
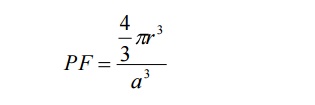
Substituting
a=2r , we get
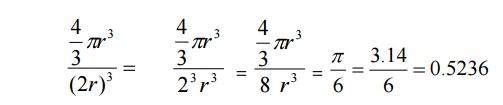
Thus
52% of the volume of the simple cubic unit cell is occupied by atomes and the
remaining 48% of the volume of the unit cell is Vacant.
Thus
the packing density is 52%. Since the packing density is very low, SC has
loosely packed structure.
Related Topics