Chapter: Introduction to Human Nutrition: Nutrition and Metabolism of Lipids
Lipids as components of the diet
Lipids as components of the diet
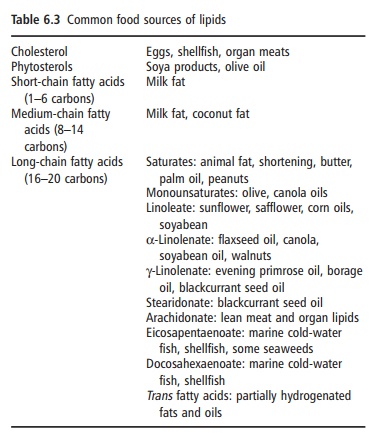
Food or dietary sources of lipids are listed in Table 6.3.
Cholesterol is found only in animal lipids, while a variety of other
phytosterols occur in plants. Soyabeans, leafy plants, and lean animal meat are
rich in dietary phospholipids. Animal fat and plant oils from seeds or nuts are
rich in TAG.
The leafy and fruit components of plants contain phospholipids
and sterols, whereas seeds contain tri-glycerides. With rare exceptions such as
flaxseed (linseed), edible green leaves are proportionally much richer in α-linolenate than are seeds. Seed oils are usually rich in either
linoleate or oleate. Common plant sterols include β-sitosterol, β-sitostanol, and campesterol. Foods
enriched with esters of plant sterols are used widely to lower blood
cholesterol via the inhibition of cholesterol absorption in the gut.
Phospholipids and cholesterol constitute the majority of lipids in tissues (gut, kidney, brain, skeletal muscle, etc.) of lean, undomesticated animals. By
contrast, in domesticated animals, TAGs or non-membrane lipids present in
subcutaneous and intra-muscular adipose tissue deposits are the dominant form
of lipid on a weight basis. This is because domes-tication usually involves
rearing animals with minimal exercise and on higher energy intakes, leading to
more subcutaneous and visceral TAG obtained through both fat synthesis and
deposition of dietary fat.
Animal meat lipids are the main dietary source of arachidonate
(20:4n-6), although it can also be obtained from tropical marine fish.
Lipoproteins are the main form of lipid in the blood. Like
lipoproteins, milk lipids also occur as globules consisting of a combination of
a mainly TAG core surrounded by a membrane con-taining proteins, cholesterol,
and phospholipids.
Phospholipids and cholesterol constitute the main lipids of
undomesticated edible fish, which usually have low amounts of TAG or stored
body fat. As in domesticated animals, it is likely that subcutaneous and
intramuscular fat deposits of TAG will increase in commercially farmed fish.
Cold-water marine fish are the main dietary source of the long-chain n-3 (omega-3)
polyunsaturates eicosapentaenoate (20:5n-3), and docosahexaenoate (22:6n-3),
but the former is also found in several types of edible seaweed. Tropi-cal fish
generally have higher arachidonate than do cold-water fish.
Partial hydrogenation is a common feature of unsaturated fatty
acids in processed foods. Complete hydrogenation makes fats very hard and is
more expensive than partial hydrogenation. Depending on the applications and
the source of the original oil or fat, partial hydrogenation is an economical
way to control the properties of fats or oils used in food production. Dietary
diacylglycerols and monoacyl-glycerols are used by the food industry for
emulsifica-tion of water- and oil-based components in foods such as ice cream
and mayonnaise.
Related Topics