Chapter: Embedded and Real Time Systems : Introduction to Embedded Computing
Important Questions and Answers: Embedded Computing
EMBEDDED COMPUTING
1. Define Embedded System. What are the components of embedded system?
An Embedded system is one that has computer hardware with software embedded in it as one of its most important component.
The three main components of an embedded system are
Hardware
Main application software
RTOS
2. In what ways CISC and RISC processors differ?
CISC
It provides number of addressing modes
It has a micro programmed unit with a control memory
An easy compiler design
Provide precise and intensive calculations slower than a RISC
RISC
It provides very few addressing modes
It has a hardwired unit without a control memory
Complex compiler design
Provide precise and intensive calculations faster than a CISC
3. Define system on chip (SOC) with an example
Embedded systems are being designed on a single silicon chip called system on chip. SOC is a new design innovation for embedded system
Ex. Mobile phone.
4. Give any two uses of VLSI designed circuits
A VLSI chip can embed IPs for the specific application besides the ASIP or a GPP core. A
system on a VLSI chip that has all of needed analog as well as digital circuits.
Eg. Mobile phone.
5. List the important considerations when selecting a processor.
Instruction set
Maximum bits in an operand
Clock frequency
Processor ability
6. What are the types of embedded system?
Small scale embedded systems
Medium scale embedded systems
Sophisticated embedded systems
7. Classify the processors in embedded system?
General purpose processor
Microprocessor
Microcontroller
Embedded processor
Digital signal processor
Media processor
Application specific system processor
Multiprocessor system using GPP and ASSP GPP core or ASIP core
integrated into either an ASIC or a VLSI circuit or an FPGA core integrated with processor unit in a VLSI chip.
8. What are the important embedded processor chips?
ARM 7 and ARM 9
i 960
AMD 29050
9. Name some DSP used in embedded systems?
TMS320Cxx
SHARC
5600xx
10. Name some of the hardware parts of embedded systems?
Power source
Clock oscillator circuit
Timers
Memory units
DAC and ADC
LCD and LED displays
Keyboard/Keypad
11. What are the various types of memory in embedded systems?
RAM (internal External)
ROM/PROM/EEPROM/Flash
Cache memory
12. What are the points to be considered while connecting power supply rails with embedded system?
A processor may have more than two pins of Vdd and Vss
Supply should separately power the external I/O driving ports, timers, and clock and
From the supply there should be separate interconnections for pairs of Vdd and Vss pins analog ground analog reference and analog input voltage lines.
13. What is watch dog timer?
Watch dog timer is a timing device that resets after a predefined timeout.
14. What are the two essential units of a processor on a embedded system?
Program Flow control Unit
Execution Unit
15. What does the execution unit of a processor in an embedded system do?
The EU includes the ALU and also the circuits that execute instructions for a program control task. The EU has circuits that implement the instructions pertaining to data transfer operations and data conversion from one form to another.
16. Give examples for general purpose processor.
Microcontroller
Microprocessor
17. Define microprocessor.
A microprocessor is a single VLSI chip that has a CPU and may also have some other units for example floating point processing arithmetic unit pipelining and super scaling units for faster processing of instruction.
18. When is Application Specific System processors (ASSPs) used in an embedded system?
An ASSP is used as an additional processing unit for running the application specific tasks in place of processing using embedded software.
19. Define ROM image.
Final stage software is also called as ROM image .The final implement able software for a product embeds in the ROM as an image at a frame. Bytes at each address must be defined for creating the image.
20. Define device driver.
A device driver is software for controlling, receiving and sending byte or a stream of bytes from or to a device.
20. Name some of the software’s used for the detailed designing of an embedded system.
Final machine implement able software for a product
Assembly language
High level language
Machine codes
Software for device drivers and device management.
21. What are the various models used in the design of an embedded system?
Finite state machine
Petri net
Control and dataflow graph
Activity diagram based UML model
Synchronous data flow graph
Timed Petri net and extended predicate/transition net
Multithreaded graph
22. Give some examples for small scale embedded systems.
ACVM
Stepper motor controllers for a robotic system
Washing or cooking system
Multitasking toys
23. Give some examples for medium scale embedded systems
Router, a hub and a gateway
Entertainment systems
Banking systems
Signal tracking systems
24. Give some examples for sophisticated embedded systems
Embedded system for wireless LAN
Embedded systems for real time video
Security products
ES for space lifeboat.
25. What are the requirements of embedded system?
Reliability
Low power consumption
Cost effectiveness
Efficient use of processing power
26. Give the characteristics of embedded system?
Single-functioned
Tightly constrained
Reactive and real time
27. What are the design metrics?
Power
Size
NRE cost
Performance
28. What are the challenges of embedded systems?
Hardware needed
Meeting the deadlines
Minimizing the power consumption
Design for upgradeability
29. Give the steps in embedded system design?
Requirements
Specifications
Architecture
Components
System integration
30. What are the requirements?
Before designing a system, it must to understand what has to be designed. This can be known from the starting steps of a design process.
31. Give the types of requirements?
Functional requirements
Non functional requirements
32. Define functional requirements?
It says the fundamental functions of an embedded system.
33. Give some examples of functional requirements?
Performance
Cost
physical size and weight
power
34. What is the use of requirements form?
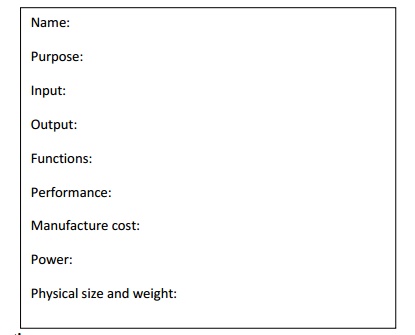
It is used as a checklist in the requirements analysis. From this the fundamental properties of a system came to be known.
35. What are the entries of a requirement form?
Name
Purpose
Inputs and outputs
Functions
Performance
Manufacturing cost
Power
Physical size and weight
36. What is meant by specification?
This is a bridge between Customer and Architect. It conveys the customer’s needs. These
needs are properly used in the design process.
37. What is architecture design?
It says the way of implementing functions by a system. Actually architecture is a plan for whole structure of a system. While will bring the design of components later.
38. Define system integration?
It is a processor of combining the components into one system.
39. What are the functions of memory?
The memory functions are
To provide storage for the software that it will run.
To store program variables and the intermediate results
Used for storage of information
40. Define RAM?
RAM refers Random Access Memory. It is a memory location that can be accessed
without touching the other locations.
41. What is data memory?
When the program is executing, to save the variable and program stack, this type of
memory is used
42. What is code memory?
The program code can be stored by using this area. The ROM is used for this purpose.
43. What are the uses of timers?
The time intervals can be completed
Precise hardware delays can be calculated
The timeout facilities are generated
44. Give short notes on RAM processor?
It is said to be the family of RISC architecture. The ARM instructions are written one
per line, starting after the first column.
45. What are the data types supported by RAM?
Standard ARM word is 32 bit long Word is splitted into 4 8 bit bytes
46. What are the 3 types of operating modes?
Normal mode
Idle mode
Power down mode
1. List the hardware units that must be present in the embedded systems.
Power Source and managing the power
Most systems have a power supply of own. The supply has a specific operation range or a range of voltages. Various units in unzip for place of Infatuation to Embedded System in one of the following four accelerator are examples of embedded systems that do not have their own power supply v and connect to pi power-supply lines. 1Z; A charge pump consists of a diode in the series followed by a charging capacitor. The diode gets forward bias input from an external signal.
Real Time Clock (RTC) and Timers for Various
Timing and Counting Needs of the System a timer circuit suitably configured is the system-clock, also called real-time clock (RTC). It is used by the schedulers and for real-time programming. More than one timer using the system clock (RTC) may be needed for the various timing and counting needs in a system.
Clock Oscillator Circuit and Clocking Unit(s)
The Clock is an important unit of a system. A processor needs a clock oscillator circuit. The clock controls the various clocking requirements of the CPU, of the system timers and the CPU machine cycles
Memories
In a system, there are various types of memories. They are as follows:
Internal RAI\4 of 256 or 5lZ bytes in a microcontroller for registers, temporary data
Internal ROM/PROMIEPROM for about 4 KB to 16 KB of program External RAM for the temporary data and stack Internal caches EEPROM or flash
External ROM or PROM for embedding software RAM Memory buffers
Caches (in superscalar microprocessors)
Pulse Dialer, Modem and Transceiver
For user connectivity through the telephone line, wireless, or a system provides the necessary interfacing circuit.
It also provides the software for pulse dialing through the telephone line, for modem interconnection for fax, for Internet packets routing, and for transmitting and connecting a WAG (Wireless Gateway) or cellular system.
A transceiver is a circuit that can transmit as well as receive byte streams
Linking and Interfacing Buses and Units of the Embedded System Hardware
The buses and units in the embedded system hardware are needed to be linked and
interfaced.
One way to do this is to incorporate a glue logic circuit.
LCD and LED Displays
System requires an interfacing circuit and software to display the status or message for a fine, for multi-line displays, or flashing displays
An LCD screen may show up a multilane display of characters or also show a graph or icon
An LCD needs little power. It is powered by a supply or battery (a solar panel in the calculator). LCD is a diode that absorbs or emits right on appreciation of 3 V to 4 V and 50 or 60 Hz voltage pulses with currents less than 50 pA. An LSI (Lower Scale Integrated circuit) display controller is often used in the cise of matrix displays.
2. Explain the Exemplary applications of each type of embedded system.
Small Scale Embedded system
A long needle rotates elderly minute such that it 'returns to same position after an hour. A short needle rotates every hour. Such that it returns to same position after twelve hours
ACVM
Stepper motor controllers for a robotic system
Washing or cooking system
Multitasking toys
Medium scale embedded systems
Router, a hub and a gateway
Entertainment systems
Banking systems
Signal tracking systems
Sophisticated embedded systems
Embedded system for wireless LAN
Embedded systems for real time video
Security products
ES for space lifeboat.
3. Explain the various form of memories present in a system
Various forms of memories are
RAM(internal External)
ROM
PROM
EEPROM
Flash
Cache memory
EEPROM or flash
Extemal ROM or PROM for embedding software
RAM Memory buffers
Caches (in superscalar microprocessors)
4. Explain the software tools in designing of an embedded system.
Tools
Editor
Interpreter
Compiler
Assembler
Cross assembler
Simulator
Source code engg software
RTOS
Stethoscope
Trace Scope
IDE
Prototype
Locator
5. Explain the processors in an Embedded System
Processors in an ES
General purpose processor Microprocessor
Microcontroller Embedded processor Digital signal processor Media processor
Application specific system processor
Multiprocessor system using GPP and ASSP
GPP core or ASIP core integrated into either an ASIC or a VLSI circuit or an FPGA core integrated with processor unit in a VLSI chip.
Explanation
A processor has two essential units
Program Flow Control Unit (CU)
Execution Unit (EU)
An embedded system processor chip or core can be one of the following.
Microprocessor.
Microcontroller.
Embedded Processor.
Digital Signal Processor (DSP).
Media Processor.
6. What are the Challenges in Embedded systems?
How much hardware do we need?
For the great deal of control over the amount of computing power ,we cannot only select microprocessor used but also the amount of memory and peripheral device etc.
The choice of hardware must meet both performance deadlines and manufacturing cost constraints.
How do we meet deadlines?
Brute-force way to meet deadline by speedup the hardware so that the program runs faster.
Increase in speed makes the system more expensive and also increasing the CPU clock rate.
How do we minimize power consumption?
In battery powered applications, power consumption is very important.
In non battery powered applications, excessive power consumption can increase heat. One way to consume less power is to run the system more slowly.
But slow down the system can obviously lead to missed deadlines.
Careful design is required to slow down the non critical parts of the machine.
How do we design for upgradeability?
Hardware platform may be used over several product generations or for several different versions of a product in the same generation with few or no changes.
Hardware is designed such that the features are added by changing software.
Does it really work?
Reliability is very important when selling products.
Reliability is important because running system and try to eliminate bugs will too late and fixing bugs will more expensive.
7. Embedded system design process?
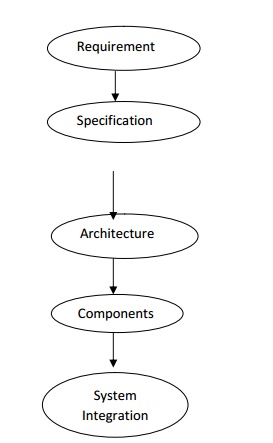
Requirements:
We must know what we are designing, the initial state of the design process capture this information for use in creating the architecture and components.
We gather an informal description from the customer known as requirements and we refine the requirement into specification that contain enough information to design the system architecture.
Requirement may be functional or non functional requirements include
Performance:
The speed of the system is major consideration for the usability of the system and for its ultimate cost.
Performance may be a combination of soft performance metric and deadline by which a particular operation must be completed.
Cost:
Manufacturing cost
Non-Recurring Engineering
Physical size and Weight:
An industrial control system for an assembly line may be designed to fit into a standard size with no limitation and weight.
A handheld device typically has tight requirement on both size and weight that can move to the entire system design.
Power consumption:
Power can be specified in requirement states in terms of
Battery Life
Describe the allowable voltage
Validating Requirements:
Checking that a system meets specifications and fulfill its purpose.
One good way to refine the user interface portion of a system requirement is to get a mock-up.
Simple Requirement Form:
Specification:
It serves as the contract between the customer and the architecture.
These specifications must be carefully written so that it reflects the customer’s requirements and it helps during design.
Designers who lack a clear idea what to build undergo a faculty assumption early in the process.
Specification must be understandable
Unclear specification will cause different types of problems.
Example for specification: GPS system
Architecture Design:
The architecture is a plan for the overall structure of the system.
It will be used later to design the component that makeup the architecture.
System Integration:
Once the components are build up then they are integrated together and see the working system.
Bugs are determi
ned during integration.
Careful attention to inserting appropriate debugging facilities during design can help ease system integration.
8. Embedded system for digital camera?
Embedded system:
Ø An embedded system is a computer system design to perform a particular task or few dedicated functions. Eg: digital camera, calculator, cell phone
It may be either an independent system or a part of a large system.
Embedded system are controlled by one or more processing coder typically either microcontroller or DSP.
It has application software and real time operating system (RTOS) in program memory and may perform series of task or multiple tasks.
Digital Camera:
The charge couple Device (CCD) contains an array of light sensitive photocells that capture an image.
The memory controller controls access to a memory chip also found in the camera, while the DMA controller enables direct memory access by other devices while the microcontroller is performing other functions.
The LCD control and Display control circuits control the display of images on the camera’s liquid crystal display device.
The system always acts as a digital camera wherein it captures, compresses, and stores frames, decompresses and displays frames and upload frames.
It is tightly constrained. The system must be lower cost so that the consumers able to afford such camera.
It must be small so that it fits into within a standard sized camera.
It must be fast so that it can process numerous images in milliseconds.
It must consume less power so that the camera’s battery will last long time.
Related Topics