Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Endocrine system
Hypothyroidism (myxoedema) - Thyroid axis
Hypothyroidism (myxoedema)
Definition
Hypothyroidism is a clinical syndrome resulting from a deficiency of thyroid hormones.
Aetiology
Hypothyroidism may be divided into primary thyroid failure, secondary hypothyroidism due to lack of pitu-itary TSH and tertiary hypothyroidism due to lack of hypothalamic thyrotrophin releasing hormone (TRH) (see Table 11.8).

Pathophysiology
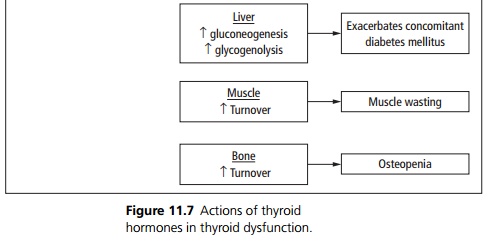
Congenital hypothyroidism causes permanent developmental retardation. In children it causes reversible delayed growth and puberty, and developmental delay. Precocious puberty may occur in juveniles, due to pituitary hypertrophy. In adults it causes decreased removal of glycosaminoglycans and hence deposition in the extracellular space, especially skin, heart and skeletal muscle. There is also increased capillary permeability to albumin.
Clinical features
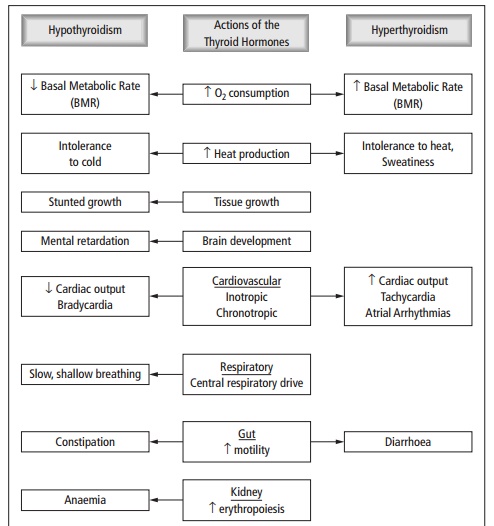
Usually insidious onset. Common symptoms are increasing lethargy, forgetfulness, intolerance to cold, weight gain, constipation and depression (see also Fig. 11.7).
· Cardiovascular system: The heart is less contractile causing bradycardia and reduced cardiac output. Hypercholesterolaemia increases the incidence of atherosclerosis.
· Respiratory system: Respiration may be slow and shallow. Respiratory failure occurs in myxoedema coma.
· Gastrointestinal system: Reduced peristalsis, leading to chronic constipation. Ileus may occur.
· Genitourinary system: Impaired ability to excrete water predisposes to water overload. Women may have menstrual irregularities, particularly heavy periods.
· Haematological: Anaemia (normally normochromic/ normocytic).
· Other signs include a cool rough dry skin, hair loss, puffy face and hands, a hoarse husky voice and slowed reflexes. The skin may be yellowish (due to reduced conversion of carotene to vitamin A).
Complications
Pericardial and pleural effusions. Carpal tunnel syndrome. Deafness due to fluid in the middle ear.
Investigations
Hypothyroidism is confirmed by a low T3 and T4 (except in end organ resistance) with a raised TSH in primary hypothyroidism. Thyroid autoantibodies are present in patients with autoimmune disease.
Other investigations are aimed at diagnosing the underlying cause and are indicated according to the history and clinical suspicion.
Management
Thyroxine replacement starting with a low dose is required for life. Treatment of elderly patients should be undertaken with care, as any subclinical ischaemic heart disease may be unmasked. Thyroxine dosing is titrated according to thyroid function tests.
Related Topics