Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Endocrine system
Hypopituitarism
Hypopituitarism
Definition
Hypopituitarism is a clinical term referring to under-function of the pituitary gland. This may imply a deficiency of single or multiple hormones.
Aetiology
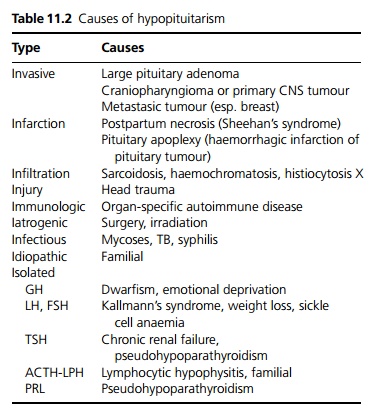
The commonest causes are pituitary or hypothalamic tumours, or secondary to pituitary surgery or cranial radiotherapy (see Table 11.2).
Pathophysiology
Hypopituitarism may be primary due to destruction of the anterior pituitary gland or secondary to a deficiency of hypothalamic stimulation (or excess of inhibition).
Clinical features
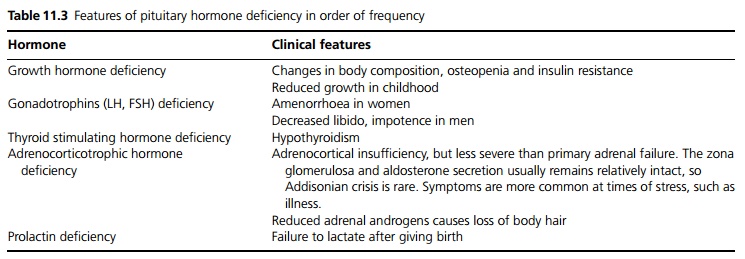
Symptoms and signs are related to the deficiency of hormones (see Table 11.3). General symptoms of panhy-popituitarism include dry, pale skin with sparse body hair. On examination postural hypotension and bradycardia may be found with decreased muscle power and delayed deep tendon reflexes.
Investigations
All functions of the pituitary should be assessed using basal levels, stimulation tests and suppression testing where appropriate.
Management
Treatment of the underlying cause may be required. Hormone replacement depends on the results of pituitary function testing:
· In ACTH deficiency, lifelong glucocorticoid replacement is essential.
· In TSH deficiency, oral thyroxine is given and titrated according to free T4. Thyroxine replacement may aggravate any partial adrenal insufficiency, if present, by increasing cortisol clearance.
· Gonadotrophin deficiency in women may be treated with cyclical oestrogen replacement to maintain secondary sexual characteristics and prevent osteoporosis. Progestagen is used to induce bleeding and prevent endometrial hyperplasia. In men testosterone replacement restores libido and potency, maintains beard growth and muscle power, prevents osteoporosis and improves sense of well-being. In ado-lescent males testosterone induces epiphyseal closure, so replacement therapy should be delayed as long as possible. Treatment of associated infertility requires complex hormone replacement to stimulate ovulation/spermatogenesis.
Growth hormone deficiency is treated with recombinant human growth hormone.
Related Topics