Sources, Properties, Types | Chemistry in Everyday Life - Hydrocarbons | 8th Science : Chapter 15 : Chemistry in Everyday Life
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 15 : Chemistry in Everyday Life
Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons are the organic
compounds consisting of carbon and hydrogen atoms. They are combustible and
produce large amount of heat energy along with carbon dioxide and water vapour,
on burning. Hence, many hydrocarbons are used as fuels.
1. Sources of
Hydrocarbons
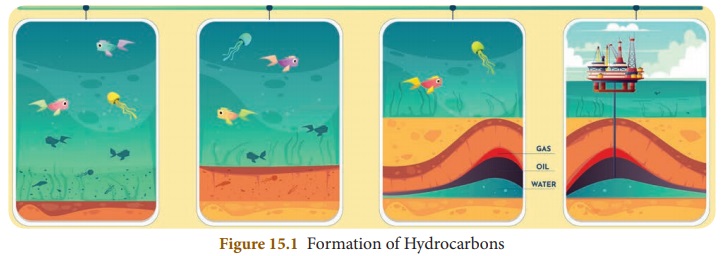
Hydrocarbons occur naturally and
they are found in fossil fuels like crude oil, natural gas and coal. About 300
million years ago plants and animals died and they were buried on the ocean
floor. Overtime they were covered by silt and soil layers.
Then they were buried deep inside
the earth and compressed through temperature and pressure and converted to
fossil fuels like oil and natural gas. These fuels are found in porous rocks
which lie below large bodies of water, especially oceans. By drilling these
rocks hydrocarbons can be extracted. Hydrocarbons are present in different
trees and plants also.
2. Properties of
Hydrocarbons
Among all the chemical compounds
hydrocarbons have some unique properties. Some of them are given below.
* Most of the hydrocarbons are
insoluble in water.
* Hydrocarbons are less dense than
water. So they float on top of water.
* Most hydrocarbons react with
oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water.
* Hydrocarbons can be gases (E.g.
methane and propane), liquids (E.g. hexane and benzene) or waxes (paraffin).
* Hydrocarbons are capable of making
bonds with one another. This property is known as catenation (chain formation).
Due to this property they form more number of complex molecules.
3. Types of Hydrocarbons
In hydrocarbons carbon and hydrogen
atoms are linked together through different chemical bonds. Depending on the
bond between these atoms there are number of hydrocarbons. The four general
classes of hydrocarbons are: alkanes, alkenes, alkynes and arenes. Some of the
common hydrocarbons are methane, ethane, propane, butane and pentane.
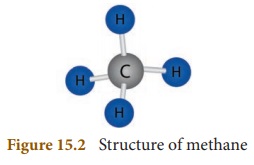
Methane is the simplest hydrocarbon
in which four hydrogen atoms are linked with one carbon atom. It is a
colourless, odourless and inflammable gas. It is an eco-friendly fuel because
it does not produce any harmful products. It is used as a fuel in electricity
generation. Methane is also known as marsh gas as it is present in marshes.
Dead and decaying plants and animals release methane gas. It is a renewable
source of energy. Sewage sludge can also be decomposed by microorganisms to
produce methane gas along with impurities like carbon dioxide and hydrogen
sulphide. After removing these impurities, methane gas can be used as an
efficient fuel.
Activity 1
Make a model using
clay and match sticks for the following hydrocarbons.
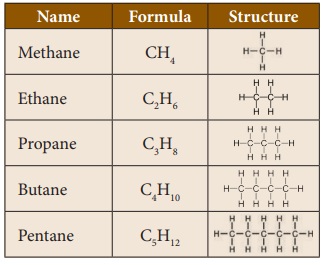
Propane is an odourless and highly
inflammable gas. It is heavier than air. It is liquefied through pressurisation
and commonly used as LPG (Liquefied Petroleum Gas) along with butane. Propane
is used as fuel in heating, cooking and vehicles. Propane can also be used as
refrigerants.

Propane is used in LPG
cylinders. Since it is an odouress gas, any leakage cannot be detected. Hence,
a chemical byname Mercaptan is mixed with LPG to help in detection of any
leakage of LPG.
Butane is a gas at room temperature
and atmospheric pressure. They are highly flammable, colorless gases that quickly
vaporize at room temperature. Butane is used as a fuel gas and propellant in
aerosol sprays such as deodorants. Pure forms of butane can be used as
refrigerants. Butane is also used as lighter fuel for a common lighter or
butane torch.
Pentanes are liquids with low
boiling point. They are used as fuels and solvents in the laboratory. They are
also used to produce polystyrene.
Related Topics