Extraction, Types, Uses, Products - Coal | 8th Science : Chapter 15 : Chemistry in Everyday Life
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 15 : Chemistry in Everyday Life
Coal
Coal
Coal is one of the fossil fuels. It
is a mixture of free carbon and compounds of carbon containing hydrogen,
oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur. Three hundred million years ago, some plants grew
into giant ferns and mosses. These plants got buried into the bottom of the
soil. They slowly started to decompose and formed a dense, sponge like material
called peat. Over time peat was compressed due to high temperature and pressure
and coal was formed. As coal contains mainly carbon, the slow process of
conversion of dead vegetation into coal is called carbonization.
1. Extraction of Coal
Coal is extracted from the coal beds
found below the surface of the earth. Coal found inside the earth is broken
into pieces by explosives and brought above. Depending on the depth of the coal
bed, coal is extracted in two ways.
Surface
mining
If the coal beds lie within 22 feet
of the earth’s surface, the top soil is removed and coal is dug out. This is
called surface mining.

Underground
mining
In some places, coal beds are found
very deep inside the earth. In that case underground tunnels are made to get
this coal. This is called underground mining or deep mining.

Coal reserves can be found in about
70 countries worldwide. The largest coal reserves are available in United
State, Russia, China, Australia and India. The US is the international leader
in coal reserves, with nearly 30% of the world’s supply. Coal mining was
started in India in 1774. India now ranks third among the coal producing
countries in the world. USA and China have two third of the world’s coal
reserve.
2. Types of Coal
Coal is classified into four main
categories based on the amounts of carbon it contains and the heat energy it
can produce. They are lignite, sub bituminous, bituminous and anthracite. Among
these four types anthracite is the most desirable one due to its high heat content.

Lignite
Lignite is a brown colored coal of
lowest grade. It has the lowest carbon content. The carbon content of lignite
is 25 – 35%. Lignite contains a high amount of water and makes up almost half
of our total coal reserves. It is used for electricity generation. The other
uses include generating synthetic natural gas and producing fertilizer
products.
Sub-bituminous
When lignite becomes darker and
harder over time sub-bituminous coal is formed. Sub bituminous coal is a black
and dull coal. It has higher heating value than lignite and contains 35-44%
carbon. It is used primarily as fuel for electricity power generation. This
coal has lower sulphur content than other types and burns cleaner.
Bituminous
With more chemical and physical changes, sub-bituminous coal is developed into bituminous coal. Bituminous coal is dark and hard. It contains 45-86% carbon. It has high heating value. It is used to generate electricity. Other important use of this coal is to provide coke to iron and steel industries. By-products of this coal can be converted into different chemicals which are used to make paint, nylon, and many other items.
Anthracite
Anthracite is the highest grade
coal. It has a very light weight and the highest heat content. Anthracite coal
is very hard, deep black and shiny. It contains 86-97% carbon and has a heating
value slightly higher than bituminous coal. It burns longer with more heat and
less dust.
Activity 4
In an outline map of
India mark the places where coal mines are found. Also identify the type of
coal found in those areas.
3. Uses of Coal
* Coal is used to generate heat and
electricity.
* It is used to make derivatives of
silicon which are used to make lubricants, water repellents, resins, cosmetics,
hair shampoos, and toothpaste.
* Activated charcoal is used to make
face packs and cosmetics.
* Coal is used to make paper.
* Coal helps to create alumina
refineries.
* Carbon fibre which is an extremely
strong but light weight material is used in construction, mountain bikes, and
tennis rackets.

* Activated carbon, used in filters
for water and air purification and in kidney dialysis machines is obtained from
coal.
4. Products obtained from
coal
Coal when heated in the absence of
air does not burn but produces many by -products. This process of heating coal
in the absence of air is called destructive distillation of coal. The
destructive distillation of coal can be carried out in the laboratories. The
apparatus is as shown in Figure 15. 13.
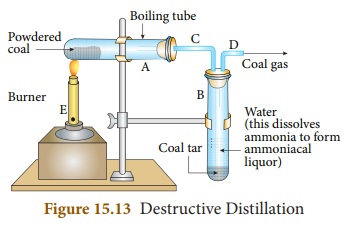
Finely powdered coal is taken in a
test tube and heated. At a particular temperature coal breaks down to produce
coke, coal tar, ammonia and coal gas. Coal tar is deposited at the bottom of
the second test tube and coal gas escapes out through the side tube. Ammonia
produced is absorbed in the water, forming ammonium hydroxide. Finally a black
residue called coke is left in the tube.
Thousands of different products have
coal or coal by-products as their components. Some of them are soap, aspirins
(tablet), solvents, dyes, plastics, and fibres, such as rayon and nylon. The
main by products obtained during destructive distillation are coke, coal tar,
ammonia and coal gas.
Coke
Coke contains 98% carbon. It is a
porous, black and the purest form of coal. It is a good fuel and burns without
smoke. It is largely used as a reducing agent in the extraction of metals from
their ores. It is also used in making fuel gases like producer gas and water
gas.
Coal
tar
Coal tar is a mixture of different
carbon compounds. It is a thick, black liquid with unpleasant smell. The
fractional distillation of coal tar gives many chemical substances like
benzene, toluene, phenol and aniline. They are used in the preparation of dyes,
explosives, paints, synthetics fibers, drugs, and pesticides. Another product
obtained from coal tar is naphthalene balls which are used to repel moth and
other insects.
Coal
gas
Coal gas also known as town gas is
mainly a mixture of gases like hydrogen, methane and carbon monoxide. The gases
present in coal gas are combustible and hence, it is an excellent fuel. It has
high calorific value.
Ammonia
The other by product obtained from
coal is ammonia. It is used for making fertilizers such as ammonium sulphate,
ammonium superphosphate etc.
It is also known as Black Diamond owing to its precious nature.
On destructive distillation, 1000 kg of coal gives 700 kg of coke, 100 litres
of ammonia, 50 litres of coaltar and 400 m3 of coal gas.
Related Topics