Types, Characteristics, Efficiency - Fuel | 8th Science : Chapter 15 : Chemistry in Everyday Life
Chapter: 8th Science : Chapter 15 : Chemistry in Everyday Life
Fuel
Fuel
Any substance that can produce heat
and energy on burning is called fuel. We use this heat for various purposes
such as cooking, heating and many industrial and manufacturing purposes. Some
of the fuels that we use in our daily life are wood, coal, petrol, diesel and
natural gas.
1. Types of fuel
Fuels are classified into different
types according to their physical state. They are classified into solid, liquid
and gaseous fuels.
Solid
fuels
Fuels like wood and coal are in
solid state and they are called solid fuels. This type of fuel was the first
one to be used by man. These fuels are easy to store and transport. The
production cost is also very low.
Liquid
fuels
Most of the liquid fuels are derived
from the fossil remains of dead plants and animals. Petroleum oil, coal tar and
alcohol are some of the liquid fuels. These fuels give more energy on burning
and burn without ash.
Gaseous
fuel
Coal gas, oil gas, producer gas and
hydrogen are some of the gaseous fuels. These fuels can be easily transported
through pipes and they do not produce pollution.
2. Characteristics of
fuel
An ideal fuel should have the
following characteristics.
* It should be readily available
* It should be easily transportable
* It should be less expensive
* It should have high calorific value
* It should produce large amount of heat
* It should not leave behind any
undesirable substances
3. Efficiency of Fuel
Any fuel contains carbon as its main
constituent. During the combustion of fuel carbon combines with oxygen and
liberates large amount of heat. It is expected that a fuel liberates maximum
amount of heat in the short time. The efficiency of a fuel can be understood
from the following terms.
Specific
Energy
Specific energy is the amount of
energy produced by unit mass of a fuel. It is defined as the energy per unit
mass. It is used to measure the stored energy in certain substances. Its unit
is Jkg-1.
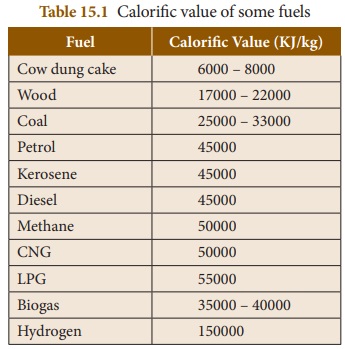
Calorific
Value
It is the quantity of heat produced
by the complete combustion of fuel at constant pressure and normal conditions.
It is measured in terms of KJ kg-1.
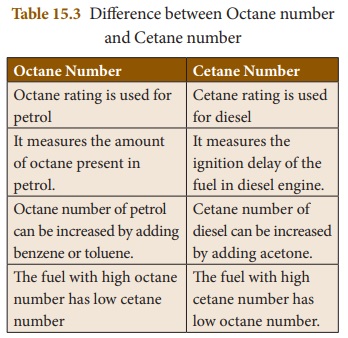
Octane
Number
Octane number denotes the amount of
octane present in petrol. The fuel having high octane number is called as an
ideal fuel.
Cetane
Number
Cetane number measures the ignition
delay of the fuel in diesel engine. When cetane number is higher the ignition
delay is shorter. The fuel with high cetane number is called as the ideal fuel.
Related Topics