Chapter: Medical Surgical Nursing: Management of Patients With Musculoskeletal Trauma
Humeral Shaft - Fracture
HUMERAL SHAFT
Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are most frequently caused by (1) direct trauma that results in a transverse, oblique, or com-minuted fracture, or (2) an indirect twisting force that results in a spiral fracture. The nerves and brachial blood vessels may be in-jured with these fractures. Wrist drop is indicative of radial nerve injury. Initial neurovascular assessment is essential to identify nerve or blood vessel injury, which requires immediate attention.
Medical Management
Initially, well-padded
splints, overwrapped with an elastic bandage, are used to immobilize the upper
arm and to support the arm in 90 degrees of flexion at the elbow. A sling or
collar and cuff support the forearm. The weight of the hanging arm and splints
reduce the fracture. External fixators are used to treat open fractures of the
humeral shaft. Open reduction with internal fix-ation of a fracture of the
humerus is necessary with nerve palsy, blood vessel damage, comminuted
fracture, or pathologic fracture.
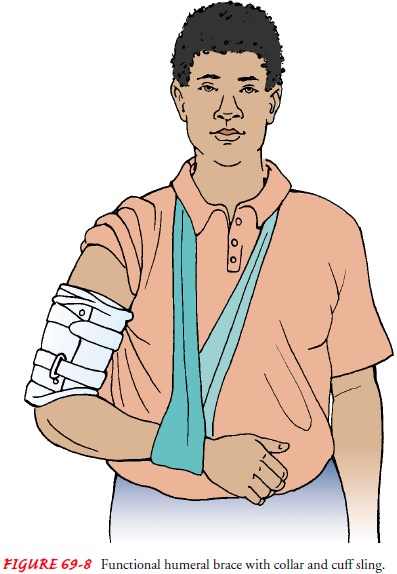
Functional bracing is another form of treatment used for these fractures. A contoured thermoplastic sleeve is secured in place with interlocking
fabric (Velcro) closures around the upper arm, immobilizing the reduced
fracture. As swelling decreases, the sleeve is tightened, and uniform pressure
and stability are applied to the fracture. The forearm is supported with a
collar and cuff sling (Fig. 69-8). Functional bracing allows active use of
muscles, shoulder and elbow motion, and good approxima-tion of fracture
fragments. Pendulum shoulder exercises are performed as prescribed to provide
active movement of the shoulder, thereby preventing adhesions of the shoulder
joint capsule. Isometric exercises may be prescribed to prevent mus-cle
atrophy. The callus that develops is substantial, and the sleeve can be
discontinued in about 8 weeks. Complications that are seen with humeral shaft
fractures include delayed union and nonunion.
Related Topics