Environmental Issues - Green House effect and Global Warming | 12th Botany : Chapter 8 : Environmental Issues
Chapter: 12th Botany : Chapter 8 : Environmental Issues
Green House effect and Global Warming
Green House effect and Global Warming
Green House Effect is a process by which radiant heat from the sun
is captured by gases in the atmosphere that increase the temperature of the
earth ultimately. The gases that capture heat are called Green House
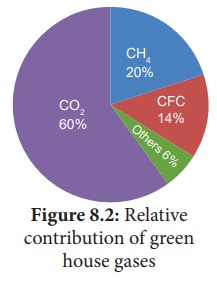
Gases which include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4),
Nitrous Oxide(N2O) and a variety of manufactured chemicals like
chlorofluorocarbon (CFC).
Increase in greenhouse gases lead
to irreversible changes
in major ecosystems and climate patterns. For
example, coral ecosystem is affected by increase in temperature, especially coral
bleaching observed in Gulf of Mannar, Tamil Nadu.
Human activities lead to produce the green house effect by
·
Burning fossil fuels, which releases CO2 and CH4
·
Way of Agriculture and animal husbandry practices
·
Electrical gadgets like refrigerator and air conditioners release
chloro fluoro carbons
·
The fertilizers used in Agriculture which release N2O
·
The emissions from automobiles.
The increase in mean global temperature (highest in 4000 years)
due to increased concentration of green house gases is called global
warming.
One of the reasons for this is over population which creates
growing need for food, fibre and fuel and considered to be the major cause of
global warming.
1. Effects of Global Warming
·
Rise in global temperature which causes sea levels to rise as
polar ice caps and glaciers begin to melt causing submergence of many coastal
cities in many parts of the world.
·
There will be a drastic change in weather patterns bringing more
floods or droughts in some areas.
·
Biological diversity may get modified, some species ranges get
redefined. Tropics and sub-tropics may face the problem of decreased food
production.
2. Sources of Green House Gases Emission (Natural and Anthropogenic)
CO2 (Carbon dioxide)
·
Coal based power plants, by the burning of fossil fuels for
electricity generation.
·
Combustion of fuels in the engines of automobiles, commercial
vehicles and air planes contribute the most of global warming.
·
Agricultural practices like stubble burning result in emission of
CO2.
·
Natural from organic matter, volcanoes, warm oceans and sediments.
Methane
Methane is 20 times as effective as CO2 at trapping
heat in the atomosphere. Its sources are attributed paddy cultivation, cattle
rearing, bacteria in water bodies, fossil fuel production, ocean, non-wetland
soils and forest / wild fires.
N2O (Nitrous oxide)
It is naturally produced in Oceans from biological sources of soil
and water due to microbial actions and rainforests. Man-made sources include
nylon and nitric acid production, use of fertilizers in agriculture, manures
cars with catalytic converter and burning of organic matter.
Global Warming Effects
on Plants
• Low agricultural productivity in tropics
• Frequent heat waves (Weeds, pests, fungi
need warmer temperature)
• Increase of vectors and epidemics
• Strong storms and intense flood damage
• Water crisis and decreased irrigation
• Change in flowering seasons and pollinators • Change in
Species distributional ranges • Species extinction
3. Strategies to deal with Global Warming
·
Increasing the vegetation cover, grow more trees
·
Reducing the use of fossil fuels and green house gases
·
Developing alternate renewable sources of energy
·
Minimising uses of nitrogeneous fertilizers, and aerosols.
4. Ozone depletion
Ozone layer is a region of Earth’s stratosphere that absorbs most
of the Sun’s ultra violet radiation. The ozone layer is also called as the ozone
shield and it acts as a protective shield, cutting the ultra-violet
radiation emitted by the sun.
Just above the atmosphere there are two layers namely troposphere
(the lower layer) and stratosphere (the upper layer). The ozone layer of the
troposphere is called bad ozone and the ozone layer of stratosphere is
known as good ozone because this layer acts as a shield for
absorbing the UV radiations coming from the sun which is harmful for living
organisms causing DNA damage. The thickness of the ozone column of air from the
ground to the top of the atmosphere is measured in terms of Dobson Units.
Ozone is a colourless gas, reacts readily with air pollutants
and cause rubber to crack, hurt plant life, damages lung tissues. But ozone
absorbs harmful ultra violet β (uv-β) and UV – α radiation from sunlight.
What is Dobson Unit? DU is the unit of measurement for total
ozone. One DU (0.001 atm. cm) is the number of molecules of ozone that would be
required to create a layer of pure ozone 0.01 millimetre thick at a temperature
of 0° C and a pressure of 1 atmosphere (atm = the air pressure at the surface
of earth). Total ozone layer over the earth surface is 0.3 centrimetres (3 mm)
thick and is written as 300 DU.
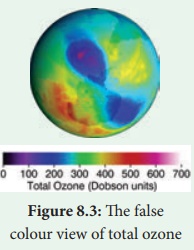
The false colour view of total ozone. The purple and blue
colours are where there is the least ozone, and the yellows and reds are where
there is more ozone.
The ozone shield is being damaged by chemicals released on the
Earth’s surface notably the chlorofluorocarbons widely used in refrigeration,
aerosols, chemicals used as cleaners in many industries. The decline in the
thickness of the ozone layer over restricted area is called Ozone hole.
September 16 is WORLD OZONE DAY
Ozone depletion in the stratosphere results in more UV radiations
especially UV B radiations (shortwaves). UV B radiation destroys biomolecules
(skin ageing) and damages living tissues. UV – C is the most damaging type of
UV radiation, but it is completely filtered by the atmosphere (ozone layer). UV
– a contribute 95% of UV radiation which causes tanning burning of skin and
enhancing skin cancer. Hence the uniform ozone layer is critical for the
wellbeing of life on earth.
During 1970’s research findings indicated that man-made
chlorofluorocarbons (CFC) reduce and convert ozone molecules in the atmosphere.
The threats associated with reduced ozone pushed the issue to the forefront of
global climate issues and gained promotion through organisation such as World
Meterological Organisation and the United Nations. The Vienna Convention was
agreed upon at the Vienna conference of 1985 but entered into force in 1988
provided the frameworks necessary to create regulative measures in the form of
the Montreal protocol. The International treaty called the Montreal Protocol
(1987) was held in Canada on substances that deplete ozone layer and the
main goal of it is gradually eliminating the production and consumption of
ozone depleting substances and to limit their damage on the Earth’s ozone
layer.
Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) is defined in the Kyoto protocol
(2007) which provides project based mechanisms with two objectives to prevent
dangerous climate change and to reduce green house gas emissions. CDM projects
helps the countries to reduce or limit emission and stimulate sustainable
development.
An example for CDM project activity, is replacement of
conventional electrification projects with solar panels or other energy
efficient boilers. Such projects can earn Certified Emission Reduction (CER)
with credits / scores, each equivalent to one tonne of CO2, which
can be counted towards meeting Kyoto targets.
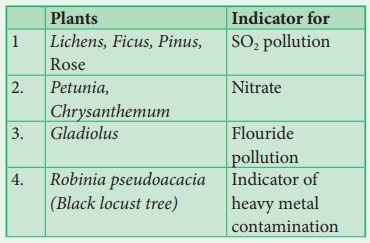
Plant indicators
The presence or absence of certain plants indicate the state of
environment by their response. The plant species or plant community acts as a
measure of environmental conditions, it is referred as biological indicators or
phytoindicators or plant indicators.
Examples
5. Effects of Ozone depletion
The main ozone depletion effects are:
·
Increases the incidence of cataract, throat and lung irritation
and aggravation of asthma or emphysema, skin cancer and diminishing the
functioning of immune system in human beings.
·
Juvenile mortality of animals.
·
Increased incidence of mutations.
·
In plants, photosynthetic chemicals will be affected and therefore
photosynthesis will be inhibited. Decreased photosynthesis will result in
increased atmospheric CO2 resulting in global warming and also
shortage of food leading to food crisis.
·
Increase in temperature changes the climate and rainfall pattern
which may result in flood / drought, sea water rise, imbalance in ecosystems
affecting flora and fauna.
Related Topics