Environmental Issues | Botany - Answer the following questions (Pure Science Group) | 12th Botany : Chapter 8 : Environmental Issues
Chapter: 12th Botany : Chapter 8 : Environmental Issues
Answer the following questions (Pure Science Group)
Botany : Environmental Issues
Answer the following questions (Pure Science Group)
16. What is ozone hole?
Answer: The ozone shield is being damaged by chemicals released on
the Earth’s surface notably the chlorofluorocarbons widely used in
refrigeration, aerosols, chemicals used as cleaners in many industries. The
decline in the thickness of the ozone layer over restricted area is called Ozone hole.
17. Give four examples of plants cultivated in commercial agroforestry.
Answer: The major species cultivated in commercial Agroforestry
include Casuarina, Eucalyptus, Malai Vembu, Teak and
Kadambu trees which were among the 20 species identified as commercial timber.
They are of great importance to wood-based industries.
18. What are agrochemicals?
Answer: (vii) An agro-chemical is useful in managing agriculture or in
farming area which is one of the major issues of the environment.
(viii) Agro-chemicals includes fertilizers, liming and acidifying agents, soil conditioners,
pesticides and chemicals used in animal husbandry, such as antibiotics and
hormones.
19. Expand CCS.
Answer: Carbon Capture and Storage.
20. How do forests help in maintaining the climate?
Answer: (i) Forest act as carbon sink. Any system having the capacity
to accumulate more atmospheric carbon during a given time interval than
releasing CO2 is called a carbon sink. Thus forests are ideal carbon
sink since the trees utilize CO2 for photosynthesis.
(ii) Carbon sequestration is the process of capturing and
storing CO2 which reduces the amount of CO2 in the
atmosphere with a goal of reducing global climate change. Carbon sequestration
is naturally done by green plants.
(iii) Trees provide micro climate for crops and maintain O2
- CO2 balance, atmospheric temperature and relative humidity.
(iv) If the atmospheric CO2 level increases it will lead to global
warming. There will be a drastic change in weather patterns bringing more
floods or droughts in some areas. This can also cause frequent heat waves.
(v) Thus forests play a major role in maintaining the climate.
21. How do sacred groves help in the conservation of biodiversity?
Answer: (i) These are
the patches or grove of cultivated trees which are community protected and are
based on strong religious belief systems which usually have a significant
religious connotation for protecting community.
(ii) 448 grooves were documented throughout Tamil Nadu.
Example: Banagudi shola
(iii) These groves provide a number of ecosystem services to the
neighbourhood like protecting watershed, fodder, medicinal plants and micro
climate control.
22. Which one gas is most abundant out of the four commonest greenhouse gases? Discuss the effect of this gas on the growth of plants?
Answer: CO2 (Carbon
dioxide) is the most abundant among green house gases.
Effects on plants:
(i) Low agricultural productivity in tropics.
(ii) Frequent heat waves (Weeds, pests, fungi need warmer
temperature).
(iii) Increase of vectors and epidemics.
(iv) Strong storms and intense flood damage.
(v) Water crisis and decreased irrigation.
(vi) Change in flowering seasons and pollinators.
(vii) Change in species distributional ranges
(viii) Species extinction
23. Distinguish between endangered, vulnerable and rare species.
Answer:
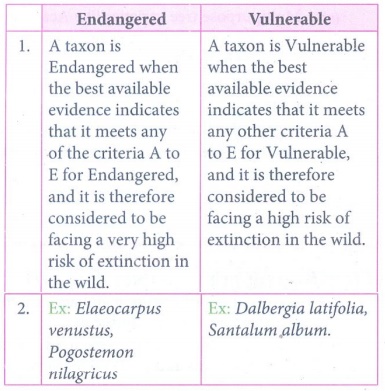
Endangered
1. A taxon is
Endangered when the best available evidence indicates that it meets any of the
criteria A to E for Endangered, and it is therefore considered to be facing a
very high risk of extinction in the wild.
2. Ex: Elaeocarpus
venustus, Pogostemon nilagricus
Vulnerable
1. A taxon is
Vulnerable when the best available evidence indicates that it meets any other
criteria A to E for Vulnerable, and it is therefore considered to be facing a
high risk of extinction in the wild.
2. Ex: Dalbergia latifolia,
Santalum album.
24. Suggest a solution to water crisis and explain its advantages.
Answer: Rain water
harvesting - RWH (Solution to water crisis - A ecological problem)
Rainwater harvesting
is the accumulation and storage of rain water for reuse in-site rather than
allowing it to run off. Rainwater can be collected from rivers, roof tops and
the water collected is directed to a deep pit. The water percolates and gets
stored in the pit. RWH is a sustainable water management practice implemented not
only in urban area but also in agricultural fields, which is an important
economical cost effective method for the future.
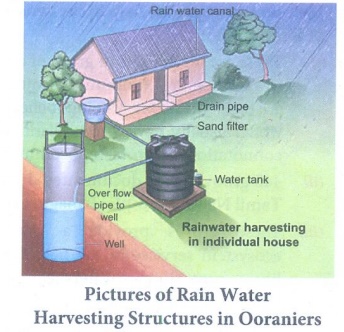
Environmental Benefits:
(i) Promotes adequacy of underground water and water
conservation.
(ii) Mitigates the effect of drought.
(iii) Reduces soil erosion as surface run-off is reduced.
(iv) Reduces flood hazards.
(v) Improves groundwater quality and water table / decreases
salinity.
(vi) No land is wasted for storage purpose and no population
displacement is involved.
(vii) Storing water underground is an eco-friendly measure and a
part of sustainable water storage strategy for local communities.
25. Explain afforestation with case studies.
Answer: Afforestation is
planting of trees where there was no previous tree coverage and the conversion
of non-forested lands into forests by planting suitable trees to retrieve the
vegetation. Example: Slopes of dams
afforested to reduce water run-off, erosion and siltation. It can also provide
a range of environmental services including carbon sequestration, water
retention.
Tamil Nadu Afforestation Project (TAP):
(i) With an aim of ecological restoration and biological
up-gradation of degraded forests and other lands, the government of Tamil Nadu
launched the project in 2 phases.
(ii) Tap I (1997-2005) it aimed to uplift the quality and life
of villagers abutting forest areas and to resolve the degraded forests in Tamil
Nadu. This is a massive joint Forest Management Programme.
(iii) TAP II (2005-2013) had 2 main objectives. To restore the
ecological equilibrium of the forests, watersheds and adjacent villages of
Tamil Nadu.
(iv) To improve the quality of the life of inhabitants through
reforestation, water conservation and sustained community action.
26. What are the effects of deforestation and benefits of agroforesty?
Answer: Effects of deforestation:
(i) Burning of forest wood release stored carbon, a negative
impact just opposite of carbon sequestration.
(ii) Trees and plants bind the soil particles. The removal of
forest cover increases soil erosion and decreases soil fertility. Deforestation
in dry areas leads to the formation of deserts.
(iii) The amount of runoff water increases soil erosion and also
creates flash flooding, thus reducing moisture and humidity.
(iv) The alteration of local precipitation patterns leading to
drought conditions in many regions. It triggers adverse climatic conditions and
alters water cycle in ecosystem.
(v) It decreases the bio-diversity significantly as their
habitats are disturbed and disruption of natural cycles.
(vi) Loss of livelihood for forest dwellers and rural people.
(vii) Increased global warming and account for one-third of total
CO2 emission.
(viii) Loss of life support resources, fuel, medicinal herbs and
wild edible fruits.
Benefits of agroforestry:
(i) It is a solution for the problem of soil and water
conservation and also to stabilise the soil (salinity and water table) reduce
landslide and water run-off problem.
(ii) Nutrient cycling between species improves and organic
matter is maintained.
(iii) Trees provide micro climate for crops and maintain O2
– CO2 balance, atmospheric temperature and relative humidity.
(iv) Suitable for dry land where rainfall is minimum and hence
it is a good system for alternate land use pattern.
(v) Multipurpose tree varieties like Acacia are used for wood
pulp, tanning, paper and firewood industries.
(vi) Agro-forestry is recommended for the following purposes.
It can be used as Farm Forestry for the extension of forests, mixed forestry,
shelter belts and linear strip plantation.
Related Topics