Ecology and Environmental Issues - Conservation | 12th Botany : Chapter 8 : Environmental Issues
Chapter: 12th Botany : Chapter 8 : Environmental Issues
Conservation
Conservation
India due to its topography, geology and climate patterns has
diverse life forms. Now this huge diversity is under threat due to many
environmental issues for this conservation becomes an important tool by which
we can reduce many species getting lost from our native land. By employing
conservation management strategies like germplasm conservation, in situ,
ex-situ, in-vitro methods, the endemic as well as threatened species can be
protected
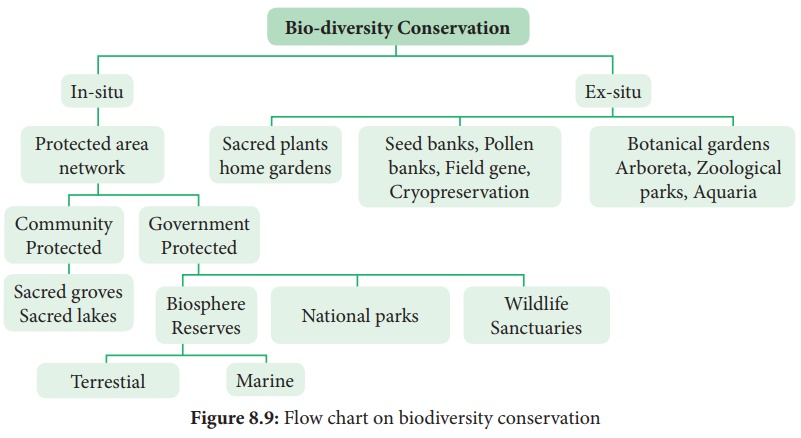
In-situ conservation
It means conservation and management of genetic resources in their natural habitats. Here the plant or animal species are protected within the existing habitat. Forest trees, medicinal and aromatic plants under threat are conserved by this method. This is carried out by the community or by the State conservation which include wildlife, National park and Biosphere reserve. The ecologically unique and biodiversity rich regions are legally protected as wildlife sanctuaries, National parks and Biosphere reserves. Megamalai, Sathyamangalam wildlife, Guindy and Periyar National park, and Western ghats, Nilgiris, Agasthyamalai and Gulf of Mannar are the biosphere reserves of Tamil Nadu.
Sacred groves
These are the patches or grove of cultivated trees which are
community protected and are based on strong religious belief systems which
usually have a significant religious connotation for protecting community. Each
grove is an abode of a deity mostly village God Or Goddesses like Aiyanar or
Amman. 448 grooves were documented throughout Tamil Nadu, of which 6 groves
(Banagudi shola, Thirukurungudi and Udaiyankudikadu, Sittannnavasal, Puthupet
and Devadanam) were taken up for detailed floristic and faunistic studies.
These groves provide a number of ecosystem services to the neighbourhood like
protecting watershed, fodder, medicinal plants and micro climate control.
Ex-situ conservation
It is a method of conservation where species are protected outside
their natural environment. This includes establishment of botanical gardens,
zoological parks, conservation strategies such as gene, pollen, seed, in-vitro
conservation, cryo preservation, seedling, tissue culture and DNA banks. These
facilities not only provide housing and care for endangered species, but also
have educational and recreational values for the society
1. International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
Founded in 1948, the International Union for Conservation of
Nature (IUCN) is the world’s oldest environmental organisation with its
headquarters at Gland, Switzerland. It is a neutral forum for Governments,
NGO’s, Scientists, business and local communities with the aim of developing
solution and implementing policies related to the conservation of environment
and sustainable development.
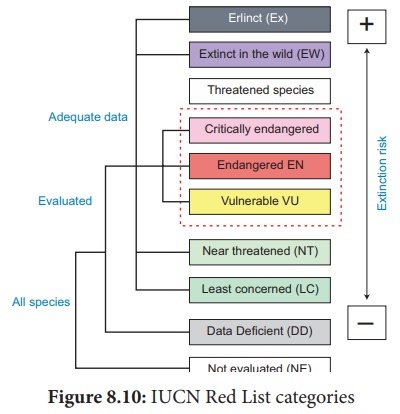
IUCN Red List
IUCN Red List categories help us to evaluate the degree of threat and conservation priorities to the flora and fauna It is also a powerful tool for persuading governments to protect threatened species and for most of the plant and animal species world-wide. IUCN has developed protected areas and developed criteria for threatened species. The criteria are as follows .
A - Population reduction
B - Geographic range
C - Small population size and decline
D - Very small or restricted population
E - Quantitative analysis
Conservation movement
A community level participation can
help in preservation and conservation of our environment. Our environment is a
common treasure for all the living organisms on earth. Every individual should
be aware of this and participate actively in the programs meant for the
conservation of the local environment. Indian history has witnessed many people
movements for the protection of environment.
Chipko Movement
The tribal women of Himalayas
protested against the exploitation of forests in 1972. Later on it transformed
into Chipko Movement by Sundarlal Bahuguna in Mandal village of Chamoli district in 1974. People
protested by hugging trees together which were felled by a sports goods
company. Main features of Chipko movement were,
·
This movement remained non political
·
It was a voluntary movement based on
Gandhian thought.
·
It was concerned with the ecological
balance of nature
·
Main aim of Chipko movement was to
give a slogan of five F’s – Food, Fodder, Fuel, Fibre and Fertilizer, to make
the communities self sufficient in all their basic needs.
Appiko Movement
The famous Chipko Andolen of Uttarakhand in the Himalayas inspired the villagers of Uttar Karnataka to launch a similar movement to save their forests. This movement started in Gubbi Gadde a small village near Sirsi in Karnataka by Panduranga Hegde. This movement started to protest against felling of trees, monoculture, forest policy and deforestation.
IUCN Red List categories
Extint (EX)
A taxon is Extinct when there is no reasonable doubt on the death
of the last individual. A taxon is presumed Extinct when exhaustive surveys in
known and/or expected habitat, at appropriate times (diurnal, seasonal,
annual), throughout its historic range have failed to record an individual.
Example: Neuracanthus neesianus.
Extinct in the wild (EW)
A taxon is Extinct in the Wild when it is known only to survive in
cultivation, in captivity or as a naturalised population (or populations) well
outside the past range. Example: Ginkgo biloba
Critically endangered (CR)
A taxon is Critically Endangered when the best available evidence
indicates that it meets any of the criteria A to E for Critically Endangered,
and it is therefore considered to be facing an extremely high risk of
extinctions in the wild. Example: Euphorbia santapaui, Piper barberi, Syzygium
gambelianum.
Endangered (EN)
A taxon is Endangered when the best available evidence indicates
that it meets any of the criteria A to E for Endangered, and it is therefore
considered to be facing a very high risk of extinction in the wild. Example: Elaeocarpus
venustus, Pogostemon nilagricus, Eugenia singampattiana.
Vulnerable (VU)
A taxon is Vulnerable when the best available evidence indicates
that it meets any other criteria A to E for Vulnerable, and it is therefore
considered to be facing a high risk of extinction in the wild. Example: Dalbergia
latifolia, Santalum album, Chloroxylon sweitenia
Near threatened (NT)
A taxon is Near Threatened when it has been evaluated against the
criteria but does not qualify for Critically Endangered, Endangered or
Vulnerable now, but is close to qualifying for or is likely to qualify for
threatened category in the near future.
Least concerned (LC)
A taxon is Least Concerned when it has been evaluated against the
criteria and does not qualify for Critically Endangered, Endangered, Vulnerable
or Near Threatened, Widespread and abundant taxa are included in this category.
Data deficient (DD)
A taxon is Data Deficient when there is inadequate information to
make a direct, or indirect, assessment of the risk of extinction based on its
distribution and/or population status.
Not evaluated (NE)
A taxon is Not Evaluated when it has not yet been evaluated against the criteria.
2. Endemic Centres and Endemic Plants
Endemic species are plants and animals that exist only in one
geographic region. Species can be endemic to large or small areas of the earth.
Some are endemic to a particular continent, some to a part of a continent and
others to a single island.
Any species found restricted to a specified geographical area is
referred to as ENDEMIC.. It may be due to various reasons such as isolation,
interspecific interactions, seeds dispersal problems, site specificity and many
other environmental and ecological problems. There are 3 Megacentres of
endemism and 27 microendemic centres in India. Approximately one third of
Indian flora have been identified as endemic and found restricted and
distributed in three major phytogeographical regions of india, that is Indian
Himalayas, Peninsular India and Andaman nicobar islands. Peninsular India,
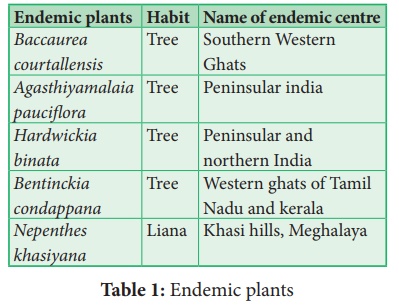
especially Western Ghats has high concentration of endemic plants. Hardwickia
binata and Bentinckia condapanna are good examples for endemic
plants. A large percentage of Endemic species are herbs and belong to families
such as Poaceae. Apiaceae, Asteraceae and Orchidaceae.
Majority of endemic species are threatened due to their narrow
specific habitat, reduced seed production, low dispersal rate, less viable
nature and human intereferences.. Serious efforts need to be undertaken for
their conservation, otherwise these species may become globally extinct.

Related Topics