Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Musculoskeletal system
Gout - Crystal arthropathies
Gout
Definition
An acute inflammatory arthritis resulting from urate crystal deposition secondary to hyperuricaemia.
Prevalence/incidence
Hyperuricaemia occurs in 5%, gout affects 1–20 per 1000 males.
Age
Peak incidence at the age of 40–50 years.
Sex
10M : 1F
Geography
Mainly a disease of developed countries.
Aetiology
High levels of uric acid cause gout but not all individuals with hyperuricaemia will develop gout. Hyperuricaemia is associated with increasing age, male sex and obesity, and in females urate levels rise after the menopause. Uric acid is formed from the breakdown of purines (see Fig. 8.5). Hyperuricaemia may occur due to increased rates of uric acid production or decreased uric acid excretion.
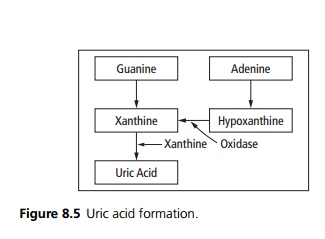
· Increased uric acid production may be idiopathic or secondary to excessive intake or high turnover as seen in malignancy (especially with chemotherapy).
· Decreased salvage of purines may occur; in Lesch– Nyhan syndrome a defect in HGPRT results in impaired salvage and hence high uric acid levels.
· Decreased renal excretion may be idiopathic or secondary to renal failure or drugs such as thiazides or low-dose aspirin.
An acute episode of gout may be precipitated by a sudden increase or decrease in urate concentration. Risk factors include surgery, infection, dehydration, severe illness, starvation, diuretics and alcohol.
Pathophysiology
In joints an acute synovitis may occur when urate crystals have been phagocytosed. The crystals cause disruption of lysosomal membranes and hence release of inflammatory mediators.
If chronic, the crystals accumulate in the synovium and sites such as the ear cartilage forming lumps termed tophi.
In the kidney, urate crystals may precipitate in the collecting ducts or cause stone formation. The result of urate damage is either tubulointerstitial disease (urate nephropathy) or acute tubular necrosis.
Clinical features
In 70–90% the initial attack of gout affects the big toe. It is known as podagra if it first affects the metatarsophalangeal joint. The joint is red, hot, swollen and very tender. There may be an associated fever. These features make it difficult to distinguish from a septic arthritis. Other joints affected include ankles, knees, fingers, elbows and wrists. Chronic gout is unusual but may cause a chronic polyarthritis with destructive joint damage with large erosions on X-ray and deformity. Tophi (smooth white skin and joint deposits) occur at cartilagenous sites particularly in the Achilles tendon and the helix of the ear. This usually reflects severe untreated gout.
Investigations
Urate levels are often high, although they may fall during an acute attack. Inflammatory markers (CRP, ESR) may be raised. Aspiration of joint fluid will demonstrate the negatively birefringent crystals.
Management
Acute gout is managed with high dose nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Hyperuricaemia is treated only if associated with recurrent gout attacks.
Non-pharmacological: Weight loss, high-fluid intake, low alcohol, low-purine diet, avoid thiazides and aspirin.
Pharmacological: Allopurinol, which inhibits xanthine oxidase. Excess purines are excreted as xanthine rather than uric acid, and the therapy is lifelong. Steroids can be injected into troublesome joints.
Related Topics