Chapter: Medicine and surgery: Musculoskeletal system
Laboratory investigations - Investigations and procedures
Investigations and procedures
Laboratory investigations
Although some of the available tests used in diagnosis of
rheumatological conditions are diagnostic, most have limited value as they may
be present in multiple conditions (non-specific), or they may only be present
in some of the patients with the disease (non-sensitive). Combining tests may
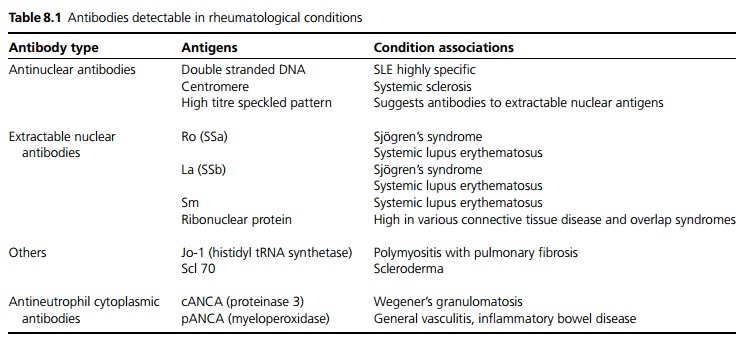
allow a clinical diagnosis to be confimed (see Table 8.1).
Rheumatoid factor: These are antibodies of any class directed against the Fc portion of immunoglobulins. The routine laboratory test detects only IgM antibodies, which agglutinate latex particles or red cells opsonised with IgG. It is the presence of these IgM rheumatoid factor antibodies that is used to describe a patient as seropositive or seronegative. Seventy to eighty per cent of patients with rheumatoid arthritis have IgM rheumatoid factor; however, it may also be detected in a number of other conditions. Seropositivity allows prediction of severity and the need for earlier aggressive therapy and increases the likelihood of extra-articular features.
Antinuclear and anticytoplasmic
antibodies: Antibodies against multiple
cellular components have been characterised and may be detected.
Related Topics