Components and Functions of GIS - Geographic Information System (GIS) | 12th Geography : Chapter 6 : Geoinformatics
Chapter: 12th Geography : Chapter 6 : Geoinformatics
Geographic Information System (GIS)
Geographic
Information System (GIS)
The Geographic
information systems have emerged in the past two decades as an essential tool for
urban and resource planning and management. It includes the functions of data entry,
data display, data management, information retrieval and analysis. While GIS deals
with entire geography of the earth including land, ocean and atmosphere, the art,
science and technology dealing with the acquisition, storage, processing, production,
presentation and dissemination of the earth’s information is called the Geoinformatics.
It is the popular means of studies in recent decades which cater the real and useful
information to the field of Geography, Environmental Studies, Town planning, Rural
development studies, and Defense and Agricultural promotion.
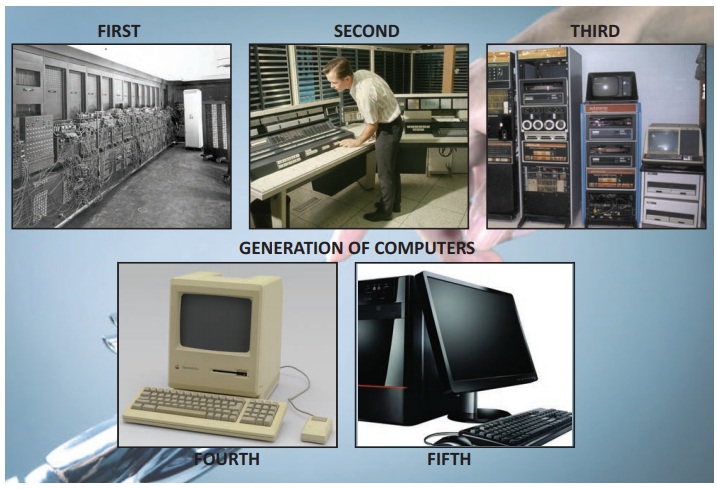
Generation of the computers
1940 – 1956:
First Generation – Vacuum Tubes
1956 – 1963:
Second Generation – Transistors
1964 – 1971:
Third Generation – Integrated Circuits
1972 – 2010: Fourth Generation – Microprocessors
2010 – Fifth Generation – Artificial Intelligence
Components of GIS
The components of GIS can be broadly
classified into five types. They are mentioned below.
A. Hardware
Hardware
is Computer on which GIS software runs. Nowadays there are a different ranges of
computer, it might be Desktop or server based. ArcGIS Server is server based computer
where GIS software runs on network computer or cloud based. For computer to perform
well all hardware components must have high capacity. Some of the hardware components
are: Motherboard, Hard drive, processor, graphics card, printer and so on. These
all component function together to run GIS software smoothly.
B. Software
Next component
is GIS software which provides tools to run and edit spatial information. It helps
to query, edit, run and display GIS data. It uses RDBMS (Relational Database Management
System) to store the data. Few GIS software list: ArcGis, ArcView 3.2, QGIS, SAGA
GIS.
C. Data
Geographic data and related tabular data can be collected in-house compiled to custom specifications and requirements (or) purchased from a commercial data provider.
A GIS can
integrate spatial data with other existing data resources often stored in a corporate
data base management System. The data can be broadly classified as
i. Attribute
data
ii. Spatial
data
iii. Remote
sensing data
iv. Global
data base.
You will
learn in detail about each of the above classification of data in higher studies.
D. People
The GIS technology
is used by a huge number of industrialists and agencies to help plan, design, engineer,
build and maintain information infrastructures that affects our everyday lives.
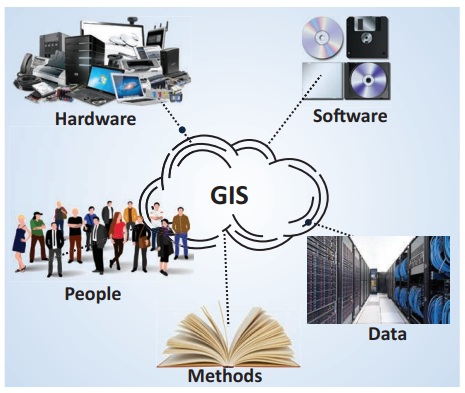
E. Methods or Procedures
Methods here
refer to well-defined, consistent procedures that are required to produce accurate,
reproducible result. A neatly conceived implementation plan and business rules are
the models and operating practices are unique to each organization. There is need
to properly integrate the sophisticated tool through bringing out well- defined
procedures in well documented form into the entire business strategy and operation
to make the technology effective. Meta data i.e., (data about the data) is the key
for documenting these processes.
Functions of GIS
The functions
of GIS describe the steps that have to be taken to implement a GIS. These steps
have to be followed in order to obtain a systematic and efficient system. The steps
involved are data capture, data storage (GIS Data Models), manipulation and analysis.
Data Capture
The input of data into a GIS can be achieved
through many different methods of gathering. For example, aerial photography, scanning,
digitizing, GNSS is just a few of the ways a GIS user could obtain data. Digitization:
A conversion process which converts paper maps into numerical digits that can be
stored in the computer. Digitizing simplifies map data into sets of points, lines
or cells that can be stored in the GIS computer. In this stage, digitization is
carried out. There are two basic methods of digitization: Manual digitizing &
scanning.
Data
Storage
Some data is stored such as a map in
a drawer, while others, such as digital data, can be as a hardcopy, stored on CD
or on your hard drive. Once the data have been digitally compiled, digital map files
in the GIS are stored on magnetic or other digital media. Data storage is based
on a Generic Data Model that is used to convert map data into a digital form. The
two most common types of data models are Raster and Vector. Both types are used
to simplify the data shown on a map into a more basic form that can be easily and
efficiently stored in the computer.
Data
Manipulation
The digital
geographical data can be edited, this allows for many attribute to be added, edited,
or deleted to the specification of the project. Once data are stored in a GIS, many
manipulation options are available to users. These functions are often available
in the form of “Toolkits.” A toolkit is a set of generic functions that a GIS user
can employ to manipulate and analyse geographical data. Toolkits provide processing
functions such as data retrieval measuring area and perimeter, overlaying maps,
performing map algebra, and reclassifying map data. Data manipulation tools include
coordinate change, projections, and edge matching, which allow a GIS to reconcile
irregularities between map layers or adjacent map sheets called Tiles.
Query
and Analysis
GIS was used widely in decision making
process for the new commission districts. We use population data to help establish
an equal representation of population to area for each district. The heart of GIS
is the analytical capabilities of the system.
Related Topics