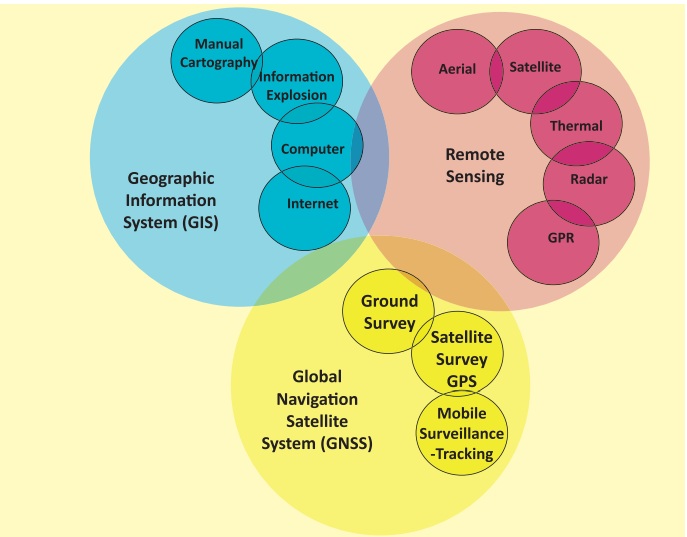
Chapter: 12th Geography : Chapter 6 : Geoinformatics
Elements of Remote Sensing
Elements of Remote Sensing
1. Energy Source
The primary requirement for remote sensing is to have an energy service, which provides electromagnetic energy to the target of interest. The sun being a major source of energy, radiation and illumination having a sharp power allows capturing reflected light with conventional cameras and films.
2. Radiation and the Atmosphere
The energy is required to illuminate the target. This energy is in the form of Electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation is a dynamic form of energy that propagates as wave motion at a velocity in space.
3. Interaction with the target
The interaction of Electromagnetic radiation with the target is important to remote sensing for two main reasons. First, information carried Electromagnetic radiation reflected by the earth’s surface is modified while traversing through the atmosphere. Second, the interaction of Electromagnetic radiation with the atmosphere can be used to obtain useful information about the atmosphere itself. The total energy is subjected to modification by the several physical process, scattering, absorption and refraction. Scattering is the re-direction of Electromagnetic radiation by particles suspended in the atmosphere or by large molecules of atmospheric gases. The amount of scattering depends upon the size of the particles and their abundance. The wave length of radiation, depth of the atmosphere through which the energy is travelling. Absorption is the process by which the gas molecules present in the atmosphere strongly absorb the Electromagnetic radiation through the atmosphere in certain spectral bands.
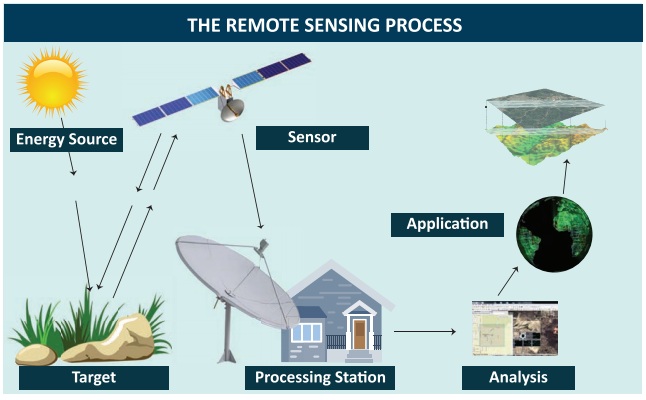
4. Recording of energy by the sensor
After the energy has been scattered by or emitted from the target, we require a sensor (remote not in contact with the target) to collect and record the electromagnetic radiation. A sensor is highly sensitive to all the wave lengths yielding spatially detailed data on absolute brightness. On the basis of the source of electromagnetic energy, the sensor can be classified into two ways. They are active sensor or passive sensor. Active sensor generates and uses its own energy to illuminate the target and records the reflected energy. It operates in the microwave regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Their wave lengths are longer than 1 mm.
5. Transmission, Reception and Processing
The energy recorded by the sensor has to be transmitted in electronic form, to a receiving and processing station where the data processed into an image. The Image processing methods may be grouped into three functional categories such as Image Restoration, Image Enhancement and Information Extraction.
Image Restoration: Restoration processes are designed to recognize and compensate for errors, noise and geometric distortion introduced into the data during the scanning transmission and recording processes. The objective is to make the image resemble the original scene. Image restoration is relatively simple because the pixels from each band are processed separately.
Image Enhancement: Enhancement is the modification of an image, to alter its impact on viewer. General enhancement distorts the original digital values; therefore enhancement is not done until the restoration processes are completed.
Information extraction: Image restoration and enhancement process utilize computers to provide corrected and improved images for study by human interpreters. The computer makes no decision in these procedures. The human operator must instruct the computer and must evaluate the significance of the extracted information.
6. Interpretation and Analysis
Image interpretation is defined as the act of examining images to identify objects and judge their significance. An interpreter studies remotely sensed data and attempts through logical process to detect, identify, measure and evaluate the significance of environment and cultural object pattern and spatial relationship.
The quality of an image is based on the inherent characteristics of the objects. Further it depends on the following aspects.
* Sensor characteristics
* Season of the year, time of the day when the photo is taken
* Atmospheric effects
* Resolution of the image
* Image motion etc
Image interpretation is essential for the efficient and effective use of the data. The elements of image interpretation such as image tone, shape, size, pattern, image texture, shadow and association are helpful to identify the exact target and to analyse.
Related Topics