Chapter: Human Nervous System and Sensory Organs : The Eye
Fundus of the Eye
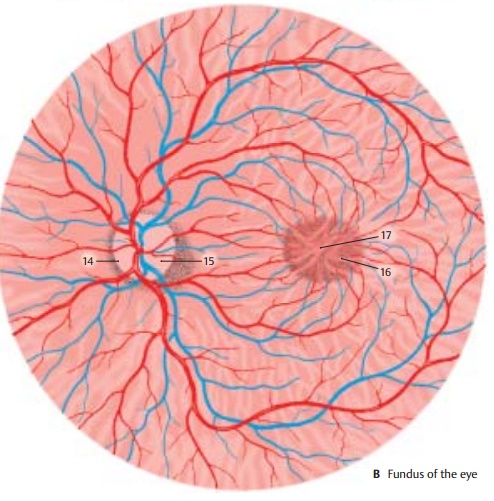
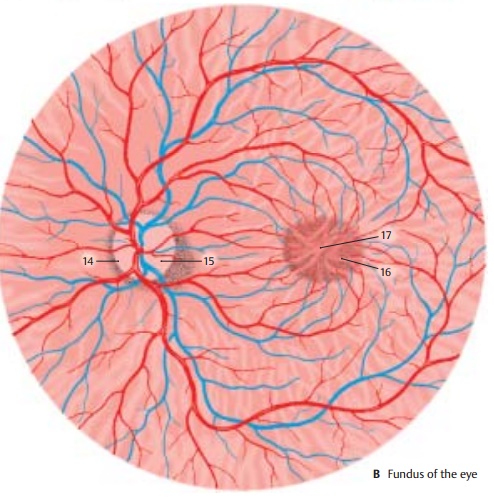
Fundus of the Eye
The
posterior pole of the eyeball, the fun-dus,
can be examined through the pupilwith an ophthalmoscope. It is reddish in
color. In the nasal half lies the papilla
of theoptic nerve (blind spot) (B14), where all nervefibers of the
retina combine to leave the eye as the optic nerve. The papilla is a whitish
disk with a central shallow depression, the excavation
of the optic disk (AB15). In the
papilla, the central artery divides into several branches, and the veins unite
to form the central vein. The arteries are rela-tively light in color and are
thin, while the veins are darker and slightly thicker. The vessels run radially
in the nasal direction, while they arch in the temporal direction. Numerous
vessels run to the macula (yellowspot) (B16), the area of highest
visual acuity.Its traversely oval, slightly yellowish surface contains a
small depression in the center, the central fovea (AB17).
Related Topics