Indian Constitution - Fundamental Rights to Indian Citizens | 10th Social Science : Civics : Chapter 1 : Indian Constitution
Chapter: 10th Social Science : Civics : Chapter 1 : Indian Constitution
Fundamental Rights to Indian Citizens
Fundamental Rights
The
Fundamental Rights are enshrined in Part of the Constitution from Articles 12
to 35. In this regard, the framers of the Constitution derived inspiration from
the Constitution of USA. Originally, the Constitution provided for seven
Fundamental Rights. At present, there are only six Fundamental Rights. Part III
of the Constitution is rightly described as the Magna Carta of India. While
Fundamental Rights are available to all persons, certain Fundamental Rights are
available only to Indian Citizens.
Right to constitutional remedies (Articles - 32)
A writ is
an order or command issued by a court in writing under its seal. It is in the
nature of a command or prohibition from performing certain acts that are
specified in the orders of the court. Both the Supreme Court and the High
Courts are empowered to issue five kinds of writs. That is why the Supreme
Court is called the “Guardian of the Constitution”. According to Dr. Ambedkar,
Article 32 is “the heart and soul of the Constitution”.
a) Habeas Corpus:
Safeguards
people from illegal arrests.
b) Mandamus:
It
protects the petitioner who requires legal help to get his work done by
respective public authorities.
c) Prohibition:
It
prohibits a subordinate court from acting beyond its jurisdiction.
d) Certiorari:
It
quashes an order issued by a subordinate court by overstepping its
jurisdiction.
e) Quo Warranto:
It
prevents usurpation of public office through illegal manner.
Suspension of Fundamental Rights
When the
President makes a Proclamation of Emergency under Article 352, the freedoms
guaranteed under Article 19 are automatically suspended. The President can
suspend other fundamental rights through specific orders. These orders must be
approved by the Parliament.
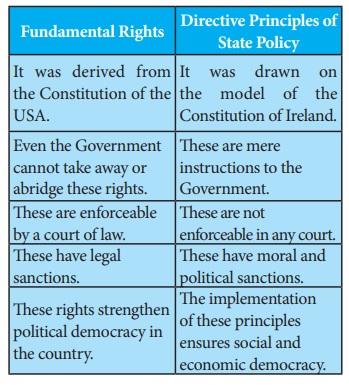
Differences between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State Policy
I. RIGHT TO EQUALITY

Art. 14 - Equality before law.
Art. 15 - Prohibition of discrimination on grounds
of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth.
Art. 16 - Equality of opportunity in matters of
public employment.
Art. 17 - Abolition of Untouchability.
Art. 18 - Abolition of titles except military and
academic.
II. RIGHT TO FREEDOM

Art. 19 - Freedom of speech and expression,
assembly, association, movement, residence and profession.
Art. 20 - Protection in respect of conviction for
offences.
Art. 21 - Protection of life and personal liberty.
Art. 21A - Right to elementary education.
Art. 22 - Protection against arrest and detention
in certain cases.
III. RIGHT AGAINST EXPLOITATION
Art. 23 - Prohibition of traffic in human beings
and forced labour.
Art. 24 - Prohibition of employment of children in
factories, etc.
IV. RIGHT TO RELIGION

Art. 25 - Freedom of conscience and free
profession, practice and propagation of religion.
Art. 26 - Freedom to manage religious affairs.
Art.
27 - Freedom from payment of taxes for promotion of any religion.
Art. 28 - Freedom from attending religious
instruction or worship in certain educational institutions.
V. CULTURAL & EDUCATIONAL RIGHTS

Art. 29 - Protection of language, script and
culture of minorities.
Art. 30 - Right of minorities to establish and
administer educational institutions.
Right to Property
(Art. 31) was deleted from the list of Fundamental
Rights by the 44th Amendment Act, 1978. It is made a legal right under Article
300-A in Part XII of the Constitution.
VI. RIGHT TO CONSTITUTIONAL REMEDIES

Art. 32 - It allows individuals to seek redressal
for the violation of their fundamental rights.
Violation of which Fundamental right
is associated with the theme depicted in the stamps?

Related Topics