Indian Constitution | Civics | Social Science - Answer in Detail | 10th Social Science : Civics : Chapter 1 : Indian Constitution
Chapter: 10th Social Science : Civics : Chapter 1 : Indian Constitution
Answer in Detail
V. Answer in Detail
1. Explain
the salient features of the Constitution of India.
• It is the lengthiest of all the written constitutions of the
world
• It has borrowed most of its provisions from the constitutions
of various countries
• It is partly rigid and partly flexible
• It establishes a federal system of government
• It makes India as a secular state
• It provides an independent judiciary
• It introduces Universal adult franchise. The voting right is
given at the age of 18 without any discrimination.
2. Point
out the Fundamental Rights.
There are Six Fundamental Rights.
They are
• Right to Equality
• Right to Rellgion
• Right to Freedom
• Cultural and Education Rights
• Right against Exploitation • Right to constitutional Remedies
Right to Equality:
• Equality before law.
• Prohibition of discrimination on grounds of religion, race,
caste, sex or place of birth.
• Equality in public appointment.
• Abolition of untouchability.
Right to Freedom:
• Freedom of speech and expression, assembly, association,
movement, residence and profession.
• Protection of life and property.
• Right to elementary education
• Right against arrest and detention in certain cases.
Right against
Exploitation:
• Prohibition of traffic in human beings and forced labour.
• Prohibition of employment of children in factories.
Right to religion:
• Right to free profession, practice and propagation of
religion.
• Freedom to manage religious affairs.
• Freedom from payment of taxes for the promotion of any
religion.
Cultural and
Educational Rights:
• Protection of language, script and culture of minorities.
• Right to minorities to establish and administer educational
institutions.
Right to
Constitutional Remedies:
• It allows individuals to seek redressal for the violation of
their fundamental rights.
3. Write
briefly on the Right to Constitutional Remedies.
• A writ is an order or command issued by a court in writing
under its seal.
• It is in the nature of a command or prohibition from
performing certain acts.
• Both the Supreme Court and the High Courts are empowered to
issue writs such as Habeas Corpus, Mandamus, Prohibition, Quo Warranto and
Certiorari.
• So the Supreme Court is called the 'Guardian of the Constitution'.
Types of Writs:
Habeas Corpus: Safeguards people from illegal arrests.
Mandamus: It protects the petitioner who requires legal help to get his
work done by respective public authorities.
Prohibition: It prohibits a subordinate court from acting beyond its
jurisdiction.
Certiorari: It quashes an order issued by a subordinate court by
overstepping its jurisdiction.
Quo Warranto: It prevents usurpation of public office through illegal
manner.
4. Mention
the differences between Fundamental Rights and Directive Principles of State
Policy.
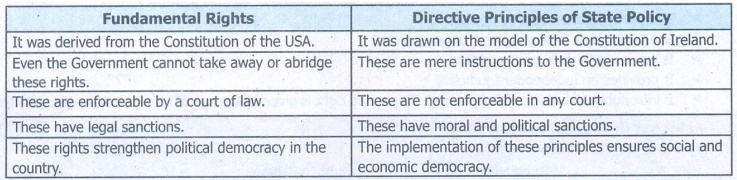
Fundamental Rights
• It was derived from the Constitution of the USA.
• Even the Government cannot take away or abridge these rights.
• These are enforceable by a court of law.
• These have legal sanctions.
• These rights strengthen political democracy in the country.
Directive
Principles of State Policy
• It was drawn on the model of the Constitution of Ireland.
• These are mere instructions to the Government.
• These are not enforceable in any court.
• These have moral and political sanctions.
• The implementation of these principles ensures social and
economic democracy.
VI. Project and activity
1. Collect
information about the various members of the Constituent Assembly and their
social background.
2. Collect
the pictures of the Members of the Drafting Committee and their social background.
Related Topics