Chapter: Mechanical : Computer Integrated Manufacturing
Flexible manufacturing system - FMS
Flexible manufacturing system - FMS
A flexible manufacturing system
consists of a group of processing stations, interconnected by means of a
automated material handling and storage systems, and controlled by an
integrated computer system.
FMS Flexibility:
The three capabilities that a manufacturing system must
process in order to the flexible
1. The
ability to identify and distinguish among the different incoming part or
product styles processed by the system.
2. Quick
changeover of operating instructions.
3. Quick
changeover of physical setup. Flexibility is an attribute that applies to both
manual and automated systems. In manual systems the human workers are often the
enables of the systems flexibility.
Types of flexibility;
The flexibility allows a mixed
model manufacturing system to cope with level of variation in part or product
style without interruptions in production for changeover between models. It is
generally a desirable feature of a manufacturing system.
The
feature of flexibility is broadly classified in to following ways
1. Machine
flexibility
2. Part
flexibility
3. Route
flexibility
4. Volume
flexibility
5. Man
flexibility.
FMS technology is approaches to
simultaneously manufacture different parts in the shortest time possible, with
the highest quality and at the lowest costs possible. To do this a maximum of
management of management information must be available for the FMS host to work
with. When this is achieved there are several types of flexibility available;
to an FMS user.
1. FMS user
flexibility
2. FMS
supplier flexibility.
1. FMS user
flexibility
The first area is that in which the FMS user is interested.
This most important area.
The available flexibilities are
provided for the FMS user to be able to satisfy the demands of their customers.
2. FMS supplier flexibility.
The second type of flexibility
concerns the method of applying FMSs.this is of extreme interest to the FMS
host supplier. Every FMS application’s different, and no. of
FMS supplier can start from scratch to supply a FMS host
solution every time for each new
FMS user. A supplier’s solution need to be flexible
enough to integrate the different machine types in to different FMS
configurations and layouts for different product mixes.
1. Components of FMS systems;
·
Workstations
·
Material handling and storage
·
Computer control system
·
Human resources
1. Workstations
The first element in the FMS is work stations; it may,
·
Load/unload stations
·
Machining stations
·
Other processing stations
·
Assembly
2. Material
handling and storage systems
For the belowmentioned functions are the material handling
device
·
Random, independent movement of workparts between
stations.
·
Handle a variety of workpart configurations.
·
Temporary storage.
·
Convenient access for loading and unloading
workpartcontrol.s.
·
Compatible with computer
The material handling is classified in ot two types they are,
§ Primary
material handling
§ Secondary
material handling
The material handling function in a FMS is often shared
between two systems:
1. Primary
handling system - establishes the basic layout of the FMS and is
responsible for moving work parts between stations in the system.
2. Secondary
handling system - consists of transfer devices, automatic pallet changers,
and similar mechanisms located at the workstations in the FMS.
3. Computer
control system
§ Workstation
control
§ Distribution
of control instructions to workstations
§ Production
control
§ Traffic
control
§ Shuttle
control
§ Work
piece monitoring
§ Tool
control
§ Performance
monitoring and reporting
§ Diagnostics
4. Human
resources
For loading and unloading the materials in the
machines and for the maintenance works the human resource are required in the
flexible manufacturing system.
2. Benefits
of FMS
The
various benefits are listed below,
·
Higher machine utilization
·
Reduced work in process
·
Lower manufacturing lead time
·
Greater flexibility in production scheduling.
3. Types of
FMS;
·
Flexible manufacturing module (FMM)
·
Flexible manufacturing cell (FMC)
·
Flexible manufacturing group (FMG)
Flexible fabrication-machining-assembly system (FFMAS)
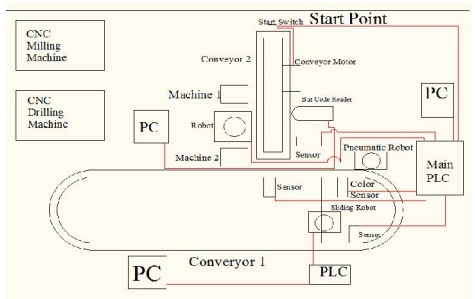
FMS layout
§ In-line
layout
§ Loop
layout
§ Ladder
layout
§ Open
field layout
§ Robot
centered layout
Glossary;
§ Production
Planning and Control - PPC
§ Master
Production Planning - MPP
§ Manufacturing
Requirements Planning - MRP
§ Manufacturing
Resource Planning - MRPII
§ Factory
Data Collection - FDC
§ Flexible
manufacturing module - (FMM)
§ Flexible
manufacturing cell - (FMC)
§ Flexible
manufacturing group - (FMG)
§ Flexible
fabrication-machining – FFM
§ Automated
Guided Vehicle – AGV.
Related Topics