Chapter: Mechanical : Computer Integrated Manufacturing : Components of CIM
Components of CIM
COMPONENTS OF CIM
Computer Integrated
Manufacturing, known as CIM, is the phrase used to describe the complete
automation of a manufacturing plant, with all processes functioning under
computer control and digital information tying them together The heart of
computer integrated manufacturing is CAD/CAM. Computer-aided design (CAD) and
computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) systems are essential to reducing cycle
times in the organization. CAD/CAM is a high technology integrating tool
between design and manufacturing. CAD techniques make use of group technology
to create similar geometries for quick retrieval.
CAD/CAM integrated systems
provide design/drafting, planning and scheduling, and fabrication capabilities.
CAD provides the electronic part images, and CAM provides the facility for tool
path cutters to take on the raw piece.
CIM Concept Vs CIM Technology
·
CIM is both
a concept and
a technology.
· For top
management, CIM is a concept,
a blueprint for success.
·
For middle
managers and line managers, CIM is a
technology
Concept or Technology
“Some people view CIM
as a concept, while others merely as a technology. It is
actually
both. A good analogy of CIM is man, for what we mean by the word man
presupposes both the mind and the
body. Similarly, CIM represents both the concept and the technology. The
concept leads to the technology which, in turn,
broadens the concept.”
The meaning and origin of CIM
The CIM will be used to mean the
integration of business, engineering, manufacturing and management information
that spans company functions from marketing to product distribution
CIM –
Definition;
CIM is the integration of the
total manufacturing enterprise through the use of integrated systems and data
communication coupled with new managerial philosophies that improve
organizational and personnel efficiency.
Computer integrated manufacturing
is defined as the effective use of computers to design the products, plan the
production ,control the operations and perform the various business related
functions needed in a manufacturing firm.
Objective of CIM;
·
The main aim of CIM is to use the advanced
information processing technology into all areas of manufacturing industry in
order
·
To make the total process more productive and
efficient;
·
increase product reliability;
·
Decrease the cost of production and maintenance
relating to the manufacturing system as well as to the product; and
·
Reduce the number of hazardous jobs and
Subsystems
in computer-integrated manufacturing
A computer-integrated
manufacturing system is not the same as a "lights-out" factory,
which would run completely independent of human intervention, although it is a
big step in that direction. Part of the system involves flexible
manufacturing, where the factory can be quickly modified to produce different
products, or where the volume of products can be changed quickly with the aid
of computers. Some or all of the following subsystems may be found in a CIM operation:
CIM system – Hardware
& Software;
·
CIM Hardware consists of manufacturing equipments
and Computer related hard ware with the office equipment.
·
CIM Software consists of computer programs to
carry out the various functions and transfer the data from various areas of the
industry.
Elements of CIM hardware;
Manufacturing equipment such as CNC machines,
robots, DNC / FMS systems, work holding and tool handling devices, Storage
devices, sensors, shop floor data collection devices, inspection machine etc.
Computers ,Controllers, CAD /CAM systems,
workstations, data entry terminals, bar code readers, printers ,plotters,
modems, cables, connectors etc.
Elements of CIM software;
·
MIS- management information system
·
Sales, marketing, finance
·
Data base management
·
Modeling and design
·
Analysis, simulation, communications
·
Monitoring, production control
·
Manufacturing area control, job tracking
·
Inventory control
·
Shop floor data collection,
·
Order entry, materials handling, Device drivers,
·
Process planning, manufacturing facilities
·
Work flow automation,
·
Business process engineering, Network management,
Automation;
Automation may be defined as the
process of having machines follow a predetermined sequence of operations with
little or no human labor, using specialized equipment and devices that perform
and control manufacturing processes.
‘Islands of automation;
The individually automated
workstations or processes are called islands of automation. In
other words the term ‘islands of automation’ represents the various
technologies
that facilitate manufacturing automation in isolation, without having
integrated with other manufacturing technologies.
Major elements of CIM systems;
·
Marketing,
·
Product design,
·
Planning,
·
Purchase,
·
Manufacturing engineering,
·
Factory automation hardware,
·
warehousing, finance, and
·
nformation management
CIM Wheel
Components:
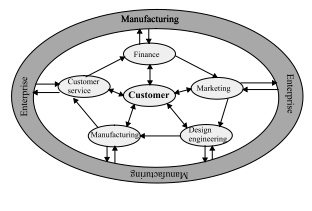
Distinct
components of CIM wheel
·
Manufacturing / Human resource management
·
Marketing
·
Strategic planning
·
Finance
·
Product and process design and planning
·
Manufacturing planning and control
·
Factory automation
Computer communication in CIM;
· Communication
in the nervous systems of CIM and this is an integral part of CIM.
· The
development in communication / network engineering have made implement of CIM
easier that before.
Various needs of communication;
·
The information need for manufacturing in a
company requires as follows.
·
Person-to-person, computer-to-computer,
machine-to-machine, person to computer or computer to person, person to machine
or machine to person, computer to machine or machine to computer
Fundamental needs of computer communications;
·
Data: entities that convey meaning
·
Information: the content or interpretation of data
·
Signals: electric or electromagnetic encoding of
data
·
Signaling: the act of propagating the signal along
a medium
·
Transmission: propagating of data by processing of
signals
Data Transmission Methods.
·
Serious & Parallel Communications.
·
Synchronous & Asynchronous methods.
·
Simplex & Duplex methods.
Communication Networks;
A communication network is the
backbone of an enterprise integration. Networks help to unify a company by
linking together all the computerized devices irrespective of their physical
location.
Through networks the whole
enterprise can be integrated, including suppliers and customers. For example,
sales and marketing can send customer requirements for new products to design
engineering.
A CAD generated bill of
materials can then be transferred to “material requirements planning(MRP)”
systems.
Product design information can be transmitted to manufacturing
for use in process planning.
There are wo
main types of communication networks:
1) Telecommunication
Networks;
2) Computer
communication Networks.
Telecommunication network is
mainly used for voice communication.Computer communication network is a system
of interconnected computers and other devices capable exchanging information.
1.Types of Computer networks;
The computer networks can be classified into four
categories depending upon the physical separations of the communication
devices.
·
Miniature - <50m
·
Small - <500m
·
Medium - <1km
·
Large - >1km
- WAN & LAN.
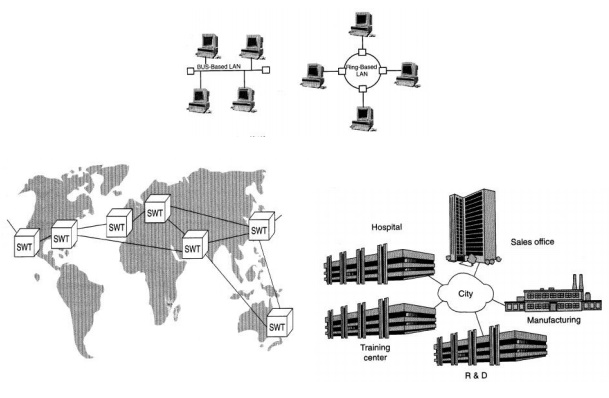
Local Area Network;
Local
Area Network is intended to serve a number of users who are physically located
close together.
Wide Area Network;
Wide Area Network more like to telephone network,
tying different people in different buildings, cities or even countries.
Network Topologies.
There are
several commonly used network topology or ways of routing the interconnections.
It classified as Star, Ring, Bus topologies.
Seven Layers of OSI model;
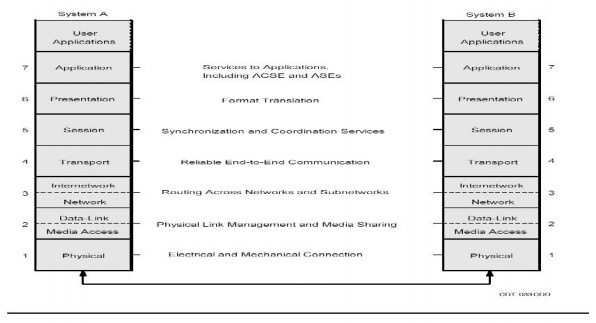
The
protocol layers are;
§ The
physical layer
§ The data
link layer
§ The
network layer
§ The
transport layer
§ The
session layer
§ The
presentation layer
§ The
application layer
Components of LAN;
The
various components of LAN are listed below;
·
Computers,
·
Network interface card,
·
Network cable,
·
Network server,
·
Central mass storage.
Network Topologies;
§ Star
topology
§ Ring
topology
§ Bus topology
§ Tree topology
There are several commonly used
network topology or ways of routing the interconnections. It classified as
Star, Ring, Bus topologies.
Star
network communications
The star network consists of a
central control station to which each of the individual devices or user
stations are connected. To send messages from one workstation to the other is
through the central station.
Ring
network communication
In ring network communication the
individual stations are connected in a continuous ring .Each station has a
neighboring station on either side. To communicate from one station to other,
the message must be relayed from station to station until it finally arrives at
its designated destination station.
Bus
network communication
The bus network consists of a
single main transmission line to which the individual devices are attached. Any
device or station can communicate with any other device in the network by
sending its message through the bus with the address of the desired recipient.
Glossary;
·
Computer-aided design (CAD)
·
Computer-aided engineering (CAE)
·
Computer-aided industrial design (CAID)
·
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM)
·
Computer-aided rule definition (CARD)
·
Computer-aided rule execution (CARE)
·
Computer-aided software engineering (CASE)
·
Computer-aided surgical simulation (CASS)
·
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD)
·
Component information system (CIS)
·
Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM)
·
Automated Guided Vehicle (AGV)
·
Manufacturing Automation Protocol (MAP)
·
Flexible manufacturing module (FMM)
·
Flexible manufacturing cell (FMC)
·
Flexible manufacturing group (FMG)
·
Flexible fabrication-machining-assembly system
(FFMAS)
· Shop Floor Control (SFC).
Related Topics