Chapter: Genetics and Molecular Biology: Advanced Genetic Engineering
Finding Clones Using Antibodies Against a Protein
Finding Clones Using Antibodies Against a
Protein
Cloning a gene becomes easier than described above
if sufficient quantities of its gene product are available to permit raising
antibodies against the protein. DNA from the organism is cloned into a vector
designed to provide for transcription and translation of the inserted DNA. The
DNA is best cloned into a site transcribed from a controllable upstream
promoter and also containing an upstream ribosome binding site and protein
translation initiation sequence as well (Fig. 10.2). A fragment of DNA inserted
into the site and containing an open reading frame is translated if it is fused
in frame with the initiation sequence. As in screening with oligonucleotides, a
replica plate is made, cells on the plate are grown, and the controllable
promoter is induced. The cells are lysed, the proteins are immobilized on a
filter, antibody is added,
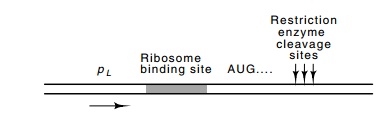
Figure
10.2 Structure of a vector suitable
for antibody screening for theinsertion of open reading frames of a specific
protein.
and then areas with bound antibody are revealed as
described below. The colony from the corresponding position on the replica
plate can then be picked and studied.
Molecules of one particular antibody type bind to
just one particular shape found in some other macromolecule. This is defined as
their antigen. Almost any protein can be used as an antigen to elicit the
synthesis of antibodies. Thus antibodies provide highly selective agents for the
detection of specific proteins. The antibody selectivity for bind-ing to the
correct shape compared to binding to incorrect shapes is roughly the same as
the hybridization selectivity of nucleic acids.
Although radioactive antibody could be used to
detect antigen syn-thesized by candidate clones, it is not efficient, for
different antibodies would then have to be made radioactive for the detection
of different proteins. The A protein from Staphylococcus
aureus provides a more general detection method. This protein binds to a
portion of the anti-body molecule so that one sample of radioactive or
enzymatically tagged Staphylococcus
aureus A protein suffices for the detection of manydifferent
antibody-protein complexes (Fig. 10.3). Another detection method is to use
antibodies themselves as labels. The protein on the filter paper can be
incubated with antibodies specific for the protein that were raised in mice.
Then rabbit antibodies that have been raised against mouse antibodies can be
added. These will detect and bind to most mouse antibodies. The enzyme alkaline
phosphatase can be linked
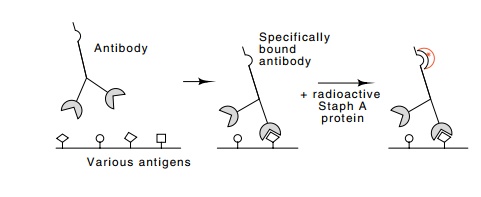
Figure
10.3 The use of radioactiveStaphylococcusA protein to identify
anti-body-antigen complexes in Western transfers.
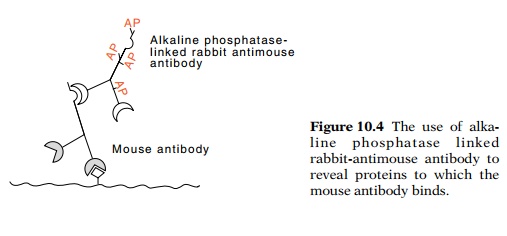
to rabbit-antimouse antibodies (Fig. 10.4). Their location
can be marked by adding colorless substrate for alkaline phosphatase whose
hydrolysis product is highly colored and insoluble. The product shows the
location of protein to which the mouse antibody bound, to which, in turn, the
rabbit antibodies containing alkaline phosphatase bound.
Related Topics