Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Modern Methods of Railway Track Maintenance
Equipment Used in Measured Shovel Packing
Equipment Used in MSP
Special types of equipment are used to carry out MSP. A brief description of each of these instruments is given in the following paragraphs.
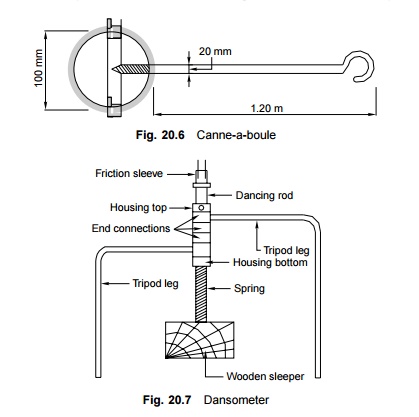
Canne-a-boule
A canne-a-boule is used for assessing the extent of voids in the packing under the sleepers. In the case of wooden sleepers, it consists of an iron ball of a diameter of 100 mm with a 1.20-m-long mild steel rod handle that has a diameter of 20 mm (Fig. 20.6). In the case of steel trough sleepers, a 1.20-m-long wooden canne-a-boule is used with a cylindrical wooden block that is 155 mm long and has a diameter of 100 mm. The canne-a-boule is dropped from a height of 40 cm at both ends of the sleeper. The height of the rebound and the sound emitted in the process determines the extent of the existence of packing voids. A value of 'zero' is given to a sleeper that gives a good rebound and produces a solid sound. The values increase as the sound gets dull and the rebound decreases.
Dansometer
A dansometer is used for measuring the voids in the packing under the sleeper ends. The tripod legs (Fig. 20.7) are fixed in the ballast bed while the dancing rod rests on the sleeper. The extent to which the friction sleeve can shift from its original position helps in determining the presence of voids under the sleeper in dynamic conditions.
Fleximeter
A fleximeter is used to measure the depression of the rail under the weight of plying traffic. It determines the degree to which voids occur in the packing together with the play in the fastenings, i.e., the gap between the rail foot and the sleeper. It is used in conjunction with the dansometer to check the tightness of fastenings.
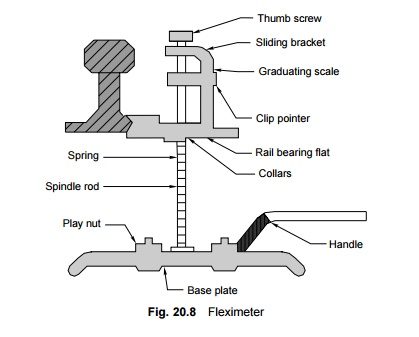
The difference between the fleximeter and dansometer readings indicates the extent to which the fittings between the rail and the sleeper have become loose (Fig. 20.8).
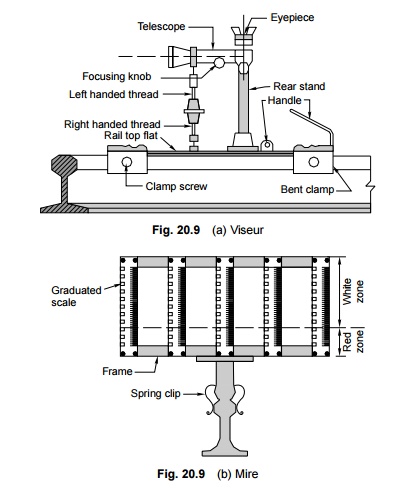
Viseur and mire
The viseur and mire are used to measure the unevenness of the tail top and for rectifying the alignment. The viseur is a type of telescope that has a magnifying power of about 12 and is supported on a stand which can be fixed to the rail seat with the help of two clamps [Fig. 20.9(a)]. The mire is a staff bearing five graduated scales, in millimetres. It has a supporting frame that can be fixed to the rail head by means of bent clamps [Fig. 20.9(b)].
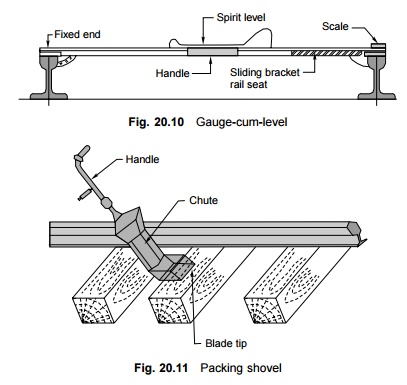
Gauge-cum-level
The gauge-cum-level is used for measuring the gauge of the track as well as the cross levels (Fig. 20.10). The cross level is measured with the help of an approximately 200-mm-long sensitive spirit level with a sensitivity of 2' 30". The cross level can be measured to an accuracy of 1 mm with the help of this instrument.
Packing shovel
A packing shovel is used for placing stone chips over the full width of the sleeper under the rail seat. It is about 1 m long and has a pan for collecting the chips under the sleeper bed. The throw of the blade is 100 mm for BG lines and 85 mm for MG lines (Fig. 20.11).
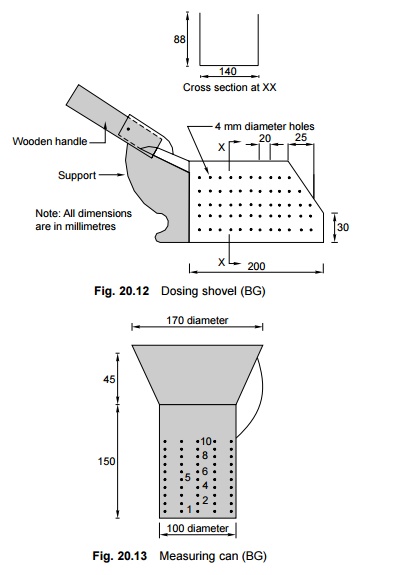
Dosing shovel
A dosing shovel is used for picking up a measured quantity of stone chips for packing. This shovel has a series of holes at different levels. By picking up chips to a specified height in the shovel (Fig. 20.12), the quantity of the chips can be measured.
Measuring can
A measuring can is used to check the accuracy of the dosing shovel. It is a cylindrical container of a height of 150 mm for BG lines and 120 mm for MG lines, with perforated holes at calibrated intervals (Fig. 20.13).
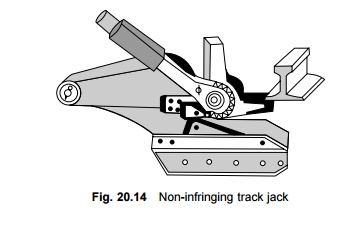
Non-infringing track jacks
Non-infringing track jacks (Fig. 20.14) are used for lifting the rail to a desired height. The jacks are referred to as 'non-infringing' because the lifted rail can easily be returned to its normal position in the case of an approaching train with little manipulation and because they can be left on the track as none of their components project above the rail level and infringe on movement. These jacks are designed for a safe working load of 5 t and for a maximum lift of 200 mm and 160 mm in the case of BG and MG lines, respectively.
Related Topics