Chapter: Civil : Railway Airport Harbour Engineering : Railway Engineering : Modern Methods of Railway Track Maintenance
Directed Track Maintenance
Directed Track Maintenance
As the name suggests, directed
track maintenance (DTM) is a method of maintaining the track on the basis of
directions that are given in this regard every day, and not as a prescribed
routine. Directed track maintenance essentially consists of need-based
maintenance rather than routine maintenance. In the case of DTM, track
maintenance is done by proper identifying any defects in track geometry and
rectifying these defects by attending to the track at the affected locations
under close supervision, thereby maintaining the track at predetermined
standards.
1 Objectives
The two main objectives of DTM are as follows.
(a) To
maintain high standards of track maintenance as per predetermined tolerances.
(b) Reduction
in the cost of maintenance mainly by the avoidance of unnecessary work.
In order to achieve the desired
objectives, the following special features are incorporated in DTM vis-à-vis
the conventional system of maintenance.
(a) The level
of supervision is improved by hiring a well-trained and qualified permanent way
mistry.
(b) A
thorough record of the track defects identified before and after the completion
of work is maintained to assess the inputs and also to help devise remedial
measures of a more permanent nature by carrying out a scientific study based on
the assimilated facts.
(c) Increasing
the length of the unit especially on single lines increases the number of the
gangmen available, resulting in an improvement in the productivity of the gang
as well as the quality of work.
(d) The track
is aimed to be brought to a predetermined level of service tolerances.
2 Work Done Under DTM
The maintenance operations to be
carried out in a section where DTM has been introduced can be placed into the
following four categories.
(a) Systematic overhauling In DTM,
while the emphasis is on need-based maintenance, the intention is not to
completely dispense with routine maintenance works such as systematic
overhauling. Instead, the frequency of systematic overhauling is suitably
increased, say by three to four years or as decided by the chief engineer,
depending on local factors such as the condition of the track and the
formation, traffic density, permissible speed, and rainfall. A certain number
of working days in the appropriate months of the year are earmarked for this
work so as to cover one-third or one-fourth of the gang length by systematic
overhauling, depending on the site conditions.
(b)
Periodic maintenance work This
includes works such as the lubrication of joints, cleaning of side
drains, catch water drains, and repairs of the formation and cess. In the
annual program, an adequate number of working days should be set aside during
the appropriate months for periodic maintenance work.
(c)Occasional
maintenance work This includes other works such as scattered renewal
of rails, sleepers, and other track components, adjusting creep, restoring
correct spacing between sleepers, building damaged rail ends, realigning
curves, overhauling level crossings as well as points and crossings, and
properly removing any deficiencies in the ballast section. The permanent way
inspector assesses the quantum of such works that are to be carried out
periodically in the order of their priority and draws up a programme in
consultation with engineers after taking into consideration the availability of
track material, ballast, welding parties, etc.
(d) Need-based
maintenance The remaining working days in the annual programme
are devoted to need-based maintenance, which is a new concept and forms the
main distinguishing feature of DTM as compared to the conventional system of
maintenance. The operations involved in need-based maintenance are as follows.
(a) Location
of defects by analysing the results of the track recording car/ oscillograph
car/hallade recorder and by foot plate/rear vehicle/trolley/foot inspection.
(b) Identification
of defects by means of systematic inspection and by ground measurements taken
by trained supervisors using precision instruments.
(c) Recording
of the observations.
(d) Rectifying
track defects by attending only to the defective portion followed by a post
check of the same portion conducted by the supervisor to check its quality and
output.
3
Annual Program for DTM
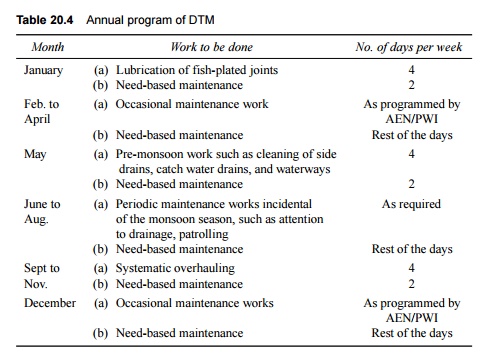
Table 20.4 depicts a typical chart showing the annual program
of track maintenance under DTM.
The following points need to be mentioned with
respect to the data given in Table 20.4.
(a) The chart
is only for guidance, and the chief engineers of zonal railways can make
variations to suit the local conditions.
The chart is for that section of
the track where manual methods of maintenance are adopted. Whenever maintenance
involves the use of machines, the DTM unit will assist in the same by taking
care of the work of pre-tamping and post-tamping and other operations not
covered by machines.
Table 20.4 Annual program of DTM
Related Topics