Chapter: Medical Electronics : Bio-Chemical and Non Electrical Parameter Measurement
Electrophoresis
ELECTROPHORESIS
In
clinical laboratories, various devices are used based on the electrophoretic
principle. These devices are used for the following applications.
Ø To
measure the quantity of protein in plasma, urine, etc.
Ø To separate enzymes into their components is enzymes.
Ø To
identify antibodies.
Basic principle
Electrophoresis
is defined as the movement of a solid phase with respect to a liquid. The
buffer solution is used to carry the current and to maintain the pH value of
the solution as a constant one during the migration.
In this
title, zone electrophoresis is explained. In this technique, the sample is
applied to the medium and under the effect of the electric field, group of
particles that are similar in charge, size, and shape migrate at the same rate.
So the particles are separated into zones.
Factors Affect the Speed of Migration
Magnitude of charge:
The
mobility of a given particle is directly related to the net magnitude of the
particles charge. Mobility is defined as, the distance in cm, a particle moves
in unit time per unit field strength.
Ionic Strength of Buffer
If the
buffer is more concentrated then the migration of the particles is slow.
Because, if greater the proportion of buffer ions present, then greater the
proportion of the current they carry.
Temperature:
Mobility
is directly related to temperature. Heat is produced when the current flows
through the resistance of the medium. So, the temperature of the medium is
increased and resistance is decreased. Finally, the rate of migration is
increased.
The water
is evaporated from the surface of the medium due to heat. So, the concentration
of particle is increased. Finally the rate of migration is increased. When the
gel is used as a medium; this heat will create a problem. So, for this medium,
constant current sources are used to minimize the heat production.
Time: The distance of migration is
related to the time period during which electrophoresis takes place.
Types of Support Media:
Cellulose
acetate, starch gel and sucrose are used as support media in various
electrophoretic applications. We can see the cellulose acetate electrophoresis
in the following sections.
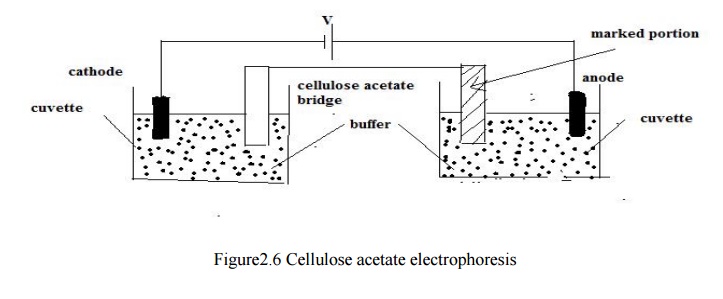
Cellulose Acetate Electrophoresis
Cellulose
acetate strip is saturated with the buffer solution and placed in the membrane
holder. It is otherwise known as bridge. The two ends of the bridge are placed
in the cuvette in which buffer solution is available.
The
sample for each test is placed on the strip at a marked location. Then, the
constant electric potential(250 V) is applied across the strip 4 – 6 mA of
initial current is obtained .After
15-20mins, the electric voltage is
removed, then, migrated protein band is stained with buffer and it is dried in
preparation for densitometry.
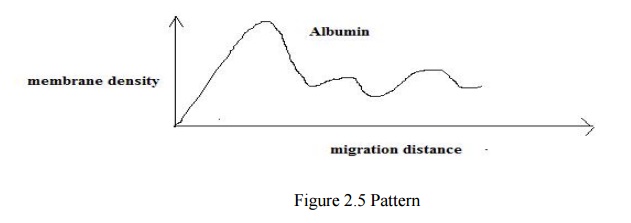
The
membrane is placed in the holder of densitometer. The path of the migration of
one of the specimen is scanned. The low voltage output is amplified and
recorded using x-y recorder.
Related Topics