Chapter: Medical Electronics : Bio-Chemical and Non Electrical Parameter Measurement
Blood Cell Counter
BLOOD CELL COUNTER
• The blood
cell counter count the number of RBC or WBC per unit of volume of blood using
either of two method:
– Electrical method called aperture impedance
change
– Optical method called flow cytometry
Aperture impedance change
•
When blood is diluted in the proper type of
solution, the electrical resistivity of blood cells (ρc) is higher
then thhe resistivity of the surrounding fluid (ρf)
•
By contriving a situation in which these
resistivities can be differentiated from each other, we can count cells
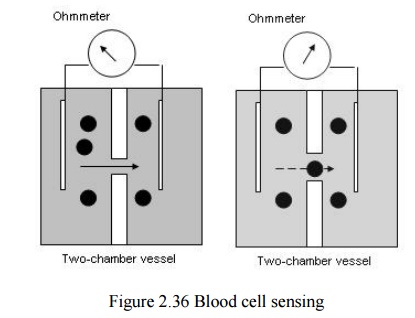
Blood cell sensing
•
The sensor consist of a two-chamber vessel in
which the dilute incoming blood is on one side of barrier, and the waste blood
to be discarded is on the other
•
A hole with a small diameter (50μm) is placed in
the partition between the tow halves of the cell
•
Ohmmeter measure the change on the resistance when
the blood cell p ass the aperture
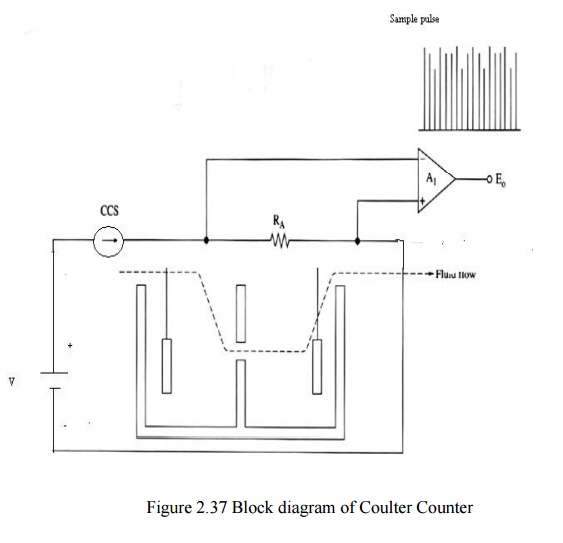
1. COULTER COUNTER
•
Constant current source (CCS) and voltage amplifier
replace the ohm meter
• RA
is the resistance of the aperture and will be either high or low, depending on
whether or not the blood cell is inside the aperture.
Amplifier convert the current pulse to voltage
pulse
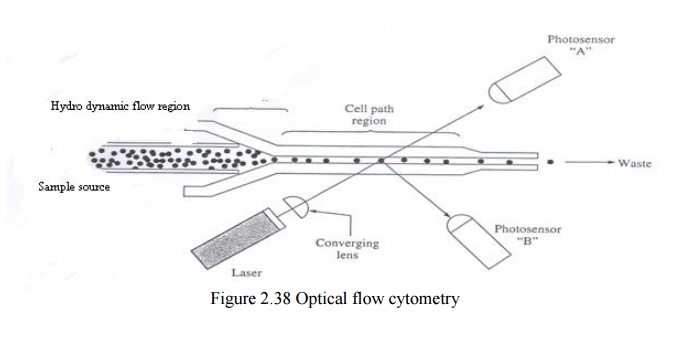
2. FLOW CYTOMETRY CELL COUNTERS
Optical flow cytometry sensing
•
The optical cytometry sensor consists of a quartz
sensing sheath designed with a
– hydrodynamic focusing region
– cell path region that passes only a single
cell at time.
•
Focusing is done by decreasing the diameter of the
aperture.
•
Light source is (He-Ne) Laser
•
Two Photodetectors (photosensors)
– Photodetector A detects forward scatted light
– Photodetector B detects orthogonal scatted
light
•
blood sample enters the analyzer
– Optical counter → WBC count
– Colorimeter → hemoglobin
– Optical flow sensor → RBC count
The blood
is actually split into different chambers, where in each chamber it is diluted
/ mixed to differentiate different cell types. WBC and RBC are separated (using
lysing)
Related Topics