Chapter: physics 11th 12th standard school college definition answer assignment examination viva question
Electric cells and Voltaic cell
Electric cells
The starting point to the development of electric cells is the classic experiment by Luige Galvani and his wife Lucia on a dissected frog hung from iron railings with brass hooks. It was observed that, whenever the leg of the frog touched the iron railings, it jumped and this led to the introduction of animal electricity. Later, Italian scientist and genius professor Alessandro Volta came up with an electrochemical battery. The battery Volta named after him consisted of a pile of copper and zinc discs placed alternately separated by paper and introduced in salt solution. When the end plates were connected to an electric bell, it continued to ring, opening a new world of electrochemical cells. His experiment established that, a cell could be made by using two dissimilar metals and a salt solution which reacts with atleast one of the metals as electrolyte.
1. Voltaic cell
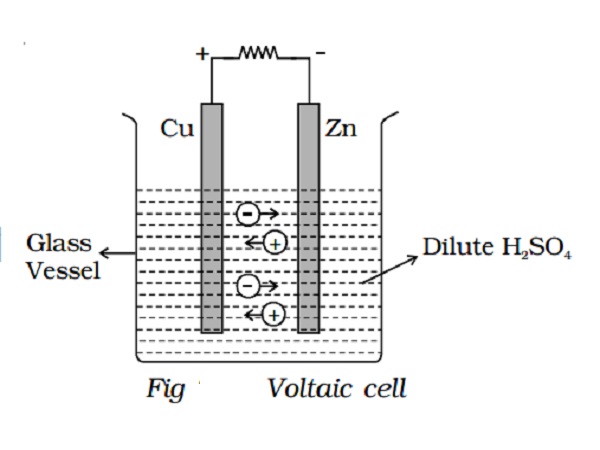
The simple cell or voltaic cell consists of two electrodes, one of copper and the other of zinc dipped in a solution of dilute sulphuric acid in a glass vessel (Fig 2.20). On connecting the two electrodes externally, with a piece of wire, current flows from copper to zinc outside the cell and from zinc to copper inside it. The copper electrode is the positive pole or copper rod of the cell and zinc is the negative pole or zinc rod of the cell. The electrolyte is dilute sulphuric acid.
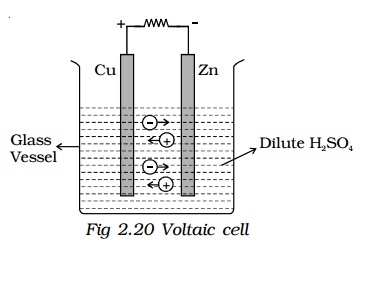
The action of the cell is explained in terms of the motion of the charged ions. At the zinc rod, the zinc atoms get ionized and pass into solution as Zn++ ions. This leaves the zinc rod with two electrons more, making it negative. At the same time, two hydrogen ions (2H+) are discharged at the copper rod, by taking these two electrons. This makes the copper rod positive. As long as excess electrons are available on the zinc electrode, this process goes on and a current flows continuously in external circuit. This simple cell is thus seen as a device which converts chemical energy into electrical energy. Due to opposite charges on the two plates, a potential difference is set up between copper and zinc, copper being at a higher potential than zinc. The difference of potential between the two electrodes is 1.08V.
Related Topics