Chapter: Physics : Higher Secondary School
Faraday's laws of electrolysis | Chemical effect of current | Verification of Faraday's laws of electrolysis
Chemical effect of current
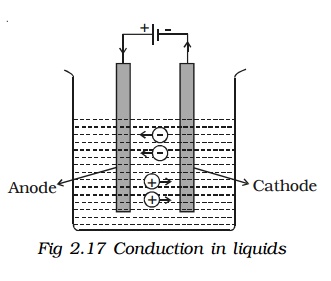
The passage of an electric current through a liquid causes chemical changes and this process is called electrolysis. The conduction is possible, only in liquids wherein charged ions can be dissociated in opposite directions . Such liquids are called electrolytes. The plates through which current enters and leaves an electrolyte are known as electrodes. The electrode towards which positive ions travel is called the cathode and the other, towards which negative ions travel is called anode. The positive ions are called cations and are mostly formed from metals or hydrogen. The negative ions are called anions.
1. Faraday’s laws of electrolysis
The factors affecting the quantities of matter liberated during the process of electrolysis were investigated by Faraday.
First Law : The mass of a substance liberated at an electrode is directly proportional to the charge passing through the electrolyte.
If an electric current I is passed through an electrolyte for a time t, the amount of charge (q) passed is I t. According to the law, mass of substance liberated (m) is
m α q or m = zIt
where Z is a constant for the substance being liberated called as electrochemical equivalent. Its unit is kg C-1.
The electrochemical equivalent of a substance is defined as the mass of substance liberated in electrolysis when one coulomb charge is passed through the electrolyte.
Second Law : The mass of a substance liberated at an electrode by a given amount of charge is proportional to the *chemical equivalent of the substance.
If E is the chemical equivalent of a substance, from the second law
m α E
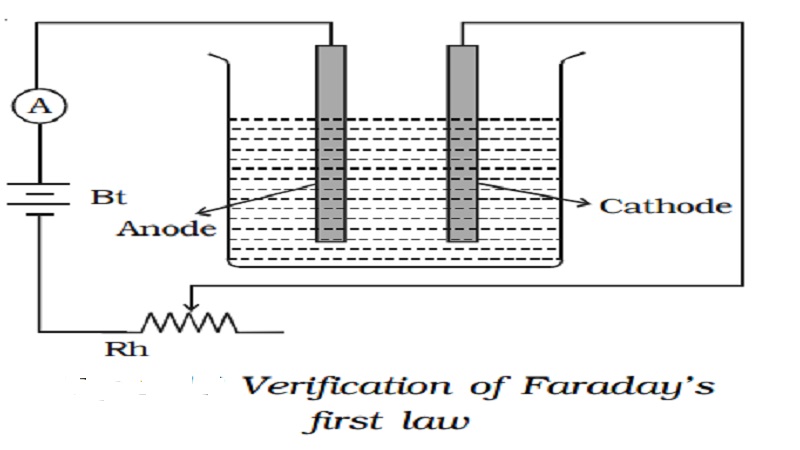
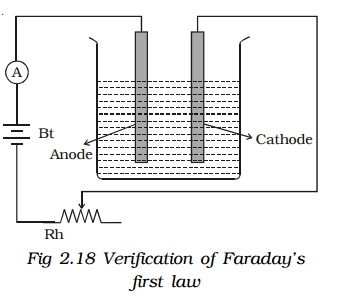
2. Verification of Faraday’s laws of electrolysis:
First Law : A battery, a rheostat, a key and an ammeter are connected in series to an electrolytic cell . The cathode is cleaned, dried, weighed and then inserted in the cell. A current I1 is passed for a time t. The current is measured by the ammeter. The cathode is taken out, washed, dried and weighed again. Hence the mass m1 of the substance deposited is obtained.
The cathode is reinserted in the cell and a different current I2 is passed for the same time t. The mass m2 of the deposit is obtained.

From relations (1) and (2)
m α It or m α q Thus, the first law is verified.
Second Law : Two electrolytic cells containing different electrolytes, CuSO4 solution and AgNO3 solution are connected in series with a battery, a rheostat and an ammeter diagram. Copper electrodes are inserted in CuSO4 and silver electrodes are inserted in AgNO3.
The cathodes are cleaned, dried, weighed and then inserted in the respective cells. The current is passed for some time. Then the cathodes are taken out, washed, dried and weighed. Hence the masses of copper and silver deposited are found as m1 and m2.
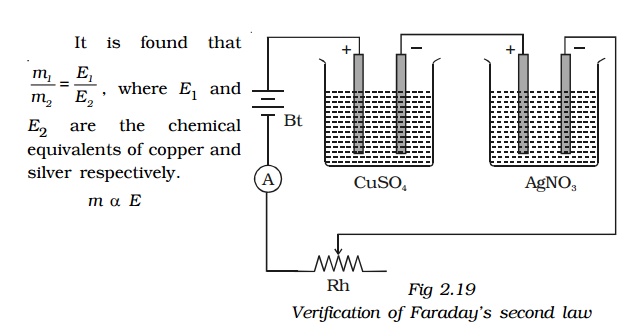
m α E
Thus, the second law is verified.
Related Topics