Chapter: Pharmaceutical Drug Analysis: Gas Liquid Chromatography (GLC)
Derivatization - High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
DERIVATIZATION
The main purpose of derivatization in HPLC is to improve
detection specifically when determining traces of solutes in complex matrices,
for example :
(i)
Pharmaceutical substances lacking an UV-chromophore in the 254 nm region but
possessing a reactive functional group,
(ii) Biological
fluids e.g., blood, serum, urine ;
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF); and
(iii)
Environmental samples.
Derivatization may be accomplished by two means, namely :
(a) Pre-column
off-line derivatization.
(b) Post-column
on-line derivatization.
These two methods shall be discussed briefly at this
juncture :
1. PRE-COLUMN OFF-LINE DERIVATIZATION
Merits :
This technique has the
following merits :
(a) Requires no
modification to the instrument i.e.,
a plus point when compared to the post-column methods, and
(b) Imposes
fewer limitations with regard to reaction-time and conditions.
Demerits :
The demerits include :
(a) Formation
of a stable and well-defined product is an absolute necessity,
(b) Presence of
excess reagent or by products may invariably interfere with separation, and
(c) Very often derivatization
may altogether change the chromatographic properties of the sample which
facilitated separation.
2. POST-COLUMN ON-LINE DERIVATIZATION
The following experimental parameters should be
maintained, namely :
(a)
Derivatization performed in a special-reactor strategically positioned between
the column and the detector,
(b) Reaction
must be completed rapidly at moderate temperatures,
(c)
Derivatization reaction need not even go to completion provided it can be made
reproducible,
(d) No
detector-response should exist due to any excess reagent present, and
(e) Reaction
must be carried out in a medium other than the mobile-phase.
Merit :
The main merit of
post-column-on-line derivatization is that ideally the separation and
detec-tion processes can be optimized individually.
3. REAGENTS FOR DERIVATIZATION
There are potentially viable reagents available that may
be employed for the derivatization of compounds either for enhancing UV/visible
radiation (called chromatags) or for
reaction of non-fluorescent reagent molecules (called fluorotags) with solutes to yield fluorescent derivatives.
Examples : (i) Derivatization for UV-Detectors :
Ninhydrin (a chromatag
is commonly employed to yield corresponding derivatives of amino acids that
show absorption specifically at about 570 nm as shown in the following reaction
:
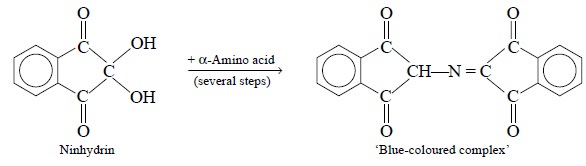
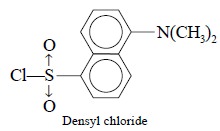
(ii) Derivatization for Fluorescence Detectors :
Dansyl Chloride (a fluorotag)
is invariably used to obtain fluorescent derivatives of proteins, amines and
phenolic compounds, the excitation and emission wavelengths being 335 to 365 nm
and 520 nm respectively.
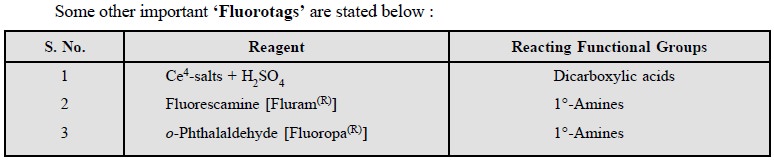
Related Topics