Chapter: Computer Networks : Application Layer
Cryptography
Security:
Security
in networking is based on cryptography, the science and art of transforming
messages to make them secure and immune to attack. Cryptography can provide
several aspects of security related to the interchange of messages through
networks. These aspects are confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and
nonrepudiation.
Cryptography:
Cryptography
can provide confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non repudiation of
messages. Cryptography, a word with Greek origins, means "secret
writing." However, we use the term to refer to the science and art of
transforming messages to make them secure and immune to attacks.
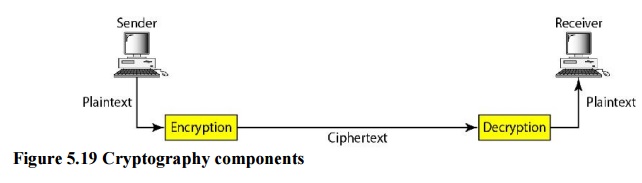
Plaintext and Ciphertext
The
original message, before being transformed, is called plaintext. After the
message is transformed, it is called ciphertext. An encryption algorithm
transforms the plaintext into ciphertext; a decryption algorithm transforms the
ciphertext back into plaintext. The sender uses an encryption algorithm, and
the receiver uses a decryption algorithm.
Two Categories
We can
divide all the cryptography algorithms (ciphers) into two groups: symmetric key
(also called secret-key) cryptography algorithms and asymmetric (also called public-key)
cryptography algorithms.
a. Symmetric·Key Cryptography
In
symmetric-key cryptography, the same key is used by both parties. The sender
uses this key and an encryption algorithm to encrypt data; the receiver uses
the same key and the corresponding decryption algorithm to decrypt the data
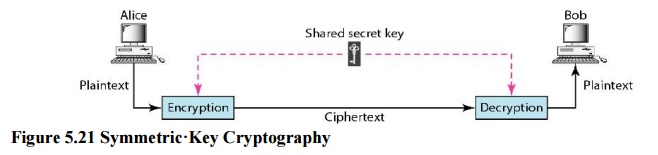
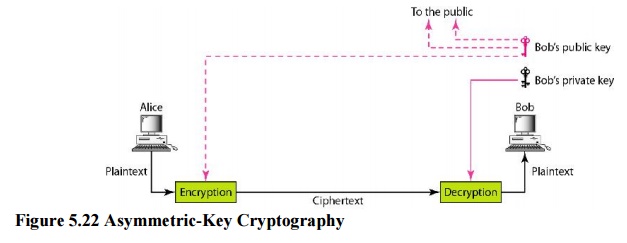
b. Asymmetric-Key Cryptography
In
asymmetric or public-key cryptography, there are two keys: a private key and a
public key. The private key is kept by the receiver. The public key is announced
to the public. In public-key encryption/decryption, the public key that is used
for encryption is different from the private key that is used for decryption.
The public key is available to the public; the private key is available only to
an individual.
Related Topics