Book Back and Important Questions Answers - Coordination Chemistry: Answer the following questions | 12th Chemistry : UNIT 5 : Coordination Chemistry
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 5 : Coordination Chemistry
Coordination Chemistry: Answer the following questions
Coordination Chemistry
Answer the following questions:
1. Write the IUPAC names for the following complexes.
i) Na2 [Ni( EDTA)]
ii) [Ag (CN)2]
iii) [Co(en)3]2 (SO4)3
iv) [Co(ONO) (NH3)5]2+
v) [Pt(NH3)2 Cl(NO2)]
Na2[Ni(EDTA)]
: Sodium ethylenediaminetetraacetato nickelate (IV)
[Ag(CN)2]−
: Dicyanidoargentate (I) ion
[Co(en)3]2(SO4)3
: Tris (ethylenediamine) cobalt (III) sulphate
[CO(ONO)(NH3)5]2+
: pentaamminenitrito -κ -O - cobalt(III)ion
[Pt(NH3)2Cl2(NO2)]
: Di ammine dichloridonitritoplatinum(II)
2. Write the formula for the following coordination compounds.
a) potassiumhexacyanidoferrate(II)
b) pentacarbonyliron(0)
c) pentaamminenitrito −κ −N -cobalt(III)ion
d) hexaamminecobalt(III)sulphate
e) sodiumtetrafluoridodihydroxidochromate(III)
a)
Potassiumhexacyanidoferrate (II) - Formula
: K4[Fe(CN)6]
b)
Pentacarbonyliron(0) - Formula : [Fe(CO)5]
c)
Pentaamminenitrito - κ -N - cobalt(III)ion - Formula : [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]2+
d)
Hexaamminecobalt (III) sulphate - Formula
: [Co(NH3)6]SO4
e)
Sodium tetrafluoridodihydroxido chromate(III) - Formula : Na3[CrF4(OH)2]
3. Arrange the following in order of increasing molar conductivity
i) Mg [Cr (NH3) (Cl)5 ]
ii) [ Cr (NH3)5 Cl ]3 [CoF6]2
iii) [Cr (NH3)3 Cl3 ]
Answer: c < a
< b
(c)
does not gives any ion in solution, (a) gives Mg2+ and [Cr(NH3)Cl5]2−
ion solution. Hence conductivity higher than (a), (b) gives 5 ions in solution.
Hence molar conductivity of (b) is greater than other two. Hence order is c<
a < b
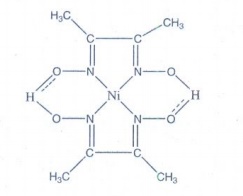
4. Ni2+ is identified using alcoholic solution of dimethyl glyoxime. Write the structural formula for the rosy red precipitate of a complex formed in the reaction.
5. [CuCl4 ]2− exists while [CuI4 ]2− does not exist why?
Size
of I− is greater than Cl−. Due to steric
effect [CuI4]2− does not exist, I− is also get oxidized to iodine.
6. Calculate the ratio of [Ag+]/[Ag(NH3)2] in 0.2 M solution of NH3. If the stability constant for the complex [Ag(NH3)2] is 1 7 x 107.

β
= [Ag(NH3)2]+ / [Ag+][NH3]2
1.7
× 107 = [Ag(NH3)2]+ / [Ag+][0.2]2
1.7
× 107 × 0.2 × 0.2 = [Ag(NH3)2]+ /
[Ag+]
0.068
× 107 = [Ag(NH3)2]+ / [Ag+]
[Ag+]
/ [Ag(NH3)2]+
= 1 / [ 0.068 × 107] = 14.7 × 10-7
7. Give an example of coordination compound used in medicine and two examples of biologically important coordination compounds.
Medicine
(1)
Ca-EDTA -Treatment of lead and radioactive poisoning.
(2)
Cis-platin - Antitumor drug in cancer treatment.
Biologically important
coordination compounds
(i)
Fe2+ − Porphyrin complex carrying oxygen from lungs to tissues and
carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs.
ii)
Chlorophyll - A coordination complex containing Mg2+, Important role
in photosynthesis, by which plants converts CO2 and water into
carbohydrates and oxygen.
8. Based on VB theory explain why [Cr (NH3)6]3+ is paramagnetic, while [Ni (CN)4]2- diamagnetic

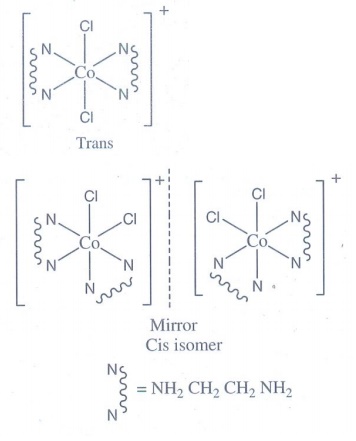
9. Draw all possible geometrical isomers of the complex [Co( en)2 Cl2]+ and identify the optically active isomer.
[Co(en)2Cl2]+ and its optically active isomer
10. [Ti ( H2O)6]3+ is coloured, while [Sc ( H2O)6 ]3+ is colourless- explain.
Ti:
[Ar]3d24s2 Sc: [Ar]3d14s2
[Ti(H2O)6]3+
[Sc(H2O)6]3+
Ti3+:
[Ar]3d14s0 Sc3+: [Ar]3d°4s°
One
d electron present in [Ti(H2O)6]3+. Due to d-d
transition the complex is coloured. In [Sc(H2O)6]3+
there is no d electron. Hence d-d transition is not possible in [Sc(H2O)6]3+
Hence it is colorless.
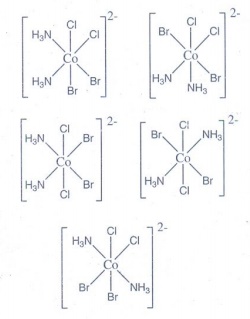
11. Give an example for complex of the type [Ma2 b2c2 ] where a, b, c are monodentate ligands and give the possible isomers.
Example
for [Ma2b2C2] is [CoCl2 Br2(NH3)2]2−
5
geometrical isomers possible for this type complex.
12. Give one test to differentiate [ Co (NH3)5Cl] SO4 and [ Co( NH3)5 SO4 ] Cl.
The
complexes show ionization isomerism.
If
SO42− ion is counter ion then the complex is [CO(NH3)5Cl]SO4. With BaCl2
it gives curdy white precipitate.
If
Cl− ion is counter ion then the complex [Co(NH3)5SO4]Cl. With silver nitrate it gives white
precipitate.
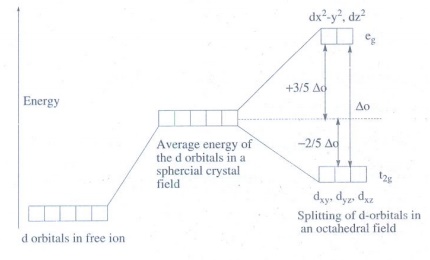
13. In an octahedral crystal field, draw the figure to show splitting of d orbitals.
During
crystal field splitting in octahedral field, in order to maintain the average
energy of the orbitals (barycentre) constant, the energy of the orbitals dx2−y2
and dz2 (represented as eg orbitals) will increase by
3/5∆o while that of the other three orbitals dxy, dyz and
dzx (represented as t2g orbitals) decrease by 2/5∆o.
Here, Δo represents the crystal field splitting energy in the octahedral field.
14. What is linkage isomerism? Explain with an example.
When
an ambidentate ligand is bonded to the central metal atom / ion through either
of its two different donor atoms gives linkage isomerism
Example:
[Co(NH3)5(NO2)]2+ [Co(NH3)5(ONO)]2+
The
nitrite ion is bound to the central metal ion Co3+ through a
nitrogen atom in one complex, and through oxygen atom in other complex.
15. Write briefly about the applications of coordination compounds in volumetric analysis.
1.
EDTA is used as a chelating ligand for the separation of lanthanides, in
softening of hard water and also in removing lead poisoning.
3.
Some metal ions are estimated by complex formation. Ni2+ ions
estimated as [Ni(DMG)2]
3.
Coordination complexes are used in the extraction of silver and gold from their
ores by forming soluble cyanido complex. These cyanido complexes are reduced by
zinc to yield metals. This process is called as Mac- Arthur -Forrest cyanide
process.
16. Classify the following ligand based on the number of donor atoms.
a) NH3 b) en c) ox2- d) triaminotriethylamine e) pyridine
Answer :
a)
NH3 - Monodentate
b)
en - Bidentate
c)
ox2− - Bidentate
d)
triaminotriethylamine - Tridentate
e)
pyridine - Monodentate
17. Give the difference between double salts and coordination compounds.

Double salt
•
The ions present in the constituents are obtained when dissolved in water
•
It does not completely lose its identity in solution
•
The properties of the double salt are nearly the same as those of the
constituent compounds
•
Example: FeSO4.(NH4)2SO4.6H2O
Coordination compound
•
Some ions present in the constituents are not obtained when dissolved in water
•
It loses its identity in solution
•
The properties of a coordination compound are usually different from those of
the constituent compounds
•
Example: K4[Fe(CN)6]
18. Write the postulates of Werner’s theory.
1.
Most of the elements exhibit, two types of valence namely primary valence and
secondary valence and each element tend to satisfy both the valences.
2.
The primary valence: It is positive
in most of the cases and zero in certain cases. They are always satisfied by
negative ions. It is referred as the oxidation states.
3.
The secondary valence: It is
satisfied by negative ions, neutral molecules, positive ions or the combination
of these. It is referred as the coordination number.
4.
The inner sphere is known as coordination sphere and the groups present in this
sphere is attached to metal. The outer sphere is called ionisation sphere and
it can be separated into ions in a suitable solvent.
5.
The primary valences are non-directional while the secondary valences are
directional. The geometry of the complex is determined by the secondary
valence.
19. [Ni ( CN)4 ]2− is diamagnetic, while [ NiCl4 ]2− is paramagnetic , explain using crystal field theory.
Ni:
[Ar]3d8 4s2
Oxidation
state of Ni in the complex = +2
Ni2+
: [Ar]3d8 4s0
CN−
is strong ligand. The complex is square planar.
Crystal
field configuration
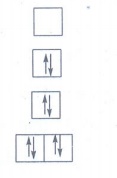
There
is no unpaired electron in square planar crystal field configuration.
µs= 0. Hence it is diamagnetic.
[NiCl4]2−
is paramagnetic
Ni : [Ar]3d84s2
Oxidation
state of Ni in the complex = +2
Ni2+ : [Ar]3d8 4s0
Cl−
is weak ligand. The complex is tetrahedral.
Crystal
field configuration of the complex = e4t24
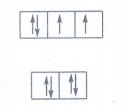
Number
of unpaired electron = 2
µs
= √[n(n + 2)] = 2.8 BM
20. Why tetrahedral complexes do not exhibit geometrical isomerism.
All
the ligands are adjacent to one another in tetrahedral complexes. Hence
tetrahedral complexes do not exhibit geometrical isomerism.
21. Explain optical isomerism in coordination compounds with an example.
Optical Isomerism
• Coordination compounds which
possess chirality exhibit optical isomerism.
• The pair of two optically active
isomers which are mirror images of each other are called enantiomers.
• The solutions rotate the plane of
the plane polarised light to clockwise are called 'd' isomers (dextro
rotatory).
• The solutions rotate the plane
polarised light to anticlockwise are called ‘l’ isomers (laevo rotatory).
• The octahedral complexes of type
[M(xx)3]n±, [M(xx)2AB]n± and [M(xx)2B2]n±
exhibit optical isomerism.
Examples: The
optical isomers of [CoCl2(en)2]+
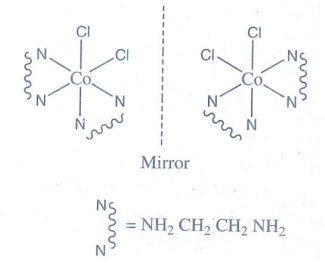
22. What are hydrate isomers? Explain with an example.
• The exchange of free solvent
molecules in the crystal lattice with a ligand in the coordination entity will
give different isomers. These types of isomers are called solvate isomers.
• If the solvent molecule is water,
then these isomers are called hydrate isomers.
Example:
CrCl3.6H2O has three hydrate isomers.
[Cr(H2O)6]Cl3
- Violet color: Gives
three chloride ions in solution
[Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2.H2O
- Pale green color: Gives
two chloride ions in solution
[Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl.2H2O
- Dark green color: Gives
one chloride ion in solution
23. What is crystal field splitting energy?
When
ligands approach the central metal ion, the d-orbitals split into two sets, one
with lower energy and other with higher energy. The difference of energy
between the two sets of orbitals is called cryatal field splitting energy.
24. What is crystal field stabilization energy (CFSE) ?
The
crystal field stabilisation energy is defined as the energy difference of
electronic configurations in the ligand field (ELF) and the isotropic field / barycentre
(EiSO).
CFSE(∆Eo)
= {ELF} – {Eiso}
=
{[n t2g(-0.4) + n eg (0.6)] ∆o + npP} - {n’p
P}
n
t2g is the number of electrons in t2g orbitals
n
eg is number of electrons in eg orbitals
nP
is number of electron pairs in the ligand field
n'P
is the number of electron pairs in the isotropic field (barycentre)
25. A solution of [Ni (H2O)6]2+ is green, whereas a solution of [Ni (CN)4 ]2+ is colorless - Explain
• The complex [Ni(H2O)6]2+
is octahedral and it has two unpaired electron in its eg orbital.
These unpaired electrons involves d-d transition and responsible for the green
colour of the complex.
• The complex [Ni(CN)4]2+
is square planar, all the electrons are getting paired and there is no
availability of unpaired electrons for d-d transition. Due to the absence of
unpaired electron [Ni(CN)4]2+ is colourless
26. Discuss briefly the nature of bonding in metal carbonyls.
M-CO σ bonding
• There is an electron pair
donation from the carbon atom of carbonyl ligand into a vacant d-orbital of
central metal atom forms
M ← CO sigma bond.

π-back bonding:
• This sigma bond formation
increases the electron density in metal d orbitals and makes the metal electron
rich. To compensate for this increased electron density, a filled metal d-orbital
interacts with the empty π* orbital
on the carbonyl ligand and transfers the added electron density back to the
ligand is called π-back bonding.
Synergic effect:
Thus
in metal carbonyls, electron density moves from ligand to metal through sigma bonding
and from metal to ligand through pi bonding, this synergic effect accounts for strong
M ← CO bond in metal carbonyls.
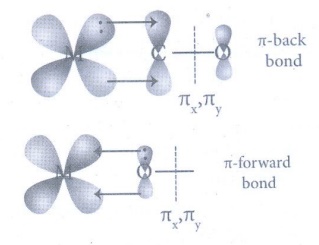
27. What is the coordination entity formed when excess of liquid ammonia is added to an aqueous solution of copper sulphate?
When
excess of liquid ammonia is added to an aqueous solution copper sulphate it
forms a tetraamminecopper complex [Cu(NH3)4]SO4
(Tetraamminecopper(II) sulphate).
CuSO4
+ 4NH3 → [Cu(NH3)4]SO4
The
coordination entity is [Cu(NH3)4]2+
28. On the basis of VB
theory explain the nature of bonding in [Co(C204)3]3-
Complex : [Co(C2O4)3]3-
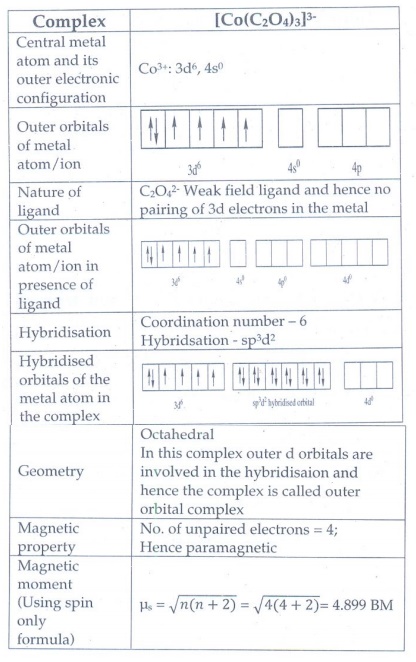
29. What are the limitations of VB theory?
1.
It does not explain the colour of the complex
2.
It consider only the spin only magnetic moments and does not consider the other
components of magnetic moments.
3.
It does not provide a quantitative explanation inner orbital complexes and the
others are outer orbital complexes for the same metal.
For
example, [Fe(CN)6]4- is diamagnetic (low spin) whereas
[FeF6]4- is paramagnetic (high spin). VB theory does not
gives any explanation of this magnetic behavior.
30. Write the oxidation state, coordination number , nature of ligand, magnetic property and electronic configuration in octahedral crystal field for the complex K4[Mn (CN)6].
Oxidation
state : +2
Coordination
Number : 6
Nature
of ligand : Strong field ligand
Magnetic
property : Only one paired electron. µs = 1.732 BM
Electronic
configuration in octahedral crystal field : t2g5 eg0
EVALUATE YOURSELF:
1. When a
coordination compound CrCl3.4H2O is mixed with silver
nitrate solution, one mole of silver chloride is precipitated per mole of the
compound. There are no free solvent molecules in that compound. Assign the
secondary valence to the metal and write the structural formula of the
compound.
Solution:
• CrCl3.4H2O
shows hydrate isomerism. The complex is mixed with silver nitrate solution; one
mole of silver chloride is precipitated per mole of the compound. There are no
free solvent molecules in that compound.
• Based on the above information it
is concluded that one Cl−
ion present as ionisable valence. All the water molecules are present inside
the coordination sphere. The complex may be [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl
2. In the complex,
[Pt(NO2)(H2O)(NH3)2Br , identify the following
i. Central metal
atom/ion
ii. Ligand(s) and
their types
iii. Coordination
entity
iv. Oxidation
number of the central metal ion
v. Coordination
number
Complex : [Pt(NO2)(H2O)(NH3)2]Br
i. Central metal atom / ion : Pt / Pt+2
ii. Ligand(s) and their types : NO2−
- Anioinic ligand, Monodentate
H2O - Neutral ligand, Monodentate
NH3 - Neutral ligand, Monodentate
iii. Coordination entity: [Pt(NO2)(H2O)(NH3)2]+
iv. Oxidation number of the
central metal ion: +2
v. Coordination number: 4
3. A solution of
[Co(NH3)4I2Cl when treated with AgNO3
gives a white precipitate. What should be the formula of isomer of the
dissolved complex that gives yellow precipitate with AgNO3. What are
the above isomers called?
• A solution of [Co(NH3)4I2]Cl
when treated with AgNO3 the Cl−
ion present outside of the coordination sphere gives a white precipitate.
• If I− is present
outside of the coordination sphere it will gives yellow precipitate when
treated with AgNO3. The formula is [Co(NH3)4(Cl)(I)]I.
The isomers is called ionization isomer.
4. Write the IUPAC
name for the following compounds
i) K2[Fe(CN)3(Cl)2(NH3)]
Potassium
ammine dichlorido tri cyanido ferrate (III)
ii) [Cr(CN)2(H2O)4][Co(ox)2(en)]
Tetra
aquadi cyanido chromium (II)
(ethylene
diamine) dioxalato cobalt (II)
iii) [CU(NH3)2Cl2]
Diammine
dichlorido copper (II)
iv) [Cr(NH3)3(NC)2(H2O)]+
Triammine
aqua dicyanido-κ Nchromium (III) ion
v) [Fe(CN)6]4
−
Hexacyanidoferrate
(II) ion
5. Give the
structure for the following compounds.
(i) Diammine silver(I)
dicyanideargentate(I)
[Ag(NH3)2]
[Ag(CN)2]
(ii) Pentaammine nitrito-κNcobalt
(III) ion
[CO(NH3)5(NO2)]+2
(iii) Hexafluorido cobaltate
(III) ion
[COF6]3-
(iv) Dichloridobis (ethylenediamine)
cobalt (III) sulphate
[Co
Cl2(en)2] SO4
(v) Tetra carbonyl nickel (0)
[Ni(CO)4]
6. Three compounds
A, B and C have the molecular formula CrCl3.6H2O. They
are kept in a container with a dehydrating agent and they lost water and
attaining constant weight as shown below.
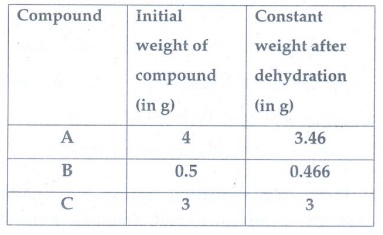
Compond A : [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl.
2H2O
Compound B : [Cr(H2O)5Cl]Cl2.
H2O
Compound C : [Cr(H2O)3Cl3]
. 3H2O
7. Indicate the
possible type of isomerism for the following complexes and draw their isomers
(i) [Co(en)3][Cr(CN)6]
(ii) [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]2+
(iii) [Pt(NH3)3(NO2)]Cl
Answer:
(i)
[Co(en)3][Cr(CN)6] - Coordination isomerism
(ii)
[Co(NH3)5(NO2)]2+ - Linkage
isomerism
(iii)
[Pt(NH3)3(NO2)]Cl - Ionisation isomerism
8. The spin only
magnetic moment of Tetra chloride manganite (II) ion is 5.9 BM. On the basis of
VBT, predict the type of hybridisation and geometry of the compound.
Tetra
chloridomanganate (II) ion [MnCl4]2−
Coordination
number of the complex is 4
It
may be either tetrahedral or square planar.
Magnetic
moment of the complex 5.9 BM shows that the complex must be a tetrahedral.
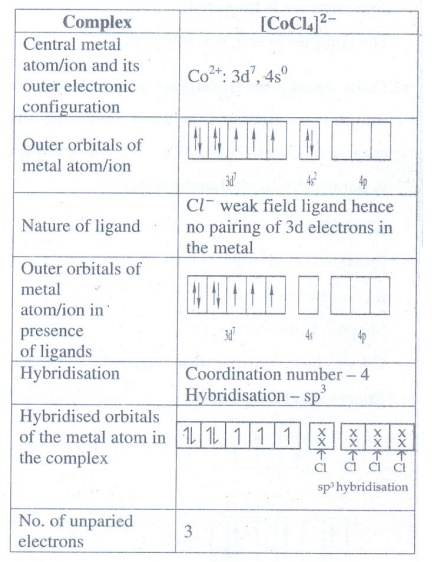
9. Predict the
number of unpaired electrons in [CoCl4]2− ion on the
basis of VBT.
10. A metal complex
having composition [Co(en)2Cl2]Br has been isolated in
two forms A and B. (B) reacted with silver nitrate to give a white precipitate
readily soluble in ammonium hydroxide. Whereas A gives a pale yellow
precipitate. Write the formula of A and B. State the hybridization of Co in
each and calculate their spin only magnetic moment.
• Complex having two portion namely
ionisable valence and coordination sphere. Ionisable valence only undergo
reaction with the added reagent.
• A given metal complex [Co(en)2Cl2]Br
shows ionization isomerism and exhibits as [Co(en)2Cl2]Br
or [Co(en)2ClBr]Cl.
• [Co(en)2Cl2]Br
gives pale yellow precipitate with silver nitrate because it ionizes to give
[Co(en)2Cl2]+ and Br − ion. Bromide ion gives pale
yellow precipitate with silver nitrate. Hence A is [Co(en)2Cl2]Br
• [Co(en)2ClBr]Cl gives
white precipitate with silver nitrate because it ionizes to give [Co(en)2ClBr]+
and Cl- ion.
Chloride ion gives white precipitate with silver nitrate and the precipitate is
readily soluble in ammonium hydroxide. Hence B is [Co(en)2ClBr]Cl
A:
[Co(en)2Cl2]Br
B:
[Co(en)2ClBr]Cl
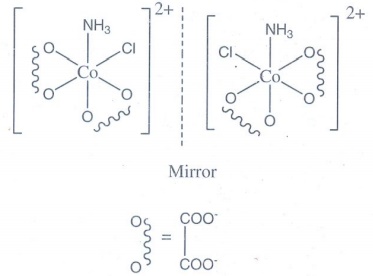
11. Draw all
possible stereo isomers of a complex Ca[Co(NH3)Cl(Ox)2]
Ca[Co(NH3)Cl(Ox)2]
shows both geometrical and optical isomerism
Geometrical isomerism
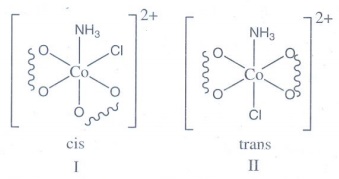
Cis isomer shows optical
isomerism.
12. The mean
pairing energy and octahedral field splitting energy of [Mn(CN)6]3-
are 28,800 cm−1 and 38500 cm−1 respectively. Whether this
complex is stable in low spin or high spin?
Pairing
energy of the complex (P) = 28,800 cm−1
Octahedral
field splitting energy of the complex (∆o) = 38,500 cm−1
[Mn(CN)6]3−
Oxidation
state = 3+
d
configuration = d4
Shape
= Octahedral
For high spin complex
Crystal
field configuration = t2g3 eg1
CFSE
(∆EO)
=
{[n t2g(-0.4) + n eg (0.6)] ∆o +np P} - {n'p
P}
n
t2g = 3
n
eg = 1
nP
=0
n'P
= 0
CFSE
(∆EO) = {[3(-0.4) + 1(0.6)] ∆o + 0P} − 0
=
[−1.2+ 0.6] ∆o = − 0.6 ∆o
=
−0.6 × 38500 = 23100 cm−1
CFSE
(∆EO) for high spin complex = 23100 cm−1
For low spin complex
Crystal
field configuration = t2g4 eg0
CFSE
(∆EO)
=
{[n t2g(-0.4) + n eg (0.6)] ∆o + np P} – {n'p
P}
n
t2g = 4
n
eg = 0
nP
=1
n'P
= 0
CFSE
(∆EO) = {[4(-0.4) + 1(0.6)] Δo + 2P} − 0
=
−1.6 ∆o + 1P
=
(−1.6 ×
38500) + (1 × 28800)
=
−61600 + 28800 = −32800 cm−1
CFSE
(∆EO) for low spin complex = −32800 cm−1
More
negative CFSE value indicates that low spin complex is favoured.
The
complex is stable in low spin.
13. Draw energy level
diagram and indicate the number of electrons in each level for the complex
[Cu(H2O)6]2+. Whether the complex is
paramagnetic or diamagnetic?
[Cu(H2O)6]2+.
Oxidation
state = 2+
d
configuration = d9
Shape
= Octahedral
Crystal
field configuration = t2g6 eg3
Energy
level diagram
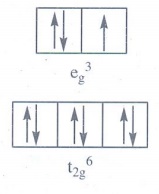
The
complex has one unpaired electron. Hence it is paramagnetic. µB = 1.73 BM
14. For the [CoF6]3-
ion the mean pairing energy is found to be 21000 cm−1. The magnitude
of ∆0 is 13000 cm−1. Calculate the crystal field
stabilization energy for this complex ion corresponding to low spin and high
spin states.
[CoF6]3−
ion
Oxidation
state = 3+
d
configuration = d6
Shape
= Octahedral
Mean
pairing energy = 21000 cm−1
Magnitude
of Δ0 = 13000 cm−1
For high spin complex
Crystal
field configuration = t2g4 eg2
CFSE
(∆EO)
=
{[n t2g(-0.4) + n eg (0.6)] ∆o + npP} − {n'p
P}
n t2g = 4
n
eg = 2
nP
=1
n'P
= 0
CFSE
(∆Eo)
=
{[4(-0.4) + 2(0.6)] ∆o + 1P} − 0
= [−1.6+ 1.2] ∆o + 1P = −0.4 Δo + 1P
=
−0.4 × 13000 + 1 ×21000 = −5200 + 21000
=
15800 cm−1
CFSE
(∆EO) for high spin complex = 15800 cm−1
For low spin complex
Crystal
field configuration = t2g6 eg0
CFSE
(∆EO)
=
{[n t2g(−0.4) + n eg (0.6)] ∆o + np P} − {n'p
P}
n t2g = 6
n
eg = 0
nP
= 3
n'P
= 0
CFSE
(∆E0)
=
{[6(-0.4) + 0(0.6)] ∆o + 3P} − 0
=
− 2.4 ∆o + 3P
=
−2.4×13000 + 3×21000 = − 31200 + 63000
=
31800 cm−1
CFSE
(∆EO) for low spin complex = 31800 cm−1
High
positive value observed for low spin complex. It indicates that low spin
complex is not favorable.
The complex is stable in high spin.
Related Topics