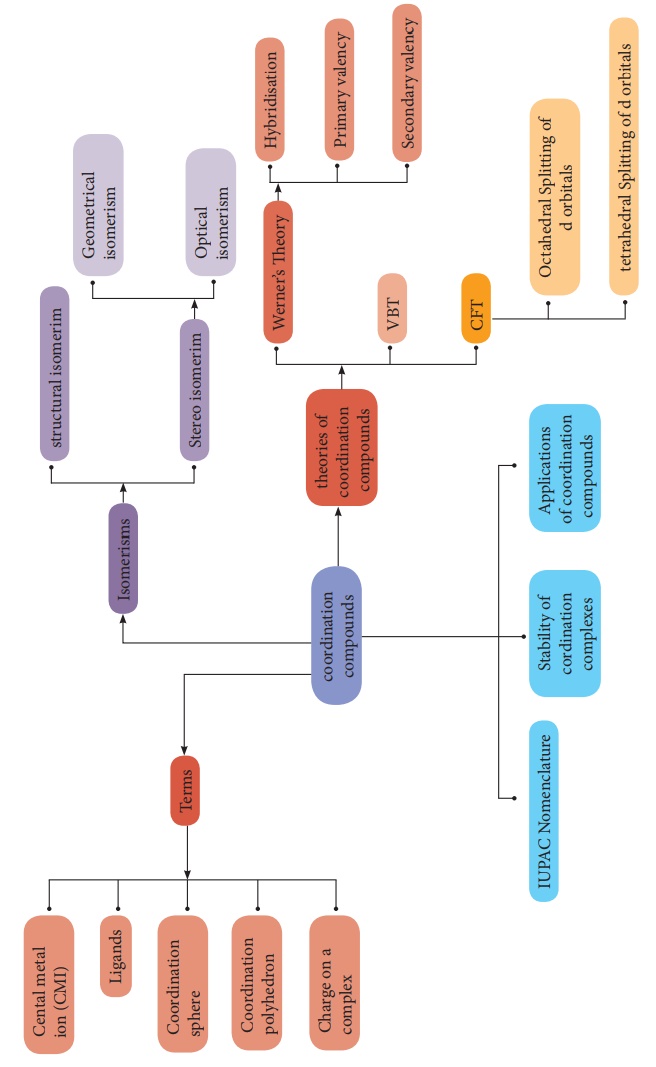
Chapter: 12th Chemistry : UNIT 5 : Coordination Chemistry
Coordination Chemistry: Summary
Summary
·
When two or more stable compounds in solution are mixed together
and allowed to evaporate, in certain cases there is a possibility for the
formation of double salts or coordination compounds. The double salts loose
their identity and dissociates into their constituent simple ions in solutions
, whereas the complex ion in coordination compound, does not loose its identity
and never dissociate to give simple ions.
·
According to werner, most of the elements exhibit, two types of
valence namely primary valence and secondary valence and each element tend to
satisfy both the valences.In modern terminology, the primary valence is
referred as the oxidation state of the metal atom and the secondary valence as
the coordination number.
·
Coordination entity is an ion or a neutral molecule, composed of a
central atom, usually a metal and the array of other atoms or groups of atoms
(ligands) that are attached to it.
·
The central atom/ion is the one that occupies the central position
in a coordination entity and binds other atoms or groups of atoms (ligands) to
itself, through a coordinate covalent bond.
·
The ligands are the atoms or groups of atoms bound to the central
atom/ion. The atom in a ligand that is bound directly to the central metal atom
is known as a donor atom.
·
The complex ion of the coordination compound containing the
central metal atom/ion and the ligands attached to it, is collectively called
coordination sphere and are usually enclosed in square brackets with the net
charge.
·
The three dimensional spacial arrangement of ligand atoms/ions
that are directly attached to the central atom is known as the coordination
polyhedron (or polygon).
·
The number of ligand donor atoms bonded to a central metal ion in
a complex is called the coordination number of the metal.
·
The oxidation state of a central atom in a coordination entity is
defined as the charge it would bear if all the ligands were removed along with
the electron pairs that were shared with the central atom.
·
This type of isomers arises when an ambidentate ligand is bonded
to the central metal atom/ion through either of its two different donor atoms.
·
This type of isomers arises in the coordination compounds having
both the cation and anion as complex ions. The interchange of one or more
ligands between the cationic and the anionic coordination entities result in
different isomers.
·
Ionisation isomers arises when an ionisable counter ion (simple
ion) itself can act as a ligand. The exchange of such counter ions with
one or more ligands in the coordination entity will result in ionisation
isomers.
·
Geometrical isomerism exists in heteroleptic complexes due to
different possible three dimensional spatial arrangements of the ligands around
the central metal atom. This type of isomerism exists in square planer and
octahedral complexes.
·
Coordination compounds which possess chairality exhibit optical
isomerism similar to organic compounds. The pair of two optically active
isomers which are mirror images of each other are called enantiomers.
·
Linus pauling proposed the Valance Bond Theory (VBT) which assumes
that the bond formed between the central metal atom and the ligand is purely
covalent. Bethe and Van vleck treated the interaction between the metal ion and
the ligands as electrostatic and extended the Crystal Field Theory (CFT) to
explain the properties of coordination compounds.
Related Topics